Lean Six Six Sigma Green Belt certification is a critical qualification for professionals aiming to excel in quality management, process improvement, and operational excellence.
This certification equips individuals with the knowledge and skills to apply Lean and Six Sigma methodologies within an organization, enabling them to lead projects that drive significant improvements in efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness.
This comprehensive overview will delve into the various aspects of Lean Six Sigma Green Belt certification, including its roles, responsibilities, training, key concepts, and the impact it can have on an organization.
Table of contents
About Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma is a powerful combination of two distinct methodologies: Lean and Six Sigma. Lean focuses on the elimination of waste, which is any activity that does not add value to the customer. The goal of Lean is to streamline processes, reduce cycle times, and improve overall efficiency.
On the other hand, Six Sigma is a data-driven approach that seeks to reduce process variability and improve quality by identifying and eliminating defects. When combined, Lean Six Sigma provides a comprehensive framework for achieving process excellence and operational efficiency.
Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
The Lean Six Sigma Green Belt is a professional certification that signifies a solid understanding and practical knowledge of Lean and Six Sigma methodologies. It equips individuals with the skills needed to lead and contribute to process improvement projects within an organization.
Role of a Green Belt in Lean Six Sigma
A Green Belt in Lean Six Sigma plays a crucial role in an organization’s process improvement initiatives. Green Belts usually hold mid-level positions like middle managers, business analysts, or project managers. They work on process improvement regularly but do not do it full-time.
Green Belts are the backbone of Six Sigma teams. They work under Black Belts or Master Black Belts, who have more experience and higher-level certifications.
Green Belts often lead smaller projects or manage parts of larger projects. They collect and analyze data, implement improvements, and make sure processes are efficient and streamlined. While they may not be full-time Six Sigma practitioners, their contribution is vital as they undertake most of the hands-on work in data collection and analysis.
Download the Six Sigma Green Belt Training Brochure!
CLICK HERE to download the brochure.
🚀 Are you ready to supercharge your career and become a Lean Six Sigma Green Belt? Our free, downloadable Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Training brochure is your gateway to unlocking a world of opportunities!
🔍 Inside the Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Training Brochure, you’ll discover:
- A detailed overview of the course content,
- Information about our certification options, including the opportunity to earn the prestigious IASSC Lean Six Sigma Green Belt certification.
- Course format and duration.
- Testimonials from successful graduates.
Whether you’re a seasoned professional looking to expand your skillset or a newcomer eager to enter the world of process improvement, our Lean Six Sigma Green Belt course can help you achieve your goals.
Key Responsibilities of a Green Belt
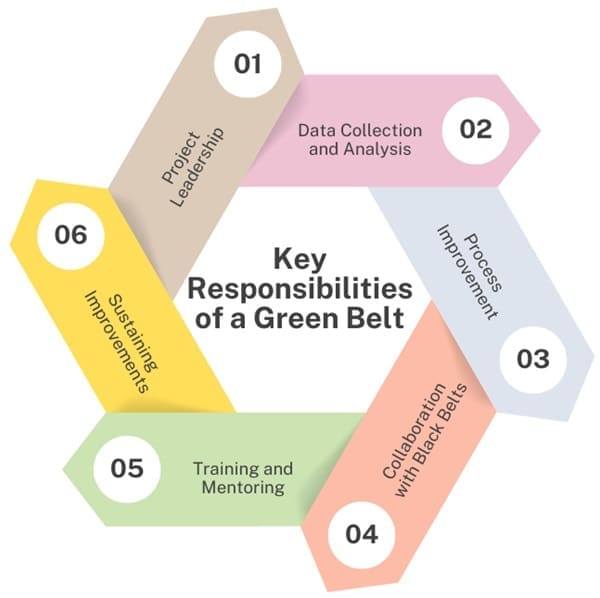
- Project Leadership: Green Belts are expected to lead Six Sigma projects from concept to completion. They are responsible for forming and facilitating Six Sigma teams, defining project goals, and ensuring that projects stay on track.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Green Belts performs the bulk of statistical data collection and analysis in Six Sigma projects. They use intermediate statistical tools to analyze data, identify root causes of problems, and measure the effectiveness of implemented solutions.
- Process Improvement: Green Belts are tasked with applying Lean and Six Sigma tools to improve processes within their organizations. This includes identifying areas of waste, reducing variability, and ensuring that processes are efficient and effective.
- Collaboration with Black Belts: Green Belts work closely with Black Belts, who provide guidance and support throughout the project lifecycle. Black Belts assist Green Belts in defining project scopes, selecting appropriate tools, and validating results.
- Training and Mentoring: Green Belts also play a role in teaching others within the organization about Lean Six Sigma methodologies. They share their knowledge and help build a culture of continuous improvement.
- Sustaining Improvements: After implementing changes, Green Belts make sure that the improvements last over time. This involves monitoring processes, making adjustments as needed, and preventing regression to previous states.
Green Belt Training and Certification
Lean Six Sigma Green Belt training helps professionals learn how to lead process improvement projects effectively. Training programs typically cover a wide range of topics, including project management, quality management tools, problem-solving techniques, and statistical analysis.
The training duration can vary, but it usually consists of around five to ten days of classroom instruction, combined with practical exercises and real-world project work.
Core Concepts Covered in Green Belt Training
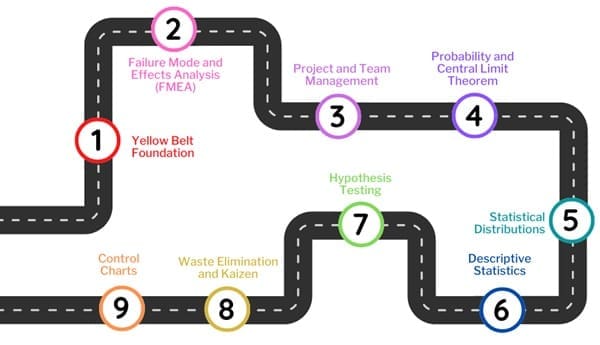
- Yellow Belt Foundation: Green Belt training builds on the foundational knowledge covered in Yellow Belt certification. This includes an understanding of basic Six Sigma concepts, Lean principles, and the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) methodology.
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): Green Belts learn how to use FMEA to identify potential failures in processes and assess their impact. This tool helps in prioritizing risks and implementing preventive measures.
- Project and Team Management: Green Belt training includes instruction on how to manage projects and teams effectively. This covers aspects such as setting project goals, planning, resource allocation, and team dynamics.
- Probability and Central Limit Theorem: Understanding probability and the Central Limit Theorem is crucial for Green Belts as they analyze data and make inferences based on sample data.
- Statistical Distributions: Green Belts learn about various statistical distributions and how to apply them in process analysis and improvement.
- Descriptive Statistics: Training covers the use of descriptive statistics to summarize and interpret data. This includes measures of central tendency, variability, and data visualization techniques.
- Hypothesis Testing: Green Belts are trained in basic hypothesis testing to make data-driven decisions and validate improvements.
- Waste Elimination and Kaizen: Lean principles, such as waste elimination and Kaizen (continuous improvement), are integral parts of Green Belt training. Green Belts learn how to identify and eliminate waste in processes, leading to increased efficiency.
- Control Charts: Green Belts are introduced to basic control charts, which are used to monitor process performance and maintain control over time.
Green Belt Effectiveness and Certification Criteria
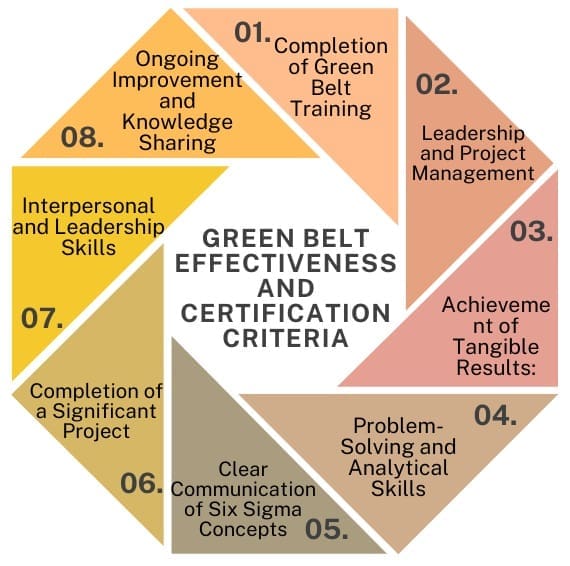
To become a certified Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, candidates must demonstrate their ability to apply Six Sigma methodologies effectively within their organization. The certification process typically involves the following criteria:
- Completion of Green Belt Training: Candidates must successfully complete a Green Belt training program that is approved by a recognized Six Sigma organization.
- Leadership and Project Management: Candidates must demonstrate their ability to lead organizational change by showcasing leadership, teamwork, project management, and communication skills.
- Achievement of Tangible Results: Certification requires candidates to achieve substantial, tangible, and sustained results through the application of Six Sigma methodologies. This could include cost savings, improved customer satisfaction, reduced cycle time, increased revenues, or other measurable benefits.
- Problem-Solving and Analytical Skills: Candidates must demonstrate a clear and rational thought process, the ability to analyze problems logically, and the use of facts and data to guide decisions.
- Clear Communication of Six Sigma Concepts: Candidates should be able to explain Six Sigma concepts and the DMAIC methodology in layman’s terms, ensuring that they can effectively communicate with others in the organization.
- Completion of a Significant Project: Candidates often complete one or more Six Sigma projects to earn certification. Appropriate personnel review and validate these projects. Candidates must document the projects in a Green Belt notebook. The projects should be arranged in the DMAIC format and employ a significant subset of Six Sigma tools.
- Interpersonal and Leadership Skills: Green Belts must demonstrate the interpersonal and leadership skills necessary to be effective change agents within their organization.
- Ongoing Improvement and Knowledge Sharing: To maintain certification, Green Belts must complete at least one Six Sigma project every 12 months. They must also share their knowledge with others. Additionally, they should help improve the culture of continuous improvement in their organization.
Impact of Green Belts on an Organization
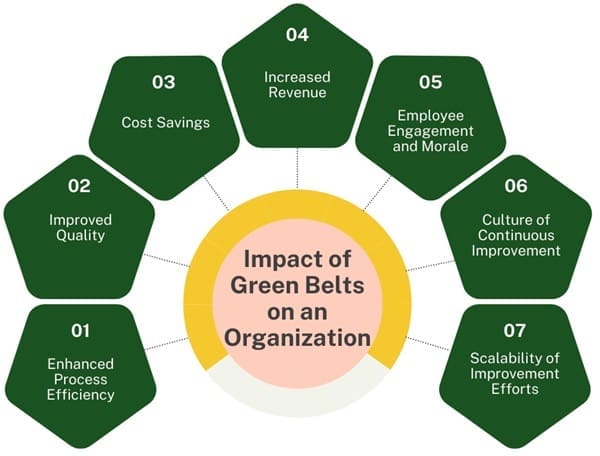
Green Belts can have a profound impact on an organization’s performance and culture. While they may not work on Six Sigma projects full-time, their role in driving process improvements is critical. The following are some ways in which Green Belts contribute to an organization:
- Enhanced Process Efficiency: By applying Lean and Six Sigma tools, Green Belts help streamline processes, reduce waste, and improve efficiency. This leads to faster cycle times, reduced costs, and higher productivity.
- Improved Quality: Green Belts focus on reducing variability and eliminating defects in processes, which leads to improved product and service quality. This, in turn, enhances customer satisfaction and reduces the cost of poor quality.
- Cost Savings: Through effective process improvements, Green Belts contribute to significant cost savings for the organization. This could be in the form of reduced operational costs, lower inventory levels, or minimized rework and scrap.
- Increased Revenue: By improving processes and quality, Green Belts can help the organization deliver better products and services to customers, leading to increased sales and revenue.
- Employee Engagement and Morale: Green Belts often lead cross-functional teams, bringing together employees from different departments to work on improvement projects. This fosters collaboration, increases employee engagement, and boosts morale.
- Culture of Continuous Improvement: Green Belts play a key role in building and sustaining a culture of continuous improvement within the organization. By sharing their knowledge and mentoring others, they help create an environment where employees are constantly looking for ways to improve processes and deliver better results.
- Scalability of Improvement Efforts: Since there are usually more Green Belts than Black Belts within an organization, Green Belt projects can have a broad impact on the enterprise. Even though these projects may not cover enterprise-wide processes, their collective impact can be significant.
Final Words
The Lean Six Sigma Green Belt certification is a valuable credential for professionals seeking to enhance their skills in quality management and process improvement. Green Belts are essential members of Six Sigma teams, contributing to the success of projects through their leadership, analytical abilities, and commitment to continuous improvement.
By obtaining this certification, professionals can play a pivotal role in driving organizational excellence, leading to better efficiency, improved quality, and significant cost savings. As organizations continue to embrace Lean Six Sigma methodologies to stay competitive in today’s market, the demand for certified Green Belts is likely to grow, making this certification a worthwhile investment in one’s career.
About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.




















