A value-added activity refers to any business activity that contributes directly to improving the product or service, making it more valuable to the customer.
These activities add worth by transforming raw materials, resources, or information into finished goods or services that meet customer needs. In simpler terms, a value-added activity increases the product’s value, thus making it more desirable and profitable in the marketplace.
Every business has a mix of activities that contribute value and activities that do not. Businesses can improve efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance customer satisfaction by focusing on value-added activities.
Table of contents
What is Value Added Activity?
A value-added activity is any action or process that directly contributes to creating or enhancing a product or service that a customer is willing to pay for. In essence, it’s work that transforms raw materials or information into something more valuable from the customer’s perspective.
Here’s a breakdown of what that means:
- Direct Contribution: The activity must directly add to the product or service.
- Customer Perspective: The customer must perceive the activity as valuable and be willing to pay for it.
- Transformation: The activity should change the product or service in a way that makes it more desirable or useful.
Example
- Manufacturing: Assembling components into a finished product.
- Software development: Writing code that adds functionality to an application.
- Customer service: Resolving a customer’s issue or providing helpful information.
- Design: Creating a product design that meets customer needs.
- Cooking: The act of preparing food for a customer.
Activities that are NOT value-added
- Moving materials unnecessarily.
- Waiting for information or resources.
- Inspecting products for defects (while necessary, it doesn’t add value, it just prevents loss).
- Excessive paperwork.
Characteristics of Value-Added Activities
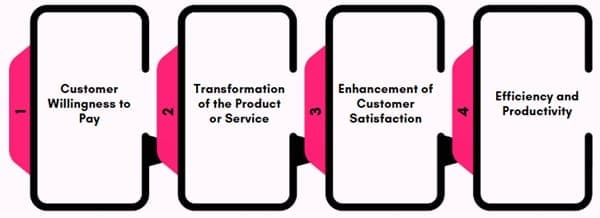
To understand value-added activities more deeply, it is essential to identify their characteristics. These activities have specific traits that distinguish them from non-value-added activities. Here are the main characteristics:
- Customer Willingness to Pay
A key feature of value-added activities is that customers are willing to pay for them. If an activity doesn’t contribute directly to satisfying customer needs or preferences, it’s not considered value-added. For instance, a service that improves the quality or usability of a product can make customers more likely to purchase it at a higher price. - Transformation of the Product or Service
Value-added activities typically transform the product or service in a meaningful way. This transformation could involve changing raw materials into a finished product or providing services that improve the product’s usability or appeal. The more the activity contributes to the product’s final value, the more it’s considered value-added. - Enhancement of Customer Satisfaction
Another key feature is the direct improvement of customer satisfaction. Value-added activities are often those that directly influence the customer’s perception of quality, usability, or overall product experience. Enhancing the end user’s satisfaction is the primary goal of these activities. - Efficiency and Productivity
Value-added activities contribute to the overall efficiency and productivity of a business. They often eliminate unnecessary waste, streamline processes, and optimize resource utilization. Businesses can enhance productivity by focusing on activities that provide the greatest return on investment.
Examples of Value-Added Activities
Let’s explore some examples of value-added activities across different industries and business functions. These activities vary depending on the type of business and its offerings, but the core principle remains the same: the activity must enhance the product or service in a way that meets customer needs.
Manufacturing and Assembly
One of the clearest examples of value-added activities occurs in manufacturing. The process of turning raw materials into finished goods, such as assembling components into a functioning product, adds value. For example, when a company assembles car parts into a completed vehicle, it transforms raw metal, plastic, and electronics into a product that is ready for sale.
This transformation adds significant value, as customers pay a premium for the finished product compared to the individual parts.
Quality Control and Testing
Quality control is another prime example of a value-added activity. This involves inspecting and testing products to ensure they meet established standards. By ensuring the product is defect-free, businesses can enhance the perceived value and ensure customer satisfaction.
Customers are more likely to pay for a product that has been carefully tested for reliability and performance. This testing guarantees the customer gets a high-quality product that will serve its intended purpose without issues.
Customization and Personalization
In industries like fashion, technology, and even food services, customization and personalization are value-added activities. These processes tailor the product to the individual preferences of the customer. A customized product may include special features, colors, packaging, or design based on the customer’s specifications.
For example, offering personalized shirts, engraved gifts, or custom-built computers adds significant value to the product. Customers are willing to pay a premium for these personalized experiences because they offer something unique and tailored to their preferences.
Packaging and Labeling
Packaging and labelling are key value-added activities, particularly in retail. A product’s packaging is often the first thing a customer notices. Attractive, functional, and informative packaging can make a product more appealing and useful. Proper labeling provides vital information, such as usage instructions, nutritional facts, and safety warnings, ensuring the customer can use the product effectively.
Moreover, packaging can protect the product, enhancing its perceived quality and increasing customer satisfaction. For example, premium packaging for high-end cosmetics or gourmet foods can significantly increase the value of these products in the eyes of consumers.
Customer Support and After-Sales Service
Customer support, including pre-sale assistance, post-sale service, and warranty programs, is a critical value-added activity. A company that offers excellent customer service and supports its products long after the sale builds customer trust and loyalty.
For instance, companies that provide troubleshooting assistance, maintenance services, or free upgrades ensure customers continue to benefit from their purchases, which enhances the overall product experience. These activities encourage repeat business, increase customer retention, and can justify higher pricing.
Identifying Value-Added Activities
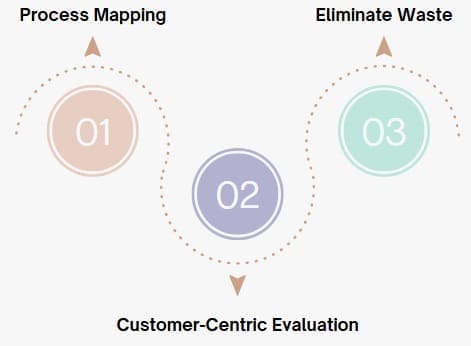
Understanding and identifying value-added activities is crucial for businesses that want to improve operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. To determine which activities in a business process are truly value-added, companies can follow several steps:
- Process Mapping
The first step in identifying value-added activities is to map out the entire process. This involves documenting every step involved in creating and delivering a product or service. Mapping the process allows companies to see which activities contribute directly to product enhancement and customer satisfaction. - Customer-Centric Evaluation
After mapping the process, businesses should evaluate which activities directly contribute to customer value. Ask yourself questions like: Does this activity make the product more desirable or usable for the customer? Does it meet customer expectations or improve customer satisfaction?
By focusing on customer needs and preferences, companies can ensure that they are spending resources on activities that directly benefit the customer. - Eliminate Waste
Once value-added activities are identified, businesses can look for non-value-added activities, often referred to as “waste.” These activities do not contribute to customer value and are often redundant, inefficient, or unnecessary. Eliminating waste helps streamline operations, reduce costs, and increase profitability.
The goal is to optimize the business process, focusing on those activities that add value and removing those that do not. Tools such as Lean and Six Sigma can help identify inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement.
Benefits of Value-Added Activities

Focusing on value-added activities brings several benefits that can enhance both operational performance and customer satisfaction. Below are some of the most significant benefits:
- Increased Customer Satisfaction
By investing time and resources into value-added activities, companies can deliver products and services that exceed customer expectations. Satisfied customers are more likely to become loyal customers, resulting in increased sales and brand loyalty. When customers see that a product or service has been designed and delivered to meet their specific needs, they are more likely to return and recommend the business to others. - Competitive Advantage
In a competitive marketplace, businesses that offer superior value through value-added activities have a distinct advantage. These companies can differentiate their offerings by delivering more value than competitors. Whether it’s through better customer support, improved product quality, or unique customization options, value-added activities help a business stand out. By delivering more value, businesses can justify higher prices and maintain a loyal customer base. - Improved Operational Efficiency
Value-added activities drive operational efficiency. By focusing on these activities and eliminating non-value-added tasks, businesses can streamline their processes. Leaner processes improve productivity, reduce waste, and lower operating costs.
Efficient operations contribute to higher profit margins and better resource utilization. Additionally, it allows businesses to allocate resources to more valuable activities. - Profitability
Value-added activities enable businesses to charge higher prices for products and services because customers perceive them as more valuable. This enhances profit margins and improves overall business profitability. Companies that consistently focus on delivering value can maintain premium pricing and secure higher profits in the long run. - Continuous Improvement and Innovation
When a company focuses on value-added activities, it fosters a culture of continuous improvement. Businesses become more adept at identifying areas for innovation and enhancement. As customer preferences evolve, companies that focus on adding value can adapt their offerings to stay relevant and competitive.
Final Words
Value-added activities are essential for any business looking to succeed in a competitive market. By focusing on activities that enhance product value and meet customer needs, businesses can improve customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and profitability.
Identifying and prioritizing value-added activities over non-value-added activities enables companies to streamline their processes, reduce waste, and increase value delivery.
Ultimately, businesses that focus on value-added activities are better positioned to create products and services that customers are willing to pay for, maintain a competitive edge, and achieve sustainable growth.
By continuously evaluating and improving these activities, companies can ensure they remain responsive to customer needs and continue to offer superior value in an ever-changing marketplace.


















