Table of Contents
Estimated reading time: 20 minutes
Six Sigma Terms & Definitions You Should Know
This Lean Six Sigma Glossary is designed to help professionals quickly find your level of Lean Six Sigma terms online. It will allow them to search for these lean six sigma terms, and get an idea of their impact on kaizen quality control, process improvement, and other topics levels. We hope that you find this useful.
Combining Six Sigma’s data-driven approach and Lean Manufacturing, you can create a truly exemplary framework. Lean Six Sigma belt-level practitioners have proven to be a powerful ROI over the years. More than half of Fortune 500 companies have adopted the framework.
Numbers
- 5 whys is a method to identify the root cause of a problem. Each answer serves as a platform for the next iterative question and discussion until the defect or root causes are finally identified.
- 5S is a five-step process that was first popularized in Japan. It aims to create a workplace that is efficient and effective. These five steps are Seiri, Seiton (Straighten), Seiso(Shine), Seiketsu [Standardize], and Shitsuke (“Sustain”).
- 6 M’s lists the six elements that can cause variation in almost all processes: Man (machine), Material, Method, and Measurement) and Mother Nature (the term 5M1P is used to replace “man”, which is more gender-neutral, with “people”.
- 6s stands for Six Sigma. The symbol “s”, which is lowercase for the Greek letter Sigma (uppercase S), is used in Statistics to indicate standard deviation and to grade the maturity of a process. A maturity of 6s means that a process produces defect-free products 99.99966% of the time.
- 7 QC Tools, also called Seven Basic Tools for Quality, is another Lean Six Sigma term that is a method that Professor Kauru Shikagawa of Japanese Engineering recommends for quality and process improvement. These tools and techniques include 1) Cause & Effect Diagrams; 2) Check Sheets; 3) Control Charts; 4) Histograms; and 5) Pareto Charts. 6) Scatter Diagrams. 7) Stratification Charts.
- 8D stands for Eight Disciplines for Problem-Solving. It is a transparent and collaborative framework for solving complex problems. These eight steps/disciplines include D1: Establish a team, D2: Describe and Verify the Root Causes, and D4: Develop a Containment plan. D5: Verify permanent solution, and D6: Define Corrective Actions. D7: Prevent recurrence. D8: Congratulate your team.
- 8 Wastes is another Lean Six Sigma term that is the eight main types of outcomes or actions that aren’t required to complete a process satisfactorily or produce desired outputs. The 8 wastes can be summarized using the acronym DOWNTIME (Defects. Overproduction, Waiting. Non-utilized talent, Transportation. Inventory Excess. Motion Waste. Excess processing).
A
- An Action plan simplifies the process of documenting tasks and task owners as well as methods and task schedules that are associated with a campaign, project, or initiative.
- Affinity charts can be visuals that organize large amounts of data based on their relationships (affinity or similarity). Often called affinity diagrams, affinity graphs make complex problems easier to understand by breaking them down into smaller parts and grouping related or similar components together.
- Agile could refer to an adaptive, cross-functional, customer-centric approach in software development/project management. Or, it may be used to describe an organization whose processes and tools can adapt to change while ensuring quality control and cost control.
- The Analyze phase is another Lean Six Sigma term and is the third stage of the DMAIC cycle. It identifies the root cause(s).
- Andon is a Japanese term for manufacturing that refers to an alert communication system or signaling system, which allows rapid response to problems within a system or process.
- ANOVA stands for Analyze Variance. It is a statistical test that determines if there are significant differences between two sets of data.
- Approval is an important step in many processes. It requires review and approval. Approval takes longer and is more difficult.
- Attribute data can refer to either 1) a binary type (also known as Qualitative Data), whose value cannot be more than one of two options (e.g. yes/no or true/false. Pass/fail. etc.). 2) A type of data (aka Discrete Data), whose values can only be whole numbers, such as the number of users of defects or complete cycles.
- Autonomy ( also known as Jidoka ) is a type of “smart automation” that stops or deactivates itself when certain, abnormal conditions are present. This allows workers to examine and solve the problem. The concept was developed by Sakichi Toyoda around the 19th century and became one of the foundations of Toyota’s production process. The four steps of autonomy are: 1) Detect the anomaly, 2) Stop the process/machine, 3) Fix it, and 4) Investigate and implement a countermeasure.
- Average (also Mean) is another lean six sigma term that refers to the mathematical result that is obtained when the sum of two values is divided by the number of elements within the set in kaizen.
B
- Bartlett’s Test uses statistical methods to identify the root cause of a problem.
- A Black Belt is the second highest level of Lean Six Sigma practitioners. It refers to a person who has attained such competency. Lean Six Sigma Black Belts serve as full-time leaders of teams and are responsible for solving problems in all areas of DMAIC, Kaizen, and more.
- A Bottleneck is another Lean Six Sigma term that refers to a point in the flow process where normal or acceptable flow is impeded by abnormally high volume or limited capacity of the system to process such volume.
- A Box Plot or Whisker Plot are way to visualize a data set in four parts or quartiles.
- Breakeven Analysis allows you to determine the minimum number of subscriptions that are required to cover your total costs.
C
- C-charts are visualizations of data groups used in defect tracking.
- CAPA stands for Corrective Action and Preventive Action.
- A Cause and cause-and-effect diagram is another Lean Six Sigma term that shows all variables in kaizen (causes, factors, etc.). A cause-and-effect diagram is a visual representation of all variables (causes, factors, etc.) that could affect a particular quantity (output or problem). It is often referred to as a Fishbone Diagram because the resulting image looks like a fish. Sometimes it is called the Ishikawa Diagram, after its creator.
- Change Management is a set of actions, methods, and processes that support individuals and teams during organizational change.
- Common Cause Variation refers to a type of variation that is either predictable or natural in a system.
- A Control Chart is a tool for statistical process control. consists of a centerline and statistically determined upper or lower control limits.
- Continuous data can be of any value. Distinctive data can only have whole numbers.
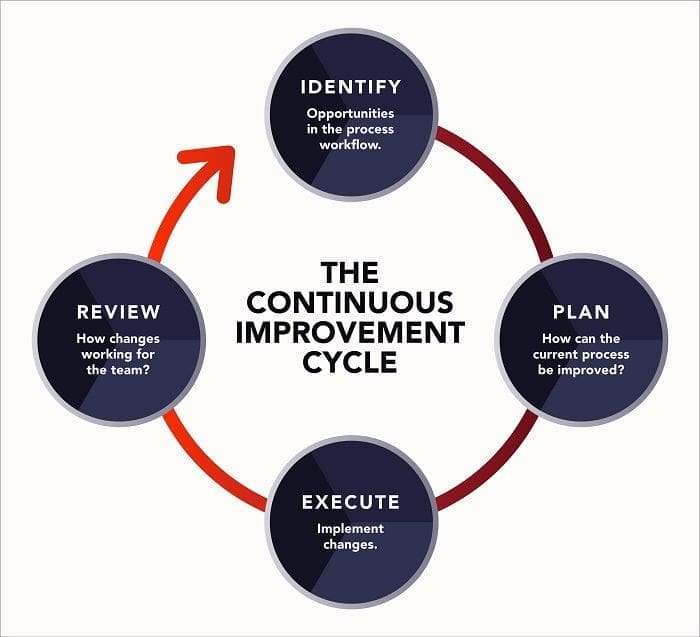
- Continuous improvement refers to a mindset and actions that are intended to improve the organization’s products and processes.
- Cost Of Poor Quality (COPQ). refers to the unneeded expenses (such as product recalls, process delays, rework, and warranty costs) that are incurred by an organization because of product defects or process inefficiencies.
- A Countermeasure is an action or plan that aims to address a problem even if it is temporary.
- Cp refers to Process Capability, which is the statistical symbol that represents Process Tolerance. It is calculated as the ratio between process variance and tolerance.
- Critical to Quality (CTQ) refers to any quantity, element, or attribute that has an impact on the quality of a product/system.
- Critical is a system or process input that has a significant impact on one or more of the outputs.
- A Cross-Functional Map shows how the process flows across departments and functions. Also known as a Wimlane, or D Employment Map.
- The time Cycle refers to the time taken from the start to the finish of a process.
D
- A Defect is any process output that does not meet a pre-defined standard or requirement. This includes color, quantity, dimensions, and temperature. A defective product or service with at least one defect.
- Defect Opportunities is another Lean Six Sigma term that refers to any instance or event where substandard output (defects) may occur.
- The Definition Phase of the DMAIC Method involves clearly and accurately defining the problems and customer requirements as well as the scope and improvement goals for a project or initiative.
- DFSS is Design For Six Sigma. It applies Lean Six Sigma-level principles to product/service design intending to increase performance, manage costs, and optimize value.
- Discrete Data is a type of quantity whose values cannot be expressed in whole numbers (such as the number defect). Variable/ data like velocity, weight, and distance, can have any numerical value.
- DMADV is an acronym for Define. Measure. Analyze. Design. Verify. This Lean Six Sigma method allows you to design new products and processes.
- DMAIC stands for Define. Measure. Analyze. Improve. Control. are the five phases of Lean Six Sigma that help to solve business and process problems.
- DOWNTIME (Defects, Overproduction, Waiting, Non-utilized Talent, Transportation, Inventory Excess, Motion Waste, Excess Processing) is the acronym for the 8 types of wastes in the Lean Manufacturing/Enterprise framework.
- DPMO (Defects Per Million Opportunities) is a Six Sigma key metric. It refers to total defects per million defect opportunities.
- DPU (Defects Per Unit) is The total number of observed defects in a particular class of units divided by the total number.
E
- Error proofing is any process, device, or mechanism that eliminates defects by detecting, preventing, or correcting them. Also known as Mistakeproofing (Yoke), it was invented by Quality Control and Lean Manufacturing pioneer Shigeo Shigo.
- Error-proofing techniques refer to the four main approaches to error control that Shigeo Shingo recommends: Elimination (flagging), Facilitation (and mitigation).
- Efficiency refers to the degree to which a process’s output meets customer expectations or conforms to specifications.
- Extra Processing refers to the addition of features or production of an output that exceeds customer specifications or quality standards.
- External Failure happens when defective items are passed through the process and reach customers. This can lead to customer dissatisfaction.
F
- A Facilitator is another Lean Six Sigma term that acts as an intermediary to facilitate collaboration among all involved in a process improvement effort, project, or initiative.
- FMEA ( Fail Modes and Effect Analysis ) is a risk management tool that allows you to analyze potential failures in terms of occurrence, severity, and detection.
- Force Field Analysis is a method of brainstorming similar to building a Pros and Cons table. Here all factors that support or against an idea are gathered weighed and analyzed.
- Four Absolutes of Quality Management Refers to the four main attributes of quality as defined by Philip Crosby:
- Conformance to requirements is quality.
- Prevention is the key to quality
- Quality performance standard has zero defects
- The price for non-conformance is a quality measurement
- A Future Map is a visual plan that visually maps the desired state (zero wasted) for a process.
G
- Gage R&R is a test to determine the level of variation in a measurement system relative to the total variation.
- A Gallery Walk is an area where Lean Six Sigma projects and improvement ideas can be formally displayed to educate a wider audience. Sometimes it is called the Solution Parking Lot.
- Gemba is another Lean Six Sigma term that is a Japanese term that means “real place”, and refers to a space where work happens.
- A Goal statement defines the desired outcomes of a process-improvement effort.
- A Green Belt is a Lean Six Sigma competency level where someone has completed approximately two weeks of training in DMAIC and Kaizen. Six Sigma Green Belts are part-time support workers and typically handle smaller-scoped projects.
H
- A Handoff refers to any point at which control/management of products, or certain aspects of the processing change ownership (i.e. hands).
- Help-Hinder can be used to identify operational or workflow problems within a group. Each member must cite instances in which they helped facilitate (help) the process, as well as instances when they hinder (hinder). To maximize efficiency, the goal is to bring together all members of the team.
- Historical Parameters provide baseline data that can be used to track progress, measure change, or compare an existing system state with a newer one.
- Huddle meetings are short meetings that last around 15 minutes and are designed to help team coordination. Huddles are for the sharing of pertinent reports.
- A Hypothesis statement is a reasonable conjecture which identifies or describes the possible causes of defects in the process.
- Hypothesis testing is another Lean Six Sigma term that is the process of verifying that an assumption or statement regarding a data set is true.
I
- An IMR Chart (Individual and Moving Range Chart ) is another lean Six Sigma term that shows averages and variations within a process. The I component detects trends and shifts in data, while the MR component displays short-term variability.
- Improvement Kita is a technique for promoting positive behavior change. It facilitates the actual transition from one state to another. Also known as Improvement Route.
- Inspections are procedures that inspect a product or process for defects. Lean Six Sigma aims to make processes error-proof to reduce the need to inspect and rework.
- Institutionalization is the process of making process improvements permanent through behavioral, cultural, and procedural changes.
- Internal Failure is any defect that has been found and corrected before it reaches a customer.
J
- Jidoka refers to a Japanese term for a type of “smart automation” that can deactivate itself or stop a process when certain, abnormal conditions are present. This action allows humans to solve the problem by using their human skills (also called Autonomation).
- Just-in-time is a method or system for delivering the correct items at the right place, at the appropriate time, and with the right measures.
K
- Kaizen, a Japanese term that combines the concepts of goodness (zen) and change (kai), is Kaizen. Kaizen has become synonymous with “continuous improvement” in the Lean Six Sigma corporate world.
- To facilitate optimal collaboration, a Kanban Board (from Japanese “signpost”) is used to visually track and visualize tasks and workflows.
- A Kano Model is an illustration that illustrates what customers get in terms of a), basic features, performance items, and c) “delighters.”
L
- Lead time is the time between the moment an order is placed and the moment it is delivered.
- Lean provides a framework to eliminate waste in manufacturing, software development, and enterprise management. Toyota’s production system is the origin of much of Lean and Kaizen in the Six Sigma world. A Lean culture encourages process improvement and leaders in organizations to support workers in fixing systemic issues they face in their work.
- Lean Six Sigma blends the principles and aims of the Lean framework (zero waste), and the Six Sigma model (60% system predictability, minimal variation). Lean Six Sigma promotes continuous improvement and employs Kaizen and DMAIC approaches for organizational change.
- Linearity is a variation (consistency or bias) between a standard or “baseline truth”, across all expected values.
- The lower Limit is the limit that is usually three standard deviations below the average and above which, a process can be considered to be under control.
- A lower Specification limit is the lower limit for a product or property. Anything below this level will be considered unacceptable.
M
- Master Black Belt – This is the highest level of Lean Six Sigma competency for someone who has achieved this level. Master Black Belts mentor, support and provide leadership to fellow Belts.
- Measurement System analysis allows you to evaluate the precision and accuracy of specific measurement methods. Also known as MSA, Gage R&R.
- MoSCoW stands for “Must Have, Should Have, Could Have, and Would Have “, a way to classify features according to importance or priority.
- Motion waste is another Lean Six Sigma term that refers to the inefficient movement of business inputs. They can be eliminated if the process is optimized. Motion waste is one of the 8 major types of waste ( DUPTIME).
- Muda is the Japanese term meaning “waste” and can refer to any product or process that does not add value to the customer’s vantage point.
N
- Non-utilized talent is an unwelcome waste that is included in the 8 Wastes of Lean Manufacturing.
- Non-Value Adding Activities are processes that often exemplify any one of the 7 Lean Six Sigma wastes. These include rework and unnecessary movement. These non-value-adding activities can increase business costs and prolong production times.
- Normal Distribution is another lean Six Sigma term that is a statistical distribution that features a gentle bell-shaped curve.
- To verify that a sample is normal, a Normality test can be used.
- An nP chart monitors the percentage of defective items within consistently sized data sets.
O
- An Operational Description describes the item or quantity, as well as the process and parameters in which it will be collected, measured, or used.
- Overproduction can be considered a significant waste in the Lean Manufacturing framework.
P
- A P chart is used to track the percentage of units with defects within a set of discrete data.
- A Paraeto Chart shows the frequency and percentage of occurrences in a graph. The Lean Six Sigma level environment refers to defective units or defects.
- The Paraeto Principle holds that a large proportion of outcomes can be attributed to a limited number of factors. The principle, also known as the 80/20 rule after Vilfredo Pareto (an Italian economist), states that only 20% of outcomes can be attributed to a small number of causes.
- PDCA is another Lean Six Sigma term that stands for Plan, Done, Check, Act. It can also be rendered as PDSA, (Plan Do Study Act).
- A Pilot refers to a limited deployment of Lean Sigma Six solutions for the purpose of verifying their effectiveness in solving a problem. Pilots participate in the Improve phase to verify root cause hypotheses and avoid taking on excessive risks and costs.
- Poka-Yoke means “error-proof” in Japanese. Poka-yoke is used in the Lean Six Sigma level to prevent human error or establish reliable alarm systems that warn of any potential defect-causing factors.
- Process Cycle Efficiency is an indicator that helps prioritize improvement opportunities. It is calculated by dividing the total lead time by the process’ value-added time.
- The Project Charter sets out the key details, intentions, and other important components of your project, like a roadmap. It is also used to create a contract between the sponsor and the team that will be implementing the project.

Q
- QDIP stands for Quality, Delivery, and Inventory.
- Quality refers to a metric that indicates whether a product or process meets customer expectations.
- QFD stands for Quality Function Deployment. This is a process that integrates customer requirements into all aspects of product design, delivery, and maintenance.
- A Quartile refers to 25% of a set of data that has been divided into four. Quartiles can be used to analyze trends, rank performance or identify causes that increase or decrease process efficiency.
R
- R&R is another lean Six Sigma-level term that stands for repeatability, and reproducibility and is the key metric used in measurement system analysis in kaizen.
- Repeatability describes a situation in which a single person receives the same results from every measurement session.
- Reproducibility describes a situation in which multiple people get the same results each time.
- Rework refers to the effort and related resources required to correct a product or process defect.
- Rolled throughput yield is a measure that shows the percentage of units that pass a process without any defects.
- Root Cause Analysis identifies the root cause of a problem.
- Root cause Hypothesis can be used to identify the root cause of a problem. It is part of the Analyze Phase of the DMAIC framework.
- RPN stands for Risk Priority Number. It is an acronym that refers to a cumulative failure rating. This score covers severity, detection, frequency, and detectability.
- RUMBA is a set criterion that validates customer requirements. It stands for Reasonable. Understandable. Measurable. Believable.
S
- Sigma Score is a statistical measure of process capability. It is the difference in standard deviations (sigma levels) between the process’s center and the nearest specification limit. You can also call the Sigma Score Z.
- SIPOC stands for Suppliers’ Inputs Process Outputs and Customers. It is a high-level view of a common business process. Sometimes it is rendered as COPIES.
- Six Sigma provides organizations with data-driven techniques, tools, and strategies to improve their processes with kaizen and lean strategies. Six Sigma is a process improvement tool that reduces variability and defects. It also aims to improve output quality and drive process performance. Six Sigma Implementation roles are a set of responsibilities Six Sigma practitioners take on as leaders and agents for organizational change. These roles are tied to the framework’s belt-based competency system.
- A Specific Cause Variation is a process variation that occurs non-randomly but irregularly, which can reduce process predictability.
- SQDC stands for Safety, Quality Delivery, and Cost.
T
- The Taguchi loss function was developed by Genichi Taguchi to explain the relationship between quality, variance, and customer dissatisfaction. Taguchi says that quality loss is a parabolic curve. This means that the customer does not see the quality drop suddenly, but rather it depends on how the product differs from their expectations.
- Genichi Taguchi’s framework for quality control, the Taguchi method, aims to satisfy customer expectations by reducing variation and cost. This framework includes several statistical methods, including those for system design and testing.
- Takt time is a German term describing the production rate required to meet customer demand. This is not the time taken to complete a unit, but rather the average time between the end of completing one unit and the end of the next.
- TOC stands for Theory of Limits. It is an acronym that refers to the Theory of Constraints. This mantra states, “A chain is only as strong and weak as its weakest link.” The concept applies to organizations and processes. Eliyahu Goldratt introduced the theory and it was adopted by those who advocate process improvement, project management, and organizational change.
- TQM stands for Total Q Management. This acronym was created in 1980 to foster a culture that promotes continuous improvement within organizations.
U
- A U-chart diagram shows how a process changes over time. It is represented in terms of the number of defects found in a sample.
- The upper Limit is the upper limit. It usually consists of three standard deviations higher than average. Below which, a process can be considered to be under control. It is also known as UCL.
- The upper specification limit is the upper limit that can be set for a product or property. Anything above this level will be considered unacceptable.
- Upstream is a term that describes activities, touchpoints, and processes that chronologically precede an item or process.
V
- Value-adding activities provide a set of steps that ensure that a product or service is completed under customer expectations.
- Analyse Value This refers to the classification of process steps or activities into one of three categories.
- Activities that add value
- Non-Value Adding Activities
- Value-Enabling Activities
- Voice of the Business refers to the organization’s priorities, including profitability and revenue.
- Voice Of The Customer (VOC) refers to customers’ needs and wants, including service requirements and customer expectations.
- Voice of the Process refers to the ability of a business or customer to use a process. VOP is often used as an efficiency-related metric.
W
- White Belt is a level of Lean Six Sigma competency or someone who has achieved this competency. White belts are the beginner’s role in the system. They understand the basic concepts of Lean Six Sigma such as DMAIC and 8 Wastes.
- Work In Process (WIP) is another Lean Six Sigma term that can refer to inventories, queued pieces, and other items pending completion.
X
- An X-bar (x) stands for the sample mean statistics.
- X-bar and R-charts are control charts that are used to verify whether a process is stable and predictable. The “R” in the term stands for “range.”
- X-bar & S (standard deviation) Charts are control charts that are used to track process variability. The “s” in the term stands for “standard deviation.”
Y
- Yellow Belt is a level of Lean Six Sigma competency and refers to someone who has attained this level. Yellow Belts are capable of supporting process improvement projects and understand the basics of Lean Six Sigma, like kaizen.
- Yield is another Lean Six Sigma term that refers to the value that indicates the percentage of good output produced by a process.
Z
- Zero Defects is a goal that Quality Control pioneer Philip Crosby created. He advised businesses to get things right the first and only time.
- Zero Quality Control aims to eliminate human error and thus eliminate the need for inspection which is considered wasteful.

About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.












