The Six Sigma Control Plan isn’t just another document; rather, it’s the bedrock for sustaining process improvements and achieving lasting operational excellence. Have you ever wondered how to lock in the significant gains from your Lean Six Sigma projects, ensuring that reduced defects and enhanced efficiency don’t just fade away?
Well, this crucial element of the DMAIC methodology provides the framework for continuous monitoring, proactive problem-solving, and effective quality control.
Therefore, to maintain process stability, minimize unwanted variation, and achieve long-term competitive advantage, your organization must master the Six Sigma Control Plan. Discover how this powerful tool empowers teams to prevent process drift and secure a future of consistent, high-quality output.
Table of contents
What is a Six Sigma Control Plan?
At its core, a Six Sigma Control Plan is a document that outlines the ongoing monitoring and response system for critical process inputs ($X$s) and outputs ($Y$s) identified during the Analyze and Improve phases of a DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) project. Essentially, this proactive strategy aims to maintain process stability and predict potential deviations before they escalate into significant problems.
Think of it this way: you’ve spent considerable time and resources optimizing a process. However, the Control Plan ensures that those optimizations don’t just become a fleeting success story. Instead, it defines:
- What needs to be monitored.
- How it will be measured.
- When measurements will be taken.
- Who is responsible for the monitoring.
- What actions will be taken if the process deviates.
- Who is responsible for those actions.
This systematic approach safeguards the gains and prevents the process from drifting back to its previous, less efficient state.
Public, Onsite, Virtual, and Online Six Sigma Certification Training!
- We are accredited by the IASSC.
- Live Public Training at 52 Sites.
- Live Virtual Training.
- Onsite Training (at your organization).
- Interactive Online (self-paced) training,
Critical Role of the Control Phase in DMAIC
The Control Plan is the cornerstone of the Control phase within the DMAIC methodology. Indeed, this final phase sustains the improvements. However, without a robust Control Plan, even the most brilliant solutions developed in the Improve phase are vulnerable to erosion.
Consequently, the Control phase ensures standardization, monitoring, and maintenance of the new, improved process, effectively locking in gains and preventing a return to the “old way” of doing things.
Key Elements of a Strong Six Sigma Control Plan

A well-structured Control Plan highly details and tailors the specific process it oversees. While the exact format may vary, certain key elements are universally present:
- Process Information:
- Process Name: Clear identification of the process being controlled.
- Process Owner: The individual or department ultimately responsible for the process’s performance.
- Project Name: Links the Control Plan back to the Six Sigma project that initiated the improvements.
- Date: Date of creation and subsequent revisions.
- Process Steps/Inputs ($X$s) and Outputs ($Y$s):
- Critical Process Steps: A breakdown of the specific stages or activities within the process that have a significant impact on output quality.
- Critical Inputs ($X$s): Identification of the key input variables that affect the process output. These are the factors that were identified as significant during the Analyze phase.
- Critical Outputs ($Y$s): The measurable results or characteristics of the process that are important to the customer and were the focus of the improvement effort.
- Measurement System Details:
- Measurement Method: How will each input or output be measured? This includes specific tools, gauges, or data collection techniques.
- Unit of Measure: Record the data in specific units (e.g., kilograms, seconds, number of defects, temperature in Celsius).
- Sampling Plan:
- Sample Size: Your sampling plan will determine how many items or observations you measure in each sample.
- Sampling Frequency: Your sampling frequency dictates how often you will take samples (e.g., hourly, daily, per batch).
- Measurement System Analysis (MSA) Confirmation: Evidence that the measurement system itself is reliable and accurate (e.g., gauge R&R studies conducted).
- Control Methods and Monitoring:
- Control Charts: Specify the type of control chart to use (e.g., X-bar and R charts, P charts, U charts) and their parameters (control limits).
- Control Limits: The statistically derived upper and lower bounds that indicate whether a process is in statistical control.
- Reaction Plan/Out-of-Control Action Plan: Define a set of actions to take when a measurement falls outside the control limits or exhibits an unusual pattern. This is crucial for rapid response and problem containment.
- Monitoring Frequency: How often will the control charts be reviewed and analyzed?
- Responsibility and Communication:
- Responsible Party: Who is accountable for taking the measurements, maintaining the charts, and executing the reaction plan?
- Communication Plan: How will you communicate deviations and corrective actions to relevant stakeholders? Who needs information, and when?
- Documentation and Review:
- Record Keeping: Where will the data and control charts be stored? For how long?
- Review Schedule: Organizations will review and update the Control Plan periodically to ensure its continued effectiveness. This typically happens on a quarterly or semi-annual basis. This is vital as processes evolve.
Developing an Effective Six Sigma Control Plan
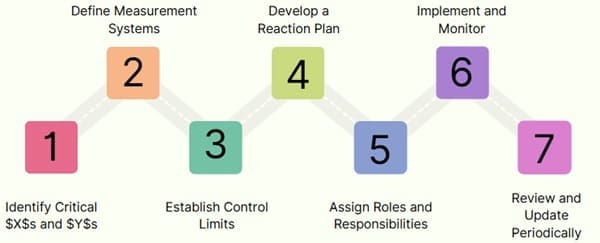
Creating a comprehensive Control Plan involves a systematic approach, often undertaken collaboratively by the Six Sigma project team and the process owner.
1. Identify Critical $X$s and $Y$s
Teams leverage insights from the Analyze and Improve phases here. Based on your statistical analysis (e.g., regression analysis, ANOVA), identify the critical process inputs ($X$s) that have the most significant impact on the desired outputs ($Y$s). Also, clearly define the critical output measures that define success for the process.
2. Define Measurement Systems
For each critical X and Y, specify how it will be measured. This includes the measurement method, unit of measure, sampling plan (size and frequency), and ensuring the measurement system is reliable (e.g., through a Gauge R&R study for continuous data).
3. Establish Control Limits
For critical output $Y$s and potentially critical input $X$s, determine appropriate control limits. Crucially, statistically, these boundaries differentiate common cause variation (inherent to the process) from special cause variation (indicating an assignable cause). For example, for continuous data, X-bar and R charts or I-MR charts are common. Conversely, for attribute data, P charts or C charts might be used.
4. Develop a Reaction Plan
This is perhaps the most crucial part of the Control Plan. Define specific, immediate actions for every potential out-of-control situation or deviation. This prevents minor issues from snowballing into major problems. The reaction plan should clearly state:
- Trigger: What constitutes an out-of-control signal (e.g., a point outside control limits, a run of points, a trend)?
- Immediate Action: Right away, take these steps to stabilize the process (e.g., stop the line, adjust a setting).
- Investigation Steps: How will the root cause of the deviation be investigated?
- Escalation Protocol: Who needs to be informed, and when?
5. Assign Roles and Responsibilities
Clarity on who is responsible for each aspect of the Control Plan is essential. This includes who takes measurements, who plots data on control charts, who analyzes the charts, who executes the reaction plan, and who reviews the plan periodically.
6. Implement and Monitor
Implement the Control Plan actively once you develop it. This involves training the process operators and owners on how to use the plan, how to interpret control charts, and how to execute the reaction plan. Regular monitoring of the process according to the plan is paramount.
7. Review and Update Periodically
A Control Plan is not a static document. Processes evolve, and so too must the Control Plan. Schedule regular reviews (e.g., quarterly, semi-annually) to assess its effectiveness. Are the control limits still appropriate? Are the reaction plans effective? Have there been any process changes that necessitate updates to the plan?
Benefits of a Well-Implemented Six Sigma Control Plan
The investment in developing and maintaining a robust Control Plan yields significant dividends for any organization committed to continuous improvement:
- Sustained Gains: The most direct benefit is the ability to maintain improvements achieved through Six Sigma projects, preventing process regression and ensuring long-term performance.
- Proactive Problem Solving: Furthermore, by continuously monitoring key process parameters, organizations can detect subtle shifts and potential problems before they escalate into major defects or customer complaints. This shifts from reactive firefighting to proactive problem prevention.
- Reduced Variation and Defects: Consequently, consistent adherence to the Control Plan helps keep the process in statistical control, inherently leading to less variation and fewer defects.
- Improved Quality and Customer Satisfaction: Moreover, stable and predictable processes consistently deliver higher quality products or services, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Additionally, by minimizing waste and rework caused by process drift, the Control Plan contributes to overall operational efficiency and cost reduction.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Through this, the ongoing data collection and analysis mandated by the Control Plan provide valuable insights, enabling informed decisions about process adjustments and further improvements.
- Standardization and Consistency: Beyond that, it promotes standardization of best practices, ensuring teams follow the improved process consistently across shifts, teams, and locations.
- Empowerment of Process Owners: Significantly, by providing clear guidelines and tools, the Control Plan empowers process owners and operators to take ownership of their processes and respond effectively to deviations.
- Foundation for Future Improvements: Ultimately, a well-controlled process provides a stable baseline for future improvement initiatives, making it easier to identify and address new opportunities.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While the benefits are clear, some common pitfalls can undermine the effectiveness of a Control Plan:
- Lack of Training: Operators and process owners do not receive adequate training on how to use the Control Plan or interpret control charts.
- “Set It and Forget It” Mentality: No one actively uses or regularly reviews the Control Plan, even after its development.
- Over-Complication: The Control Plan is overly complex, making it difficult to implement and maintain. Keep it practical and user-friendly.
- Inadequate Reaction Plans: The reaction plans are vague or do not specify clear responsibilities, leading to indecision when issues arise.
- Lack of Management Support: Senior leadership does not reinforce the importance of the Control Plan, leading to a decline in adherence.
- Poor Data Collection: We do not collect data consistently or accurately, which renders the control charts meaningless.
- Ignoring Out-of-Control Signals: Operators or supervisors ignore signals that indicate the process is out of control, hoping the problem will resolve itself.
Final Words
In conclusion, the Six Sigma Control Plan isn’t just an optional add-on; it’s the fundamental safeguard that protects your investment in process improvement. Specifically, by meticulously defining how to monitor critical inputs and outputs, establishing clear control limits, and outlining precise reaction plans, it empowers your team to proactively manage process stability.
Ultimately, embracing a robust control plan ensures that the efficiency gains, defect reductions, and enhanced customer satisfaction achieved through your Six Sigma initiatives are not just fleeting successes but enduring characteristics of your operations.
Implement these best practices, empower your process owners, and unlock the true potential of sustained quality control. Make your improvements last, because in the journey toward operational excellence, stability is the ultimate measure of success.

About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.




















