When it comes to making sure that products meet high-quality standards, two important terms often come up: Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC). Though they sound similar, they play different roles in ensuring the quality of products and processes. Understanding the differences between QA and QC is essential for businesses, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, and software development.
Table of contents
Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance is about making sure that the processes used to develop and produce products are of high quality. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines QA as covering all matters that influence the quality of a product. In the pharmaceutical industry, QA covers development, quality control, production, distribution, and inspections.
ISO 9000 defines QA as “part of quality management focused on providing confidence that quality requirements will be fulfilled.” QA aims to prevent defects by ensuring that processes are designed and managed well. It is a proactive and preventive approach, focusing on planned and systematic activities, including documentation and process standardization.
Functions of Quality Assurance
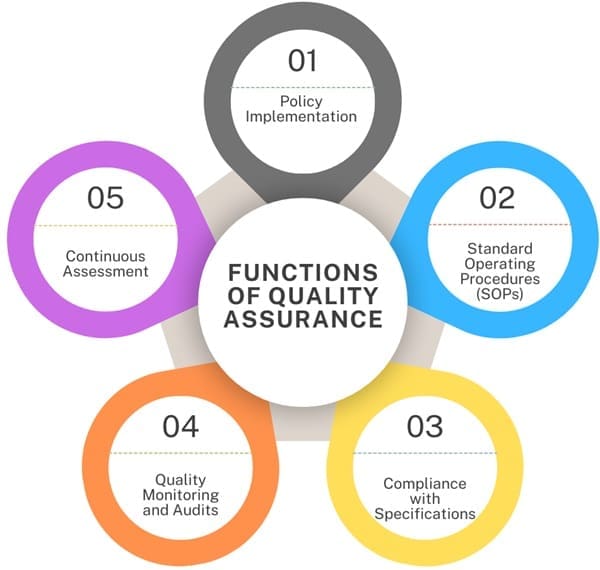
- Policy Implementation: Making sure that the quality policies adopted by a company are followed.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Creating necessary SOPs related to quality control.
- Compliance with Specifications: Ensuring that the product meets all applicable specifications and is made according to internal Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) standards.
- Quality Monitoring and Audits: Conducting quality checks and audits.
- Continuous Assessment: Regularly assessing operations and guiding them to comply with internal and external regulations.
Quality Control
Quality Control focuses on identifying and correcting defects in finished products. ISO 9000 defines QC as “a part of quality management focused on fulfilling quality requirements.” QC involves sampling, specification testing, documentation, and release procedures to ensure that necessary tests are done and products are only released after their quality has been verified.
QC activities are usually carried out by a dedicated team responsible for testing products for defects. The main goal of QC is to find defects in products after they are developed but before they are released, ensuring that only products meeting quality standards reach the market.
Functions of Quality Control
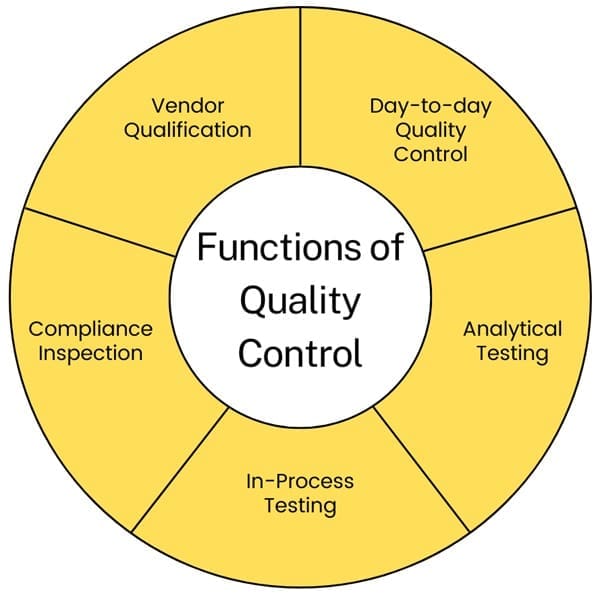
- Day-to-day Quality Control: Managing daily quality control within the company.
- Analytical Testing: Testing incoming raw materials and inspecting packaging components, including labeling.
- In-Process Testing: Performing required in-process testing and environmental monitoring.
- Compliance Inspection: Inspecting operations to ensure compliance with GMP.
- Vendor Qualification: Selecting qualified vendors for raw materials, including testing samples and auditing vendor operations.
Key Differences Between Quality Assurance and Quality Control
Definition and Focus
- Quality Assurance: QA focuses on processes used to develop and produce products. It aims to prevent defects by ensuring that processes are well-designed and managed. QA is proactive and preventive.
- Quality Control: QC focuses on products themselves, aiming to find and correct defects in finished products. It is reactive and involves inspecting and testing products to ensure they meet quality standards.
Objective
- Quality Assurance: The objective of QA is to improve development and test processes to prevent defects during production. It emphasizes prevention through planned and systematic activities.
- Quality Control: The objective of QC is to find defects in products after they are developed but before they are released. It emphasizes detection and correction of defects.
Responsibility
- Quality Assurance: QA is the responsibility of everyone involved in the product development process. It involves cross-functional teams working together to ensure process quality.
- Quality Control: QC is usually the responsibility of a dedicated team that tests products. This team focuses on identifying defects in finished products.
Tools and Techniques
- Quality Assurance: Tools and techniques used in QA include documentation, process standardization, SOPs, audits, training, and preventive measures. Verification of processes is a common QA activity.
- Quality Control: Tools and techniques used in QC include sampling, specification testing, inspection, and corrective actions. Validation of final product quality is a common QC activity.
Also See: Lean Six Sigma Certification Programs, St. Paul, Minnesota
Detailed Comparison: Quality Assurance vs. Quality Control
| Basis | Quality Assurance (QA) | Quality Control (QC) |
| Definition | A wide-ranging concept covering all matters that influence the quality of a product, focusing on the process used to make the product. | A part of quality management focused on fulfilling quality requirements, mainly through testing and inspecting finished products. |
| Focus | Ensuring quality in the processes by which products are developed. | Ensuring quality in the products themselves by identifying and correcting defects. |
| Proactivity vs. Reactivity | Proactive: Aims to prevent defects by focusing on processes. | Reactive: Aims to identify and correct defects in the finished product. |
| Objective | Improve development and test processes to prevent defects during production. | Identify defects after product development and before release. |
| Tools & Techniques | Documentation, process standardization, SOPs, audits, training, and preventive measures. | Sampling, specification testing, inspection, and corrective actions. |
| Responsibility | Shared by everyone involved in the product development process. | Typically the responsibility of a dedicated team that tests the product. |
| Examples | Verification of processes. | Validation of final product quality. |
Quality Assurance in the Pharmaceutical Industry
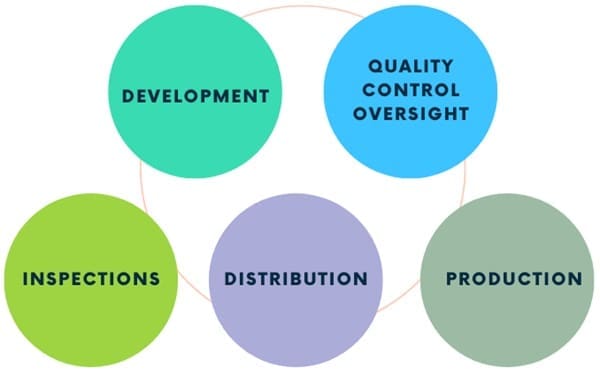
In the pharmaceutical industry, QA is crucial for ensuring that products are safe, effective, and of high quality. This involves thorough planning, documentation, and systematic activities throughout the product lifecycle. QA activities include:
- Development: Ensuring strict quality standards for developing new products.
- Quality Control Oversight: Supervising quality control processes to ensure effectiveness.
- Production: Ensuring that manufacturing processes are consistent and comply with GMP.
- Distribution: Make sure you store and transport products in ways that keep their quality.
- Inspections: Regularly inspecting facilities and processes to ensure compliance with internal and external regulations.
Quality Control in the Pharmaceutical Industry
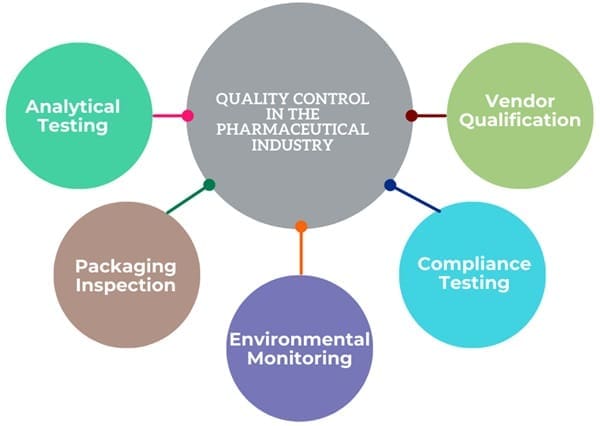
The pharmaceutical industry rigorously tests and inspects products to ensure they meet required standards before releasing them to the market. QC activities include:
- Analytical Testing: Testing incoming raw materials, in-process materials, and finished products for compliance with specifications.
- Packaging Inspection: Inspecting packaging components to ensure they meet quality standards.
- Environmental Monitoring: Monitoring the manufacturing environment to prevent contamination.
- Compliance Testing: Testing products to ensure they comply with GMP and other regulatory requirements.
- Vendor Qualification: Testing and auditing vendors to ensure they can provide quality raw materials.
Sources of Quality Variation
Several factors can contribute to quality variation in pharmaceutical products, including:
- Raw Materials: Variability in the quality of raw materials can impact the final product.
- In-Process Variations: Variations during the manufacturing process can affect product quality.
- Packaging Materials: The quality of packaging materials can influence the integrity and stability of the product.
- Labeling: Incorrect or inconsistent labeling can lead to quality issues.
- Finished Products: Variability in the final product itself.
- Manual Errors: Human errors during production and quality checks.
Control of Quality Variation
To control quality variation, pharmaceutical companies implement strict quality management systems, including:
- Raw Material Control:
- Developing precise and detailed raw material specifications.
- Sampling and testing raw materials according to standard procedures.
- Properly labeling and storing approved materials.
- In-Process Items Control:
- Ensuring environmental and microbiologic control.
- Implementing Manufacturing Working Formula Procedures.
- Controlling raw materials, manufacturing equipment, and packaging materials.
- Monitoring and controlling labels and finished products.
Final Words
Quality Assurance and Quality Control are two fundamental aspects of quality management that, although closely related, serve different purposes. QA proactively focuses on processes to ensure the development of products according to quality standards. QC, on the other hand, is a reactive approach that focuses on identifying and correcting defects in finished products.
Both QA and QC are essential for maintaining high-quality standards in industries where product quality is critical, such as pharmaceuticals. Understanding the differences between these two concepts and their respective roles and functions helps organizations implement effective quality management systems and ensure the delivery of high-quality products.

About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.



















