Table of contents
What is a Data Collection Plan in Six Sigma?
A six sigma data collection plan is a detailed sheet template that outlines the steps and sequence required to gather data for a particular project. The six Sigma data collection plan is a statistical method that aims to achieve breakthrough improvements by reducing variation or defects. Six Sigma is 3.4 defects per million opportunities. The defect rate is determined by the value of sigma.
DMAIC is the most popular Six Sigma data collection approach. Also known as the DMAIC Data Collection Plan, DMAIC stands for D-Define; M-Measure, A-Analyze; I-Improve, and C-Control. The Six Sigma Foundations course explains in detail the DMAIC approach and its methodology.
The Importance of Data Collection Plan
Because the people involved in data collection may differ from those who created the plan, it is crucial to have a detailed data collection document. This document will ensure:
- All members of the Six Sigma project team are on the same page about the data plan.
- The corrected information is transmitted to those in the company who will supply the required data.
Why Do You Need a Data Collection Plan?
If one is unable to derive meaningful insights from the data, then gathering and analyzing all types of data will not yield great results. A data collection plan can help you save time and money. It may not always be possible to obtain all of the data that you need. A data collection plan allows a business to focus its efforts on specific questions that are of business value.
When and How to Use a Data Collection Plan?
The proper data collection plan will ensure that the data collected is properly sorted and used. This plan can be used to assess the current status of a process or to improve a project. The plan is usually completed before gathering and analyzing process performance data. It is also useful during the project completion phase when new metrics are established and the evaluation procedures for those metrics.
Proper data collection requires a systematic approach to:
- Identify the data to be collected
- How data will be collected
- Collection
- Revision
This data collection plan illustration illustrates a common approach for data collection. It also shows how the data collection plans are incorporated into the process.

Five Data Collection Methods with Examples
There are many data-gathering methods available. These include simple, traditional, and advanced data collection and analysis. The type of business will determine the method that is used. Therefore, not all data collection methods are suitable for every project. Below are some Data collection plan options.
1. Surveys and questionnaires
This method collects data from specific respondents and attempts to generalize the results to wider audiences. This method is used by academic and business sectors. These are the benefits:
- Surveys are easy to conduct online and accessible from any location.
- A less expensive way to analyze data is more flexible than other methods.
2. Interviews
This method can be used to collect personal and other information and gain insight into personal abilities. It is done through a formal meeting between two people. These are the benefits:
- Provides more information about the subject. It can help to understand, explain, and examine the perspectives, behavior, and experiences of the individual being interviewed.
- Allows for an open conversation. It is more accurate because such data cannot later be denied or falsified.
An example is mentioned below:
3. Observations
They are used by researchers to study the behavior of individuals or the environment they are studying. This includes observing and seeing people at a specific time and place. These are the benefits:
- Allows for data collection and detailed analysis without any technical skills.
- It is independent of active participation by the participant. They don’t need to actively share any data about them that they are uncomfortable disclosing.
4. Documents and records
This method involves analyzing existing records and documents of a business to track changes over a period. This data includes email logs, staff reports, and call logs as well as databases, information logs, minutes of meetings, information logs, and databases. These are the benefits:
- Data is readily available without the need to conduct active research or interview.
- It is simple to check or track the data collected.
5. Focus Groups
This method involves six to twelve people who have similar qualities or common interests being interviewed by a moderator, who guides the group through a series of planned topics. In addition to providing a safe environment for participants to freely express themselves, the moderator also helps them create that atmosphere. This is qualitative data collection and cannot be quantified statistically.
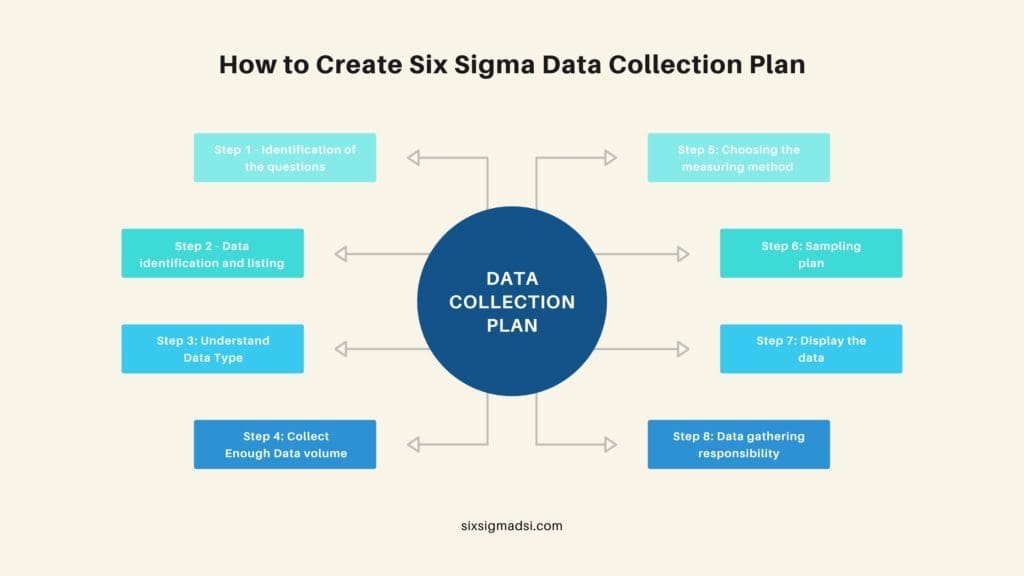
How to Create Six Sigma Data Collection Plan: 8 Steps
Six Sigma uses the DMAIC framework to create data collection plans. A Six Sigma Green Belt certified project manager will be able to handle them well. These steps will help you create a data collection program. There are 8 steps to creating a data collection plan.
Step 1 – Identification of the questions
The data collected must be relevant to the project. These questions can be answered:
- What’s the project hypothesis?
- What questions do we need to answer?
These questions should reflect the reality of the process. DMAIC’s main goal is to improve processes. SIPOC (Supplier Input Process Output Customer) is a good guide for data collection.
Data collection must meet certain criteria. Here’s a list of these criteria:
- Is it possible to collect the data in a timely manner, within budget, and with maximum effort?
- Do the data consider related or influencing conditions?
- Do the data give a good insight into the process?
- Can it appear on the Input–Process–Output diagram of SIPOC?
Step 2 – Data identification and listing
The next step is to break down the questions into smaller pieces and determine what data can be used to answer them (parts or whole). Sometimes a single piece of data may provide multiple answers. We might also need to examine data that is related to other pieces.
Next, a list must be created of all data that is available to answer the questions.
Step 3: Data Type
We have already briefly discussed different data types. This is where we must understand the “data type” that will be measured. If you have continuous data, it’s better to use a histogram, or a run graph, while a Pareto or pie chart for attributes will be more helpful.
At this stage, a ‘data collection sheet’ is required. This form records the approach to obtaining data needed to conduct the analysis. Here is an example of a data-collecting form:
Step 4: Data volume
To see trends and patterns, you will need enough data. For each element of the data list, it is necessary to note how much data is required.
Step 5: Measuring method
There are many ways to measure data. These include check sheets, survey answers, and check sheets. In the next section, we will discuss these in greater detail. The type of data required will determine the method that is used. This checklist could be used:
- Choosing an operational definition
- Identify the measurement specification and it should be based upon the customer’s accepted limits of acceptableness.
- Determining the target values and the direction that the process should go.
- Allocating an objective, the real value to each target.
Step 6: Sampling decisions
It would be impractical to measure a whole population of data when the data is not required. However, it is possible to obtain the data from a small sample. Here again, it is important to answer some questions. These are:
- What percentage of the parent population is required to make statistically sound judgments or decisions?
- How is data sampling done?
- How can we avoid measurement bias?
Step 7: Data display
There are many ways data can be presented, including run charts, control charts, Pareto diagrams, and other types. You need to decide which display tool is best for you.
Step 8: Data gathering responsibility
It is important to determine whether data must be collected by hand, or via automated software. If automated software is used, it is important to identify the person responsible for ensuring that data are available at the agreed time and in the correct format.
Data Collection Plan Template
The main purpose of the data collection plan is to provide a clear approach to data collection. It identifies the goal of data collection, the type of data required, the method of collection, and the responsible person to collect and present the data in the appropriate format. It helps determine if a process is stable and capable and if the measurement system works well.
You can make a data collection plan worksheet in many different ways using either Google worksheets or Microsoft Excel. Below are two types of templates. The first capture basic data while the second is more detailed and allows for detailed information. This template can also be used by Six Sigma practitioners. Both will require you to first identify the goals of data collection and the main study variables.
1. Data collection plan sheet template Excel (Compact)
Locate the data collection sheet template
2. Data collection plan sheet template Excel (Comprehensive)
Get the complete data collection plan sheet template
Importance of Data
Let’s look at the five important ways data can benefit companies of any size, small or large, and especially SMBs.
1. Data helps in making better decisions
Websites, social media presences, and electronic payments are all required to collect data on customers. This data can be used to improve web traffic, bounce rate, and other metrics. These benefits can include:
- Finding new clients
- Customer service and retention
- Improve Marketing
- Making the most of social media interaction likes and comments
- Predicting future business or sale trends
2. Data can help with problem-solving
Tracking and gathering data from business processes. This helps to understand why there are slow sales and unsatisfactory results.
3. Data helps in understanding performance
A great example is the Sports sector. It allows for better performance by collecting and analyzing data. Similar to the above, data can be collected and reviewed by different teams within a company. A team manager or department head must also know the performance of their team members.
4. Data is a tool for process improvement
Only data can improve business processes and reduce waste. Every company should know what is happening and how to prevent it. A company can waste a lot of money by making a poor or rash advertisement decision. Analyzing competitor advertisements and their performance can help a company determine which marketing efforts will bring the best ROI.
5. Data helps in better customer understanding
Data is the only way a company can learn about its customers and determine what type of service or product they want. Only then can a company strategize its product or service offering and market effectively.
Too much data can be overwhelming. Businesses must learn how to extract the maximum value from existing data in order to take advantage of analytics and data. Businesses often look for Business Intelligence solutions as they grow in data. This allows them to better understand and interpret the consumer data, and then leverage it to increase profits.
Types of Data
Every moment we create data, without even realizing it. You can send a text message, post a photo on social media or browse websites (the sites use cookies to collect visitors’ browsing history). Every second, 2.5 quintillions were generated in 2020!
Data is the foundation of every business and project. There are many data types that can be classified.
- Structured and Unstructured
- Qualitative and Quantitative Data
- Continuous and discrete data.
Projects and businesses use different types of data depending on the situation.
Big Data, a term that describes data sizes in the petabyte or higher range, is often used. It can also be described using the 5Vs – Variety, Volume Value, Velocity, and Veracity. This type of Big Data is the foundation and asset of web-based eCommerce businesses like Amazon. Big Data has many benefits, including increased sales, customer service, and efficiency.
Conclusion
We’ve covered the importance of data and types of data as well as how to create Six Sigma data collection plans. It is important to remember that Six Sigma data collection plans require special expertise. KnowledgeHut’s top Six Sigma courses are the best options for anyone who wants to practice or participate in Six Sigma projects.
Have you created a Data Collection Plan for your project?
Let us know your tips and tricks in the comments below.












