Failure Modes and Effects Analysis or FMEA is a systematic method used in engineering and design. The aim is to identify and analyze potential failure modes. The US Department of Defense developed FMEA initially for system design. Various industries have since widely adopted it to reduce failures and minimize associated risks.
The goal is to minimize the negative safety, economic, and environmental impacts of these failures. The International Maritime Organization (IMO), Classification Societies, and other regulatory agencies mandate FMEAs in the marine industry to improve safety, and reliability, and minimize unwanted events.
FMEA is a risk management tool that proactive companies incorporate into their design process.
Table of contents
- What is FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis)?
- FMEA in practice
- Video: How to Complete an FMEA
- Understanding Failure Mode Analysis (FMEA)
- Two main types of FMEA
- When to perform Failure Mode and Effects Analysis?
- FMEA Relationship to Problem-Solving
- The Steps to Complete an FMEA
- Failure Analysis
- FMEA Key Terms
- Final Words
- About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
- Related articles
What is FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis)?
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis is a method that identifies and addresses potential problems before they happen. A team of experts analyzes a system to determine the possible failure modes, as well as why they might occur.
To begin, the process begins by listing the various steps in the system. Then, analysts determine what can go wrong. The team evaluates each failure and its severity, likelihood, and ease of detection. Analysts rate the factors and then multiply them by a number to determine a Risk Priority Number (RPN). Higher RPN values indicate that more serious issues need to be addressed.
FMEA allows organizations to improve systems proactively by focusing more on prevention than simply reacting after problems occur. This approach improves safety, reliability and efficiency and reduces the costs associated with failures.
Many industries, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and manufacturing, use this approach to ensure high-quality products and processes.
The series covers four tools:
- The SIPOC(R) Diagram
- The Input (or Variables) Map
- The C&E Matrix
- The FMEA (Failure Modes and Effects Analysis)
In this post, we will be discussing FMEA or the Failure Modes and Effects Analysis.
FMEA in practice
Public forums often discuss high-profile product recalls, which frequently stem from poorly designed products or processes. This highlights the perceived inability of manufacturers, suppliers, and service providers to deliver safe products.FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) is a method that allows organizations to identify all possible failures during the design phase.
FMEA was developed in the 1950s and is one of the oldest structured reliability improvement techniques. It is still an effective way to lower the chance of failure.
FMEA relies on a team of representatives from every area of the process being reviewed. The team meets to identify potential failure points, analyze their causes and assess their effects. FMEA reviews consist of:
Steps in the process
- Failure modes: Identifying what can go wrong in each step.
- Failure causes: Analyse why failures can occur.
- Failure effects: Assess the consequences of failure.
It is better to address process flaws proactively than to react to negative events once they have occurred. Companies fin
Video: How to Complete an FMEA
Understanding Failure Mode Analysis (FMEA)
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a structured approach that identifies potential failures in the design of a product, process, or product.
Failure modes refer to the possible failures of a process. These failures can cause waste, defects, or other negative outcomes for customers. Failure Mode and Effects Analysis is used to identify, prioritize, and limit these failure modes.
FMEA does not replace good engineering. FMEA enhances engineering rather than replacing it. It uses the expertise and knowledge of a Cross-Functional Team to review the progress of a product/process and assess its risk of failure.
Two main types of FMEA
Process FMEA
Process FMEA (PFMEA), identifies product quality and reliability issues, customer dissatisfaction, safety, or environmental hazards.
- Machines utilized
- Acceptance is affected by measurement systems
- Process performance is affected by the environment
- Human Factors
- Processing methods
- Materials used
Design FMEA
Design FMEA (DFMEA), which examines the potential for product malfunctions, reduced product lives, and safety and regulatory concerns derived:
- Tolerances
- Interfaces with other components or systems
- Engineering Noise: Environments, user profiles, degradation, and systems interactions
- Material Properties
- Geometry
Why perform Failure Mode and Effects Analysis?
The cost of a failure will be lower if it is detected early. The impact of a failure discovered later in product development and launch is more severe.
FMEA is one tool that can be used to detect failure early in product and process design. FMEA is a tool that allows you to identify a product development (PD) failure early.
- Improved Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFM/A)
- Solutions at a lower cost
- Standard Work, Legacy, Tribal Knowledge, and Tribal Knowledge
- There are many options for reducing the risk
- Higher capacity for Validation and Verification of Changes
- Design of the product and manufacturing process requires collaboration
This methodology can be used to identify and correct process failures early so you can avoid the negative consequences of mediocre performance.
Advantages of FMEA
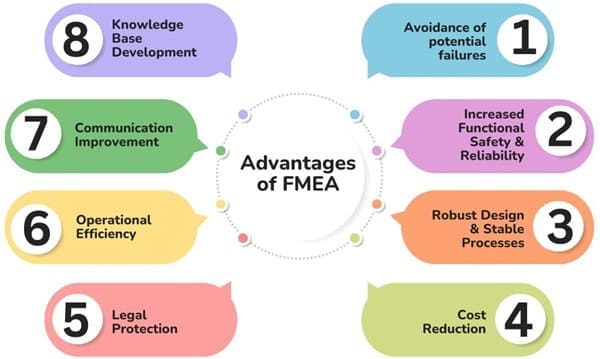
- Avoidance of potential failures: Identifies, and prevents, possible failures in processes and products.
- Increased Functional Safety & Reliability: Enhances safety and reliability for products and processes.
- Robust Design & Stable Processes: Facilitates robust designs and stable, capable processes.
- Cost Reduction: Reduces the costs of internal and external failures and minimizes product modifications.
- Legal Protection: Provides exoneration from product liability claims.
- Operational Efficiency: Eliminate disturbances during the start-up of production.
- Communication Improvement: Improved communication between the customer and supplier chain.
- Knowledge Base Development: Develop a valuable base of knowledge within your company.
When to perform Failure Mode and Effects Analysis?
It is an innovative idea to conduct a Failure Mode Analysis and Effects Analysis at least once in your life.
- If you set a goal to improve the quality of a particular process,
- You need to learn from and fix the mistakes in a process
- Designing a new product, service, or process
- If you plan to perform an existing process in another way
It is also a clever idea to conduct FMEA periodically throughout the life of a process. For optimal results, quality and reliability must always be checked and improved.
Success Factors of Effective FMEA
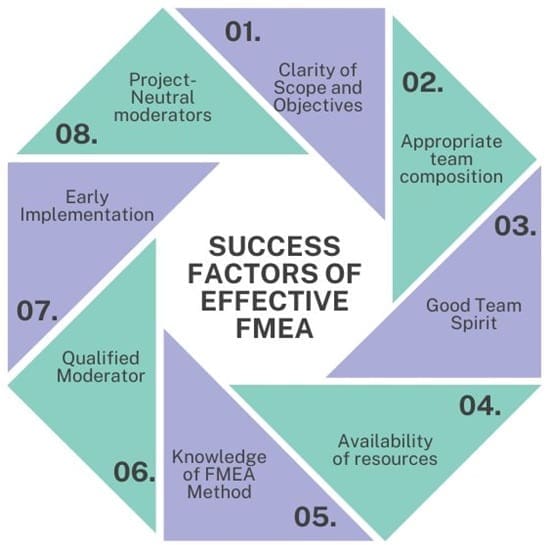
- Clarity of Scope and Objectives: Define the FMEA objectives and scope clearly.
- Appropriate team composition: Make sure the team has members who are from the relevant fields.
- Good Team Spirit: Foster a collaborative team environment.
- Availability of resources: Include the necessary resources (people and infrastructure) in your project planning to ensure smooth execution.
- Knowledge of the FMEA Method: Ensure that team members have a good understanding of the FMEA method.
- Qualified Moderator: A qualified moderator can guide the process.
- Early Implementation: Conduct FMEA along with development to ensure early implementation of findings and improvements.
- Project-Neutral moderators: Utilize moderators who hold no bias towards the project.
FMEA Relationship to Problem-Solving
FMEA’s Failure Modes are the same as the Problem Statement and Problem Description in Problem Solving. FMEA causes are the same as potential root causes in Problem Solving. FMEA failures are problem symptoms in Problem Solving. This relationship is illustrated by:
- FMEA’s design and process controls are used to verify the root cause of an issue and Permanent Corrective Action (PCA).
- FMEA and Problem Solving can reconcile every failure and cause by cross-documenting failure modes, problem statements, and plausible causes.
- Both the problem statements and descriptions can be linked between the two documents. You can solve problems faster by using easy-to-find, pre-brainstormed information in FMEA.
- For future planning of new products and process quality, data from problem-solving can be added to an FMEA. FMEAs can now be able to identify actual failures and their causes. This makes them more efficient and complete.
- To jump-start Fishbone and Ishikawa diagrams, it is possible to identify potential causes of FMEA. It is not an innovative idea to brainstorm information that is already known.
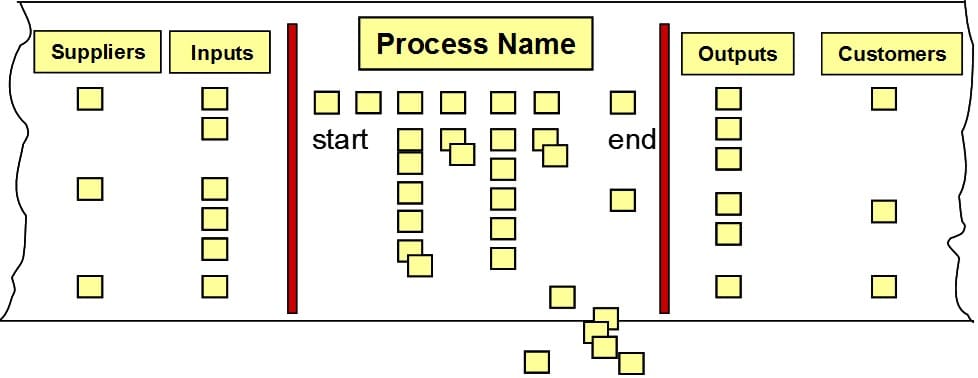
The Steps to Complete an FMEA
Review and label the Process Steps (using your process map) and the intended function or functions of those steps.
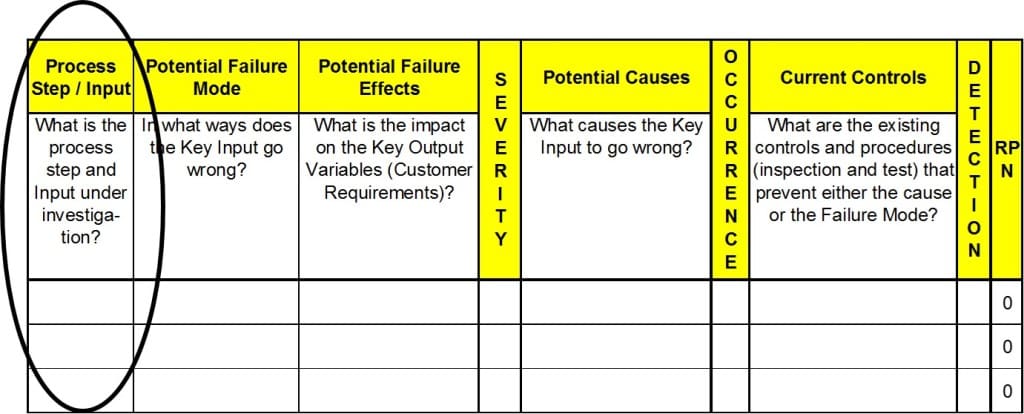
Consider the Potential Failure Modes
Consider the Potential Failure Modes for each component and its corresponding function.
- A potential failure mode represents any way the component or process step could fail to perform its intended function or functions.
Determine the Potential Failure Effects
Determine the Potential Failure Effects associated with each failure mode. The effect is related directly to the ability of that specific component to perform its intended function.
- State the effect in terms meaningful to product or system performance.
- Defining the effects in general terms makes it difficult to identify and reduce true potential risks.
Determine Potential Root Causes
For each failure mode, determine all the Potential Root Causes. Use tools classified as root cause analysis tools, as well as the best knowledge and experience of the team.
Identify Current Process Controls
For each cause, identify Current Process Controls. These are tests, procedures, or mechanisms that you now have in place to keep failures from reaching the customer.
Assign a Severity ranking
Assign a Severity ranking to each effect that has been identified.
- The severity ranking is an estimate of how serious an effect would be should it occur.
- To determine the severity, consider the impact the effect would have on the customer, on downstream operations, or on the employees operating the process.
The severity ranking is based on a relative scale ranging from 1 to 10.
- A “10” means the effect has a dangerously high severity leading to a hazard without warning.
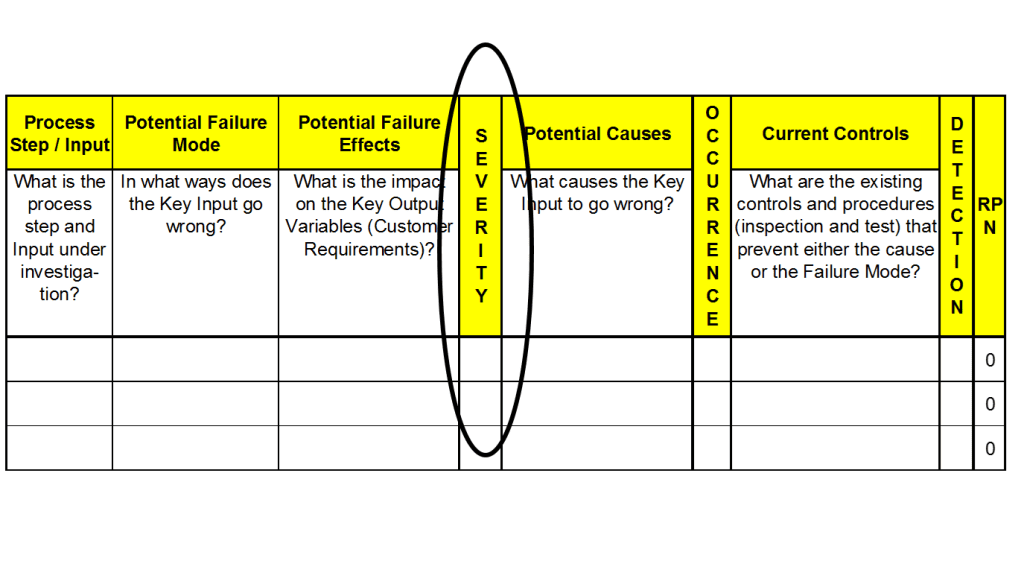
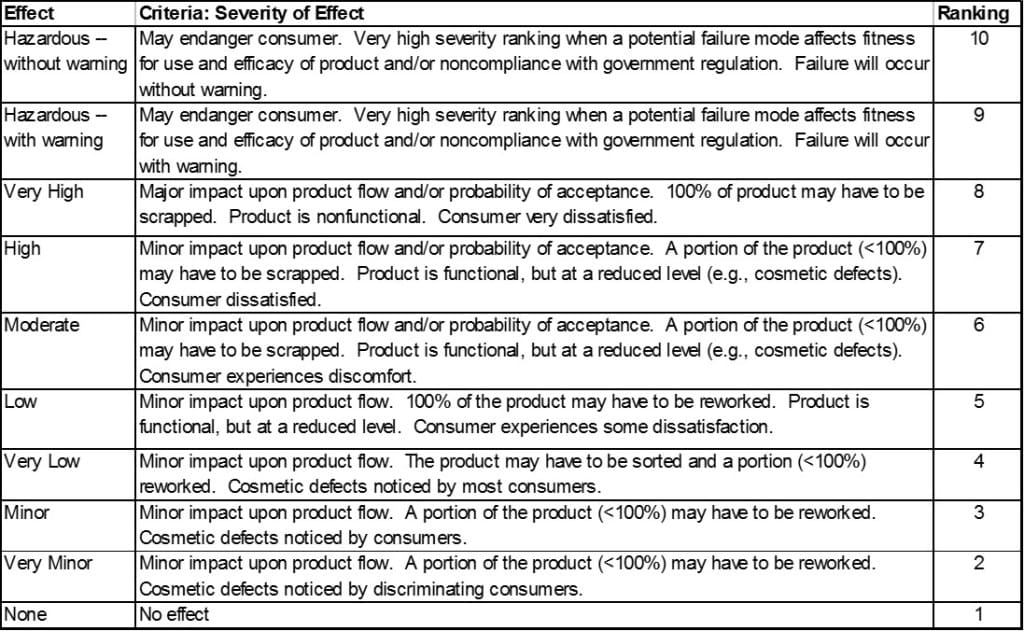
Assign the Occurrence Ranking
- The Occurrence ranking is based on the likelihood, or frequency, that the cause (or mechanism of failure) will occur.
- Once the cause is known, capture data on the frequency of causes. Sources of data may be scrap and rework reports, customer complaints, and equipment maintenance records.
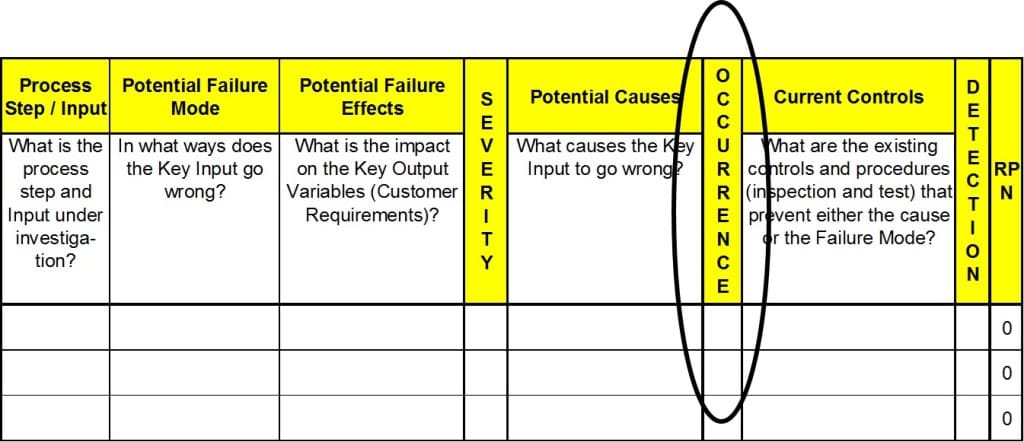
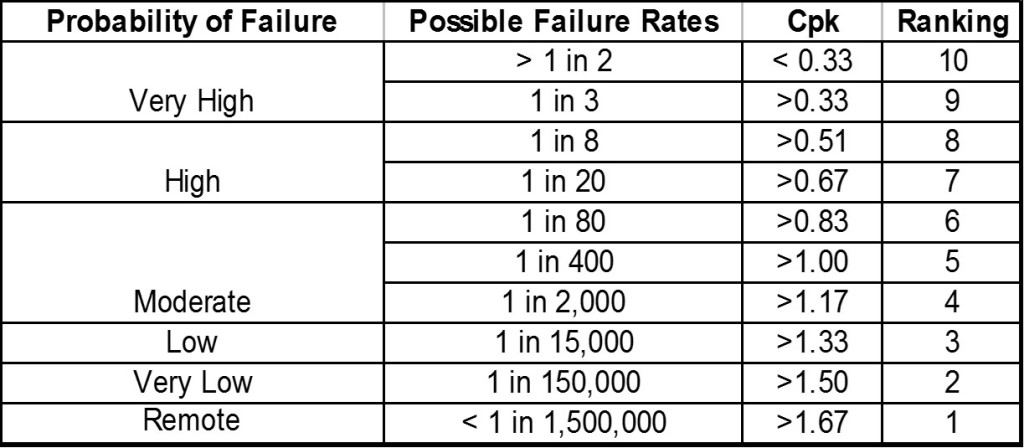
Assign the Detection Rankings
- To assign detection rankings, identify the process or product-related controls in place for each failure mode and then assign a detection ranking to each control. Detection rankings evaluate the current process controls in place.
- A control can relate to the failure mode itself, the cause (or mechanism) of failure, or the effects of a failure mode.
To make evaluating controls even more complex, controls can either prevent a failure mode or cause from occurring or detect a failure mode, cause of failure, or effect of failure after it has occurred.

Calculate the Risk Priority Number (RPN)
- The RPN is the Risk Priority Number. The RPN gives us a relative risk ranking. The higher the RPN, the higher the potential risk.
- The RPN is calculated by multiplying the three rankings together. Multiply the Severity ranking times the Occurrence ranking times the Detection ranking
- Calculate the RPN for each failure mode and effect
Prioritize the Risks by Sorting the RPN from Highest Score to Lowest Score. This will help the team determine the most critical inputs and the causes of their failure.
Develop Action Plan
- Acting means reducing the RPN. You can reduce the RPN by lowering any of the three rankings (severity, occurrence, or detection) individually or in combination with one another.
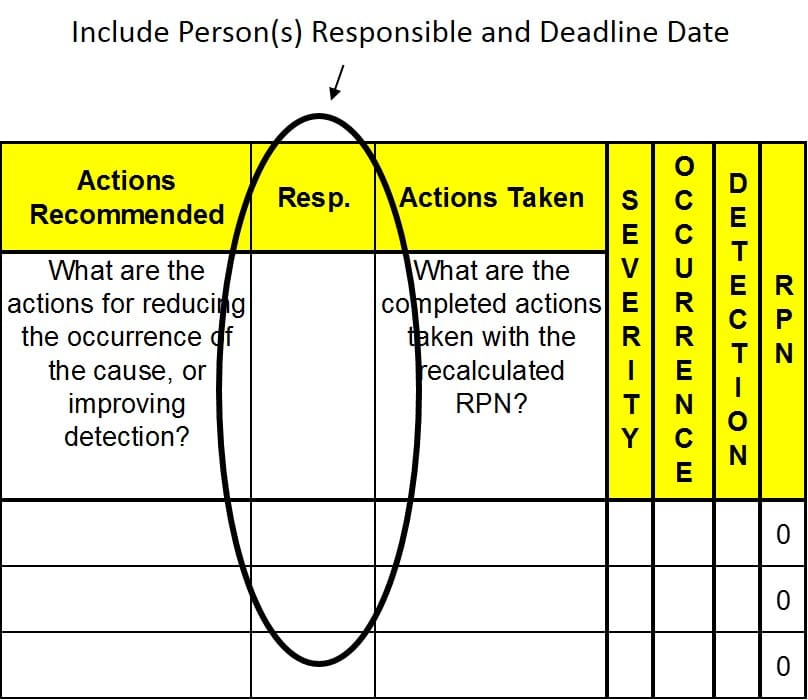
Who is Responsible
- This is an especially crucial step in Acting!
- Be sure to include the person(s) responsible and the deadline
Action Plan
- The Action Plan specifies the steps to implement the solution, assigns who will complete them, and sets deadlines for their completion.
- Most Action Plans identified during a PFMEA will be of the simple “who, what, & when” category.
- Identify who is responsible for specific actions and set target completion dates.
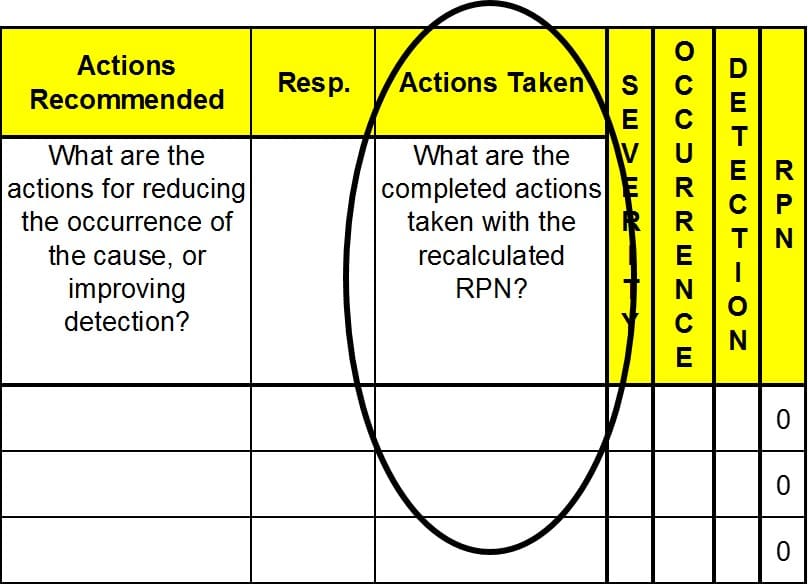
Recalculate the Resulting RPN
- This step in a PFMEA confirms the action plan had the desired results by calculating the resulting RPN.
- Recalculate the RPN by reassessing the severity, occurrence, and detection rankings for the failure modes after completing the action plan.
Failure Analysis
Failure analysis is the process of identifying potential failures in each function. It involves:
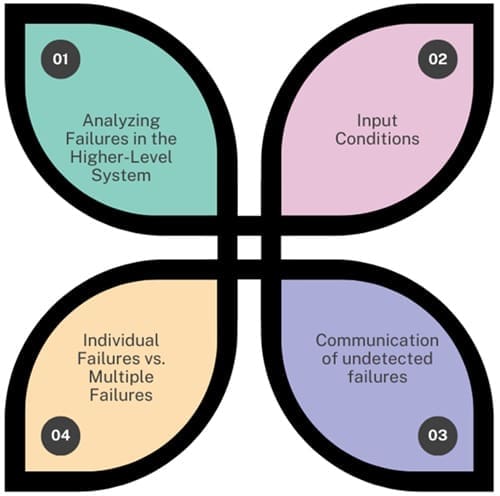
- Analyzing Failures in the Higher-Level System: In the FMEA of the higher-level system, analysts analyze failures occurring within that system.
- Input Conditions: Ensure input conditions are in accordance with specifications. If there have been previous findings of incorrect input, we will make exceptions.
- Communication of undetected failures: Any undetected failures should be communicated to the higher levels.
- Individual Failures vs. Multiple Failures: While analyzing individual failures, analysts use methods like Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) to analyze multiple failures, which are logical combinations of failures.
FMEA Key Terms
Failure mode: Identifies actual or potential defects in a design or process with an emphasis on those that affect the end-user or customer.
Failure Effect: The effect of a failure on a product or system’s function, as perceived by an end-user.
Severity: It is the severity of the consequences of failure.
Frequency: It is the frequency of failures.
Detectability: It is the difficulty of detecting failures.
Final Words
FMEAs are a vital tool to mitigate risks, as they prioritize actions that will prevent failures or reduce the severity and frequency of them. It helps in the selection of remedial actions that reduce the impact and consequence of failures. Companies employ FMEA from the conceptual design stages through the development and testing process and onto the ongoing operation of the system or product.

About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.




















I read your information and it’s very useful. The article has help to increase my knowledge on how to analyze and create a pfmea. Thanks for sharing.
I think this is a very good platform to upgrade our knowledge or to be a master in this field. I could prepare a FMEA without any ones help after reading this article.
lot of thanks to Kevin..
To understand the FMEA, it should be to learn by doing. Thank you for Improving our knowledge.
Good quick overview.
very concise step by step procedure and well explained.
thank you so much for sharing.
One question that always comes up, how to quantify the requirements for closure of an FMEA? Or more to the point, what is or are the criteria used for closure?
Mike, great question. In reality, you are never finished. The FMEA matures with the process. When the process changes and experiences new failure modes, then the FMEA is updated. In the short term for the a LSS Project, the FMEA is closed when the Revised RPN’s are below what the company sets as a max RPN.