Table of contents
- What is DOE Engineering?
- What is the Design of Experiments?
- Real-world Examples of Successful DOE Applications
- How DOE Enhances Problem-solving and Decision-making
- Key Components of DOE Engineering
- Types of DOE Experiments
- Real-world Applications
- Common Challenges in DOE Engineering
- The Bottom Line
- Related articles
What is DOE Engineering?
Design of Experiments (DOE) Engineering isn’t just another buzzword; it’s an approach that empowers engineers to make informed decisions and improve designs and processes with unprecedented precision. This blog explores this fascinating world of DOE Engineering by uncovering its principles, methodologies, and incredible potential to transform how engineers create solutions.
No matter your level of experience as an engineer or your interest in scientific experimentation, this blog can serve as your guide through the complex landscape of DOE Engineering. Join us as we uncover its mysteries, explore its applications in real-life scenarios, and uncover how this discipline is changing industries worldwide!
Do not fall asleep as we embark on an expedition of discovery where knowledge and innovation combine to open up endless opportunities. Welcome to DOE Engineering–where science meets creativity and every experiment offers hope of unlocking a brighter tomorrow.
What is the Design of Experiments?
Design of Experiments, or DOE, is a systematic and statistical approach used by engineers and scientists to optimize processes, improve product quality, and make informed decisions. At its core, DOE involves planning and conducting experiments to explore the relationships between various factors (variables) and the outcomes (responses) they influence. This method allows for the identification of critical factors and their optimal levels, leading to data-driven decision-making.
DOE Engineering operates on several key principles, including randomness, replication, and control. The primary objectives include improving efficiency, reducing waste, minimizing errors, and achieving consistent and predictable results.
Real-world Examples of Successful DOE Applications
To illustrate the real-world impact of DOE, we will explore a range of case studies across various industries. These examples will showcase how DOE has been instrumental in optimizing fuel efficiency in the automotive industry, streamlining drug formulation in pharmaceuticals, fine-tuning manufacturing processes, and improving aircraft performance in aerospace.
How DOE Enhances Problem-solving and Decision-making
One of the most compelling aspects of DOE Engineering is its ability to enhance problem-solving and decision-making. We will discuss how engineers can harness the power of experimentation to tackle complex problems systematically. By examining data and making informed decisions, organizations can achieve sustainable growth and innovation.
DOE Engineering offers a multitude of benefits to engineers and organizations. It enables efficient resource utilization, faster problem-solving, enhanced product development, cost reduction, and improved overall quality. By systematically testing and analyzing variables, engineers can make data-driven decisions that lead to more efficient processes and superior products.
Key Components of DOE Engineering
Factors, Levels, and Responses (FALARs)
Understanding the core components of DOE is paramount to successful experimental design. Here, we will examine how factors, levels, and responses play a vital role in experimental design: factors are the variables being tested; levels represent specific values or settings for each factor; responses represent outcomes or measurements of interest.
Experimental Design and Planning
Successful experimental design is key to any DOE project’s success. Here, we explore all aspects of planning experiments from selecting appropriate designs to determining sample sizes and randomizing data as needed in order to prevent biases from emerging.
Statistical Analysis Techniques for Dummies
Statistics is at the core of DOE engineering. Here, we will explore various statistical techniques used in DOE such as ANOVA (analysis of variance), regression analysis, and hypothesis testing that enable engineers to gain meaningful insights from their experiments.
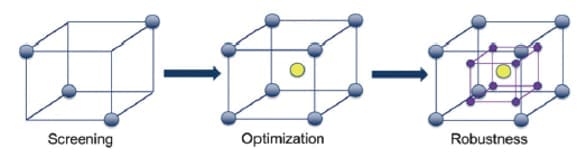
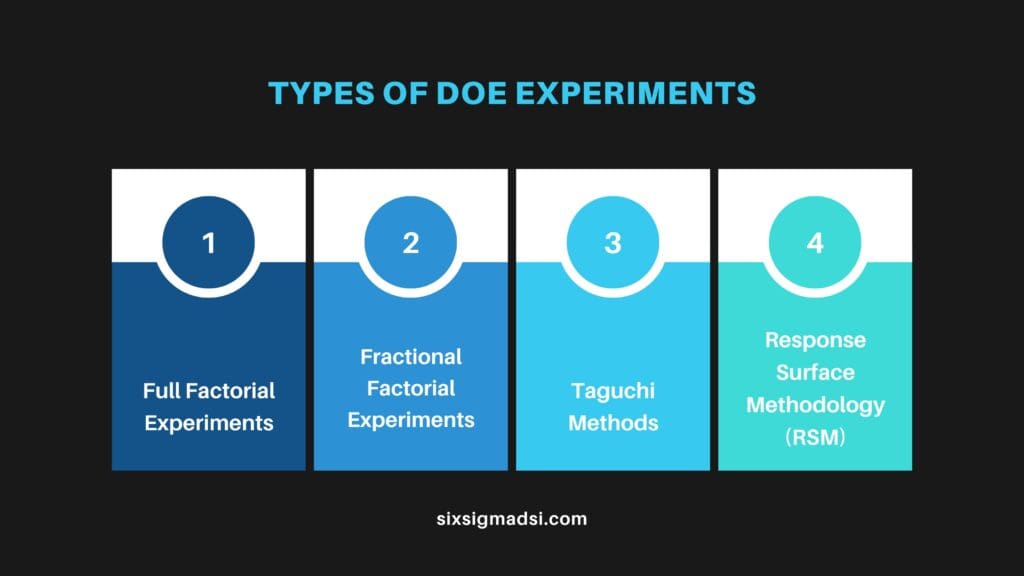
Types of DOE Experiments
Full Factorial Experiments
Full factorial experiments represent the gold standard in Design of Experiments (DOE) Engineering. In these experiments, engineers meticulously test every conceivable combination of factors and their respective levels. This exhaustive approach provides a comprehensive understanding of how each factor influences the outcomes. While full factorial experiments offer unparalleled insights into the relationships between variables, they can be resource-intensive. Conducting such experiments requires substantial time, effort, and resources, making them most suitable for scenarios where precision is paramount.
Fractional Factorial Experiments
Fractional factorial experiments present a pragmatic and resource-efficient alternative to full factorial designs. Instead of testing all possible combinations, engineers strategically select a fraction of the factor combinations to study. This approach significantly reduces experimentation time and costs while still yielding valuable insights. Careful planning and statistical analysis are essential in fractional factorial experiments to ensure that the chosen subset of combinations provides representative data. Engineers leverage these experiments when seeking a balance between accuracy and resource conservation, making them a popular choice in many real-world applications.
Taguchi Methods
The Taguchi method, pioneered by the renowned Japanese engineer and statistician Genichi Taguchi, represents a specialized branch of DOE Engineering. Taguchi’s methods prioritize robust design and optimization, making them particularly well-suited for industries where reliability and performance consistency are critical. By systematically identifying and minimizing the impact of variability and external factors, Taguchi’s methods enable engineers to create products and processes that exhibit resilience in the face of real-world conditions. This approach contributes to the development of robust and reliable solutions, reducing the likelihood of defects or performance deviations.
Response Surface Methodology (RSM)
In complex engineering scenarios with multiple interacting variables, Response Surface Methodology (RSM) emerges as a powerful tool. RSM is designed to optimize processes by mapping out the relationship between factors and responses, even in multi-dimensional systems. Engineers employing RSM create mathematical models that predict how changes in factor settings impact desired outcomes. This approach allows for the identification of optimal factor settings that maximize or minimize responses, leading to efficient process optimization. RSM is particularly valuable in industries such as chemical engineering, where intricate interactions between factors necessitate sophisticated analysis to achieve desired results.
Each of these types of DOE experiments offers unique advantages and applications, allowing engineers to choose the most appropriate approach based on the specific requirements of their projects. Whether pursuing precision through full factorial experiments, resource optimization with fractional factorial designs, robustness using Taguchi methods, or complexity management through RSM, DOE Engineering provides a versatile toolkit for tackling diverse engineering challenges.
Real-world Applications
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, DOE Engineering has been instrumental in optimizing fuel efficiency, reducing emissions, and enhancing vehicle performance. We will explore how experiments and statistical analysis have led to groundbreaking advancements in this sector.
Pharmaceuticals
In pharmaceuticals, precise drug formulation is critical for safety and efficacy. We will examine how DOE has been applied to develop pharmaceutical formulations with the right balance of ingredients, leading to improved patient outcomes.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing processes benefit greatly from DOE. We will discuss how experimentation has helped streamline production, reduce defects, and increase overall efficiency in manufacturing settings.
Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, the stakes are high, and safety is paramount. We will explore how DOE Engineering has contributed to improving aircraft performance, reducing maintenance costs, and ensuring passenger safety.
Common Challenges in DOE Engineering
Data Collection and Accuracy
Accurate data collection is fundamental to the success of DOE projects. We will address common challenges related to data collection and offer strategies to mitigate them.
Choosing the Right Experimental Design
Selecting the appropriate experimental design can be challenging. We will discuss how to choose the right design based on project goals, available resources, and the complexity of the problem.
Interpreting Complex Results
Interpreting the results of DOE experiments can be daunting, especially when dealing with complex data sets. We will provide guidance on how to decipher and extract meaningful insights from intricate
The Bottom Line
Lean Six Sigma offers a structured framework that integrates DOE principles with other powerful methodologies, equipping you with the expertise to lead process improvements, enhance product quality, and drive organizational excellence. With this certification, you’ll not only advance your career but also contribute significantly to the success of your organization.
Explore the world of DOE Engineering and Six Sigma certification, and embark on a journey toward becoming an exceptional problem-solver and a catalyst for positive change in your industry. Your commitment to learning and applying these methodologies will undoubtedly shape a brighter future for both your career and the organizations you serve.
Ready to become a DOE Engineering expert?
We can help you get there! Leave a comment down below.