Kaizen, a Japanese term meaning “change for the better,” refers to a philosophy and set of practices aimed at continuous improvement. It embodies a culture of ongoing enhancement in all areas of an organization, from top management to the operational level.
The concept is rooted in the idea that small, incremental changes can lead to significant improvements over time. Originally popularized in the manufacturing sector by Toyota, Kaizen has expanded its reach into various domains including healthcare, psychotherapy, government, and banking.
Table of contents
- What is Kaizen?
- Kaizen Methodology Process
- Kaizen Methodology
- Wastes in Kaizen
- Six Phases for Implementing Kaizen
- Kaizen vs. Innovation
- Implementing Kaizen Methodology
- Kaizen Methodology and Lean Manufacturing
- Total Employee Involvement
- Kaizen and Quality Management
- Masaaki Imai’s Contribution
- Final Words
- Related Articles
What is Kaizen?
The term Kaizen comes from two Japanese words: “Kai,” which means continuous, and “Zen,” which means improvement. “Kai” can also be translated as change, while “Zen” can be interpreted as better or good.
This philosophy asserts that improvement should be a continuous, everyday endeavour rather than a series of large, sporadic changes. It emphasizes that every day should see some form of enhancement within the company.
Kaizen, a Japanese term meaning “continuous improvement,” is a philosophy and methodology focused on enhancing processes, improving productivity, and fostering a culture of excellence within organizations.
The Kaizen approach emphasizes small, consistent changes rather than large, disruptive ones, involving all employees in identifying and solving problems.
By focusing on eliminating waste, improving workflows, and enhancing overall performance, Kaizen aims to create a culture of continuous development and operational excellence. Its core principles include problem-solving, teamwork, and a commitment to ongoing refinement and optimization of processes.
Core Principles of Kaizen Methodology
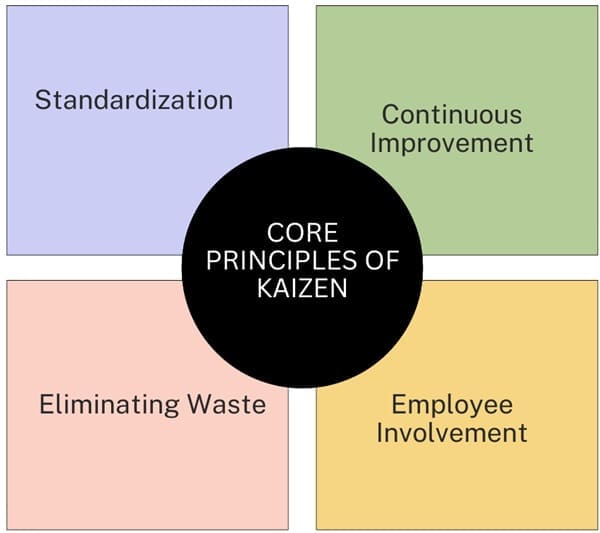
1. Continuous Improvement: Kaizen is based on the principle that improvement is an ongoing process. Unlike major overhauls or radical changes, Kaizen focuses on making small, incremental improvements consistently. This approach helps in achieving long-term success by gradually refining processes.
2. Employee Involvement: Kaizen emphasizes the involvement of all employees in the improvement process. From the CEO to the lowest-level worker, everyone is encouraged to contribute ideas for improvement. This collective engagement fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility.
3. Eliminating Waste: At the heart of Kaizen is the objective of eliminating waste, known as “Muda” in Japanese. Waste can be in the form of excess inventory, unnecessary movements, defects, or other inefficiencies. By systematically addressing these wastes, organizations can enhance productivity and efficiency.
4. Standardization: Once you make improvements, standardize them to maintain gains and build on further advancements. This involves documenting the new processes and ensuring consistent adherence.
Historical Background
Kaizen was first adopted in Japan after World War II, heavily influenced by American industrial practices and quality management techniques. During this period, the focus was on improving productivity with limited resources. The principles of Kaizen were formally introduced to Japan by Dr. W. Edwards Deming and others who contributed to the development of quality management practices.
Toyota’s implementation of Kaizen became a benchmark for its success, leading to widespread adoption across various industries. The methodology has evolved and integrated into diverse fields beyond manufacturing. This demonstrates its versatility and effectiveness.
Kaizen Methodology Approaches
You can implement the Kaizen methodology through various approaches. Each approach is suited to different types of improvements and organizational needs. Two prominent approaches are Kaizen Blitz (Point Kaizen) and Kaizen Burst (System Kaizen).
1. Kaizen Blitz (Point Kaizen): This approach involves rapid, focused improvements on specific processes or areas. It is characterized by quick implementation and immediate results. For example, if a supervisor notices inefficiencies in a process, a Kaizen Blitz may involve making quick, small changes to address those issues.
2. Kaizen Burst (System Kaizen): Unlike Point Kaizen, Kaizen Burst is a more strategic approach that targets systemic issues across processes or departments. It involves comprehensive planning and aims for significant improvements over a set period. This approach includes:
- Line Kaizen: Focuses on improvements within a single process or production line.
- Plane Kaizen: Extends improvements across multiple processes or departments.
- Cube Kaizen: Encompasses improvements throughout the entire organization, including suppliers and customers.
Kaizen Methodology Process
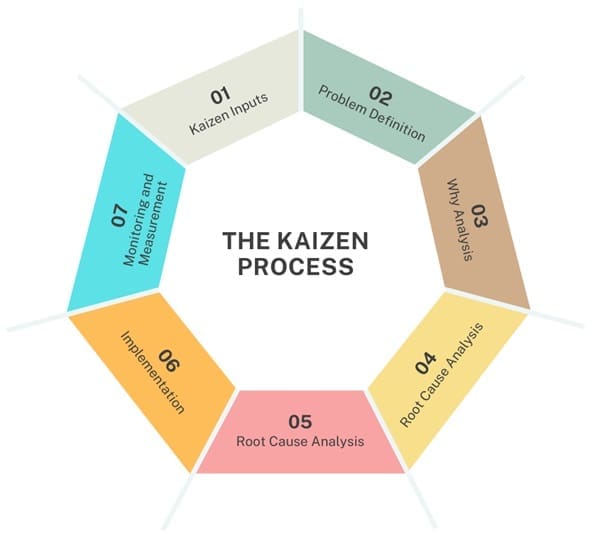
The Kaizen process involves several key steps, each crucial for effectively identifying and addressing issues within an organization. Here’s a detailed look at each stage:
1. Kaizen Inputs
The initial phase of the Kaizen process involves gathering inputs from various stakeholders, including employees, customers, and suppliers. These inputs serve as the foundation for identifying areas that require improvement. At this stage, the primary focus is on recognizing problems and understanding the need for Kaizen activities. This preliminary step sets the stage for the subsequent phases by ensuring that the issues are accurately identified and documented.
2. Problem Definition
After collecting the inputs, define the problem clearly. Specify the exact nature of the issue so that it can be effectively addressed. A well-defined problem statement is crucial as it provides a clear focus for the Kaizen team, enabling them to develop targeted solutions.
3. Why Analysis
The “Why Analysis” or “5 Whys” technique is employed to delve deeper into the root causes of the problem. By repeatedly asking “Why” about the problem, the team can trace back to the fundamental cause.
This step is essential for understanding the underlying issues rather than just addressing the symptoms. It helps in identifying the root cause, which is critical for implementing effective solutions.
4. Root Cause Analysis
After conducting the Why Analysis, the next step is to analyze the root cause of the problem. This involves examining the reasons behind the issue and understanding how these causes contribute to the problem. Identifying the root cause is crucial for developing solutions that address the core issue rather than just providing temporary fixes.
5. Kaizen Planning
With a clear understanding of the problem and its root cause, the next phase is Kaizen planning. This involves devising a plan to address the identified issues. The planning phase includes determining the methods and strategies that will be used to implement Kaizen effectively.
It also involves setting goals, defining roles and responsibilities, and establishing timelines for the implementation.
6. Implementation
The implementation phase involves putting the Kaizen plan into action. This step involves executing the planned improvements and ensuring their effective implementation. During the implementation, you must monitor the process to confirm that the changes are being carried out as intended.
Additionally, you need to verify that these changes are addressing the identified problems.
7. Monitoring and Measurement
After implementing the Kaizen activities, you should monitor and measure their effectiveness. Assess whether the changes have led to the desired improvements. Check if the problem has been resolved. Monitoring ensures that the Kaizen process delivers tangible results and provides a basis for making further adjustments if necessary.
Kaizen Methodology
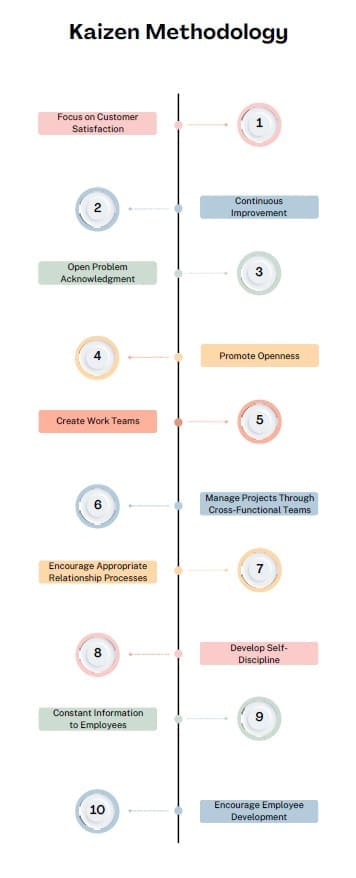
The Kaizen methodology is rooted in the philosophy of continuous improvement and is applied on a daily basis to enhance both individual and organizational performance. It emphasizes the importance of regular, incremental changes rather than radical overhauls. Key aspects of the Kaizen methodology include:
- Focus on Customer Satisfaction: Kaizen prioritizes improving processes to enhance customer satisfaction. This involves ensuring that products and services meet or exceed customer expectations.
- Continuous Improvement: The philosophy emphasizes the need for ongoing, incremental improvements. This approach helps in maintaining a constant focus on enhancing processes and achieving better results.
- Open Problem Acknowledgment: Kaizen encourages open communication and transparency within the organization. Recognizing and addressing problems openly fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
- Promote Openness: Effective Kaizen implementation requires open sharing of information and interfunctional communication. Leadership should be visible and supportive of the Kaizen initiatives.
- Create Work Teams: Teamwork is central to Kaizen. Collaborative efforts among team members contribute to more effective problem-solving and process improvement.
- Manage Projects Through Cross-Functional Teams: Kaizen promotes the involvement of various departments and external resources, such as suppliers and customers, in project management.
- Encourage Appropriate Relationship Processes: Investing in interpersonal skills and fostering positive relationships within the organization supports effective Kaizen implementation.
- Develop Self-Discipline: Self-discipline helps individuals adapt to changes and challenges, contributing to a culture of continuous improvement.
- Constant Information to Employees: Keeping employees informed about organizational developments and their roles in improvement initiatives is crucial for maintaining engagement.
- Encourage Employee Development: Empowering employees through training and development helps them acquire new skills and take on more responsibilities, driving overall organizational improvement.
Wastes in Kaizen
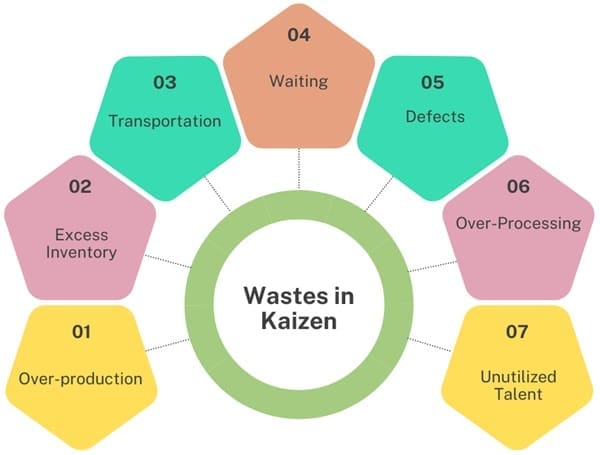
A fundamental principle of Kaizen methodology is the elimination of waste, or “muda.” Identifying and eliminating waste is crucial for enhancing efficiency and productivity. The seven types of waste that Kaizen aims to address include:
- Overproduction: Producing more than what is needed leads to excess inventory and increased costs. It can result from inaccurate sales forecasts or inefficient production processes.
- Excess Inventory: Holding excessive amounts of inventory ties up resources and increases storage costs. This includes raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods.
- Transportation: Excessive transportation or movement of materials and products can lead to inefficiencies and increased costs. It often results from poor layout or process design.
- Waiting: Time lost due to delays, such as waiting for materials, machine setup, or approvals, affects overall productivity. Reducing waiting times is essential for improving process efficiency.
- Defects: Defective products result in rework, warranty claims, and loss of customer trust. Addressing defects and ensuring quality is critical for maintaining customer satisfaction.
- Over-Processing: Waste occurs when processes are more complex than necessary, such as redundant steps or excessive paperwork. Simplifying processes can reduce this type of waste.
- Unutilized Talent: Not leveraging the skills and knowledge of employees effectively can lead to missed opportunities for improvement. Engaging employees in problem-solving and decision-making enhances organizational performance.
Six Phases for Implementing Kaizen
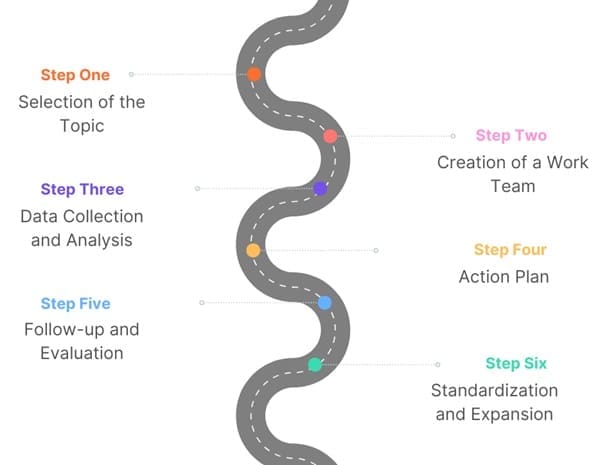
Implementing Kaizen methodology involves a systematic approach based on the Deming Cycle (PDCA: Plan, Do, Check, Act). The six phases for implementing Kaizen are:
- Selection of the Topic: Identify the focus areas for improvement, such as productivity, quality, or safety. The topic should align with organizational goals and priorities.
- Creation of a Work Team: Form a multidisciplinary team with members from various departments. A diverse team brings different perspectives and expertise to the improvement process.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Gather data related to the problem and analyze it to determine the root causes. Use tools like Pareto diagrams, Ishikawa diagrams, and flowcharts for analysis.
- Action Plan: Develop a plan to address critical issues identified during the analysis. The action plan should outline specific countermeasures, responsibilities, and timelines.
- Follow-up and Evaluation: Monitor the implementation of the action plan and evaluate the results. Use charts and metrics to track progress and make necessary adjustments.
- Standardization and Expansion: Once improvements are successfully implemented, standardize the new processes and expand them to other areas of the organization.
Practical Examples
Kaizen can be applied to various scenarios within an organization. Here are some practical examples:
- Employee and Management Meetings: Regular meetings between employees and managers can help identify and resolve conflicts, fostering a collaborative work environment.
- Work Group Organization: Organizing work into small groups can enhance employee involvement and efficiency. Teams can focus on specific tasks or projects, leading to better results.
- Goal Setting: Establishing common goals for employees encourages collective effort and drives performance. Aligning individual goals with organizational objectives ensures a unified approach to improvement.
- Workspace Optimization: For example, a furniture factory improved workspace organization by creating a team to enhance cleanliness and order. They collected feedback, implemented organizational strategies, and tracked results, leading to improved efficiency.
Kaizen vs. Innovation
| Basis | Kaizen | Innovation |
| Definition | A methodology focusing on continuous, incremental improvements in processes. | The introduction of new ideas, products, or methods that lead to significant change. |
| Objective | To make small, ongoing improvements that cumulatively result in substantial enhancements. | To create breakthroughs or entirely new concepts that drastically alter processes or markets. |
| Approach | Incremental, step-by-step improvements; focuses on refining existing processes. | Radical, often disruptive changes; involves creating something novel or significantly altering existing paradigms. |
| Scope of Change | Focuses on gradual changes within existing processes or systems. | Aims for transformational changes that may create new industries or disrupt existing ones. |
| Process | Structured process involving problem identification, root cause analysis, planning, implementation, and monitoring. | Often involves brainstorming, prototyping, testing, and scaling novel ideas. |
| Employee Involvement | Emphasizes involvement of all employees in continuous improvement activities. | Typically involves a smaller, specialized team or individuals with creative expertise. |
| Principles | Focuses on principles like continuous improvement, customer satisfaction, waste elimination, and team collaboration. | Centers around principles like creativity, experimentation, and market differentiation. |
| Implementation | Uses established methods like the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle for implementation. | Involves pilot projects, experimental phases, and scaling successful innovations. |
| Monitoring and Control | Regular monitoring and measurement to ensure improvements are effective and problems are solved. | Often requires market feedback, performance metrics, and adaptability to refine innovations. |
| Examples | Incremental improvements in manufacturing processes, reducing waste, optimizing workflows. | Development of new technologies, revolutionary product designs, or new business models. |
| Focus on Waste | Targets the elimination of specific types of waste such as overproduction, excess inventory, and defects. | May not focus directly on waste but on creating value through new approaches or products. |
| Measurement | Success is measured through improvements in efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. | Success is measured by market acceptance, revenue growth, and competitive advantage. |
Implementing Kaizen Methodology
1. 5S Kaizen: One of the foundational tools in Kaizen is the 5S methodology, which stands for Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain. This approach aims to create an organized, efficient, and clean workspace, which is crucial for continuous improvement. Implementing 5S helps in reducing waste and improving overall productivity.
2. Organizational Structure for Kaizen: Successful implementation of Kaizen requires a structured approach. The typical Kaizen organizational structure includes:
- Kaizen Steering Committee (KSC): This committee is composed of top management, external consultants, Kaizen managers, and team leaders. The KSC sets the direction for Kaizen activities, allocates resources, and ensures that improvements are made effectively.
- Kaizen External Consultants (KEC): These consultants provide specialized expertise and objective feedback. They help guide the Kaizen process and address any challenges that arise.
Kaizen Methodology and Lean Manufacturing
Kaizen is closely associated with Lean Manufacturing, a philosophy aimed at reducing waste and enhancing value. Key concepts within Lean, such as “Muda” (waste), “Mura” (unevenness), and “Muri” (overburden), are integral to Kaizen. By addressing these areas, organizations can streamline operations and improve efficiency.
1. Muda: Refers to any activity that does not add value to the product or service. Kaizen seeks to identify and eliminate these non-value-adding activities.
2. Mura: Focuses on reducing unevenness in production processes. Kaizen helps in smoothing out variations and ensuring consistent performance.
3. Muri: Addresses overburden on workers or machines. Kaizen aims to balance workloads and prevent excessive strain on resources.
Total Employee Involvement
A fundamental aspect of Kaizen is Total Employee Involvement (TEI). This principle emphasizes that every employee should actively engage in the improvement process. It applies to all employees, regardless of their role. Involving all levels of the organization fosters a culture of continuous improvement and encourages innovation.
- Individual Contributions: Employees are encouraged to identify areas for improvement and suggest solutions. This bottom-up approach helps in uncovering issues that may not be visible to top management.
- Small Group Activities: Small groups, often led by line supervisors, work together to implement improvements in their specific areas. These groups are instrumental in driving localized improvements and fostering a collaborative environment.
- Broader Impact: Kaizen often begins with small-scale improvements. These improvements can have a widespread impact across the entire organization. By continually refining processes and systems, Kaizen contributes to overall organizational success.
Kaizen and Quality Management
Kaizen Methodlogy aligns with various quality management principles, including Deming’s P-D-C-A cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Act) and Ishikawa’s Fishbone diagrams. These tools complement Kaizen by providing structured approaches to problem-solving and process improvement.
1. P-D-C-A Cycle: This cycle involves planning improvements, implementing them, checking the results, and acting on findings to make further improvements. It is a systematic approach that supports the Kaizen philosophy of continuous enhancement.
2. Fishbone Diagrams: Also known as Ishikawa diagrams, these are used to identify the root causes of problems. They help in visualizing the relationships between different factors and are a valuable tool for Kaizen projects.
Masaaki Imai’s Contribution
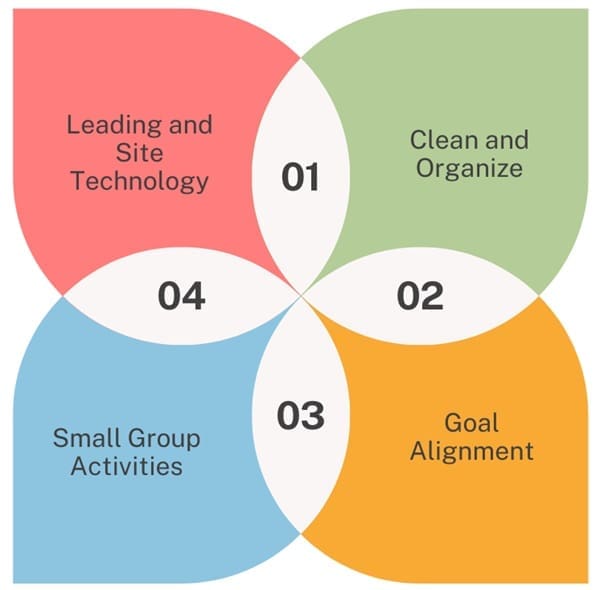
Masaaki Imai, a key proponent of Kaizen, emphasized its role in achieving competitive success. His book, “Kaizen: The Key to Japan’s Competitive Success,” highlighted the importance of continuous improvement and provided practical guidelines for implementation. Imai identified four foundational keys for successful Kaizen:
1. Clean and Organize: Implementing 5S to create an efficient and organized workspace.
2. Goal Alignment: Ensuring that improvement goals are aligned with organizational objectives.
3. Small Group Activities: Encouraging small, focused groups to drive improvements.
4. Leading and Site Technology: Utilizing technology and leadership to support Kaizen efforts.
Final Words
Kaizen methodology is more than just a set of techniques; it is a philosophy that drives continuous improvement in all aspects of an organization.
By fostering a culture of incremental change and involving every employee, Kaizen helps organizations enhance productivity, reduce waste, and achieve long-term success. Whether in manufacturing, healthcare, or any other field, the principles of Kaizen offer valuable insights and strategies for ongoing improvement.

About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.



















