Table of contents
Estimated reading time: 7 minutes
6 Best Root Cause Analysis Tools
In the intricate world of organizational challenges, the importance of Root Cause Analysis (RCA) cannot be overstated. It serves as the compass, guiding businesses toward the heart of their list of root causes, enabling effective types of problem-solving analysis and sustainable growth. To embark on this journey of precision, one must equip themselves with the best root cause analysis tools. This article explores the diverse landscape of root cause methods, unveiling the power of six essential tools that delve into the intricacies of identifying and addressing the core issues that hinder progress. From the strategic insights of Pareto Charts to the systematic approach of the DMAIC Template, each tool plays a crucial role in unraveling the mysteries behind problems.
1. The Pareto Chart
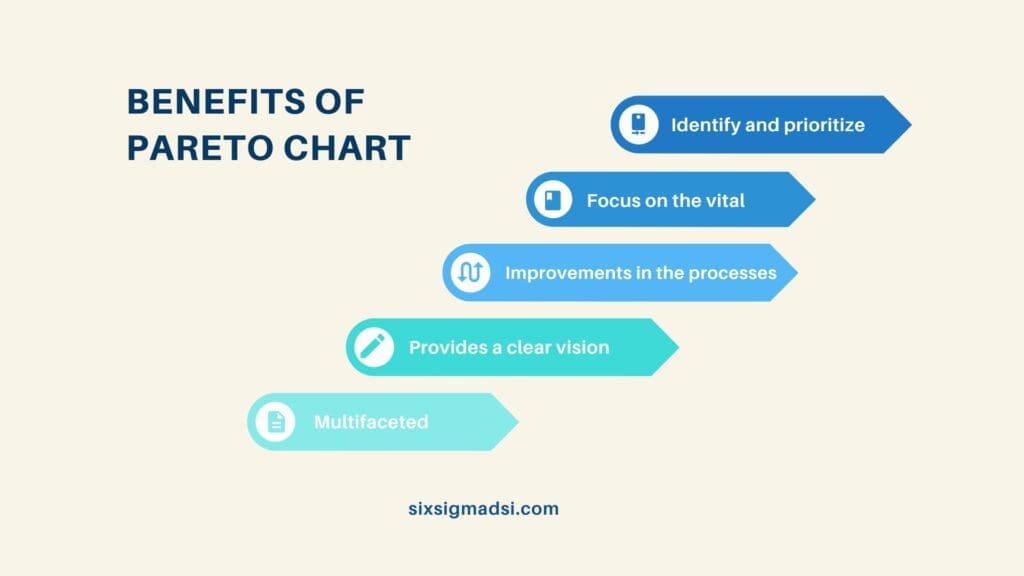
The Pareto Chart stands as a beacon in the realm of root cause analysis types. Developed by Vilfredo Pareto, this visual representation of data allows organizations to identify and prioritize the most significant issues affecting their processes. The Pareto Chart enables a strategic approach by focusing on the vital few root causes rather than getting lost in the noise of the trivial many.
Benefits and Purpose: The benefits of utilizing a Pareto Chart are multifaceted. It provides a clear visualization of the distribution of issues, allowing teams to allocate resources more efficiently. By addressing the major contributors first, organizations can witness substantial improvements in their processes.
Real-World Impact: Consider a manufacturing scenario with defects plaguing the production line. The implementation of a Pareto Chart revealed that a handful of issues were responsible for the majority of defects. By targeting these root causes, the company significantly reduced defects, showcasing the transformative impact of strategic problem-solving.
2. The 5 Whys
The 5 Whys method is a powerful tool in the arsenal of root cause analysis, providing a structured approach to understanding the cause-and-effect relationships underlying a problem. This method involves repeatedly asking “why” until the types of root cause give us an analysis of the problem. Organizations can move beyond surface-level symptoms by peeling back the layers and directly addressing the root causes. Keep asking “why” until you reach a fundamental cause. Sometimes, this may take more or fewer than five iterations.
Benefits and Purpose: The 5 Whys method encourages a culture of curiosity and thorough investigation. It enables teams to go beyond addressing symptoms, fostering a deep understanding of the issues at hand. This method is particularly effective in identifying root causes that might otherwise remain hidden. It doesn’t require sophisticated tools or resources, making it a cost-effective method for problem-solving.
Real-World Impact: Picture a software development team grappling with recurring system crashes. Through the application of the 5 Whys, they discovered that a coding error was at the heart of the problem. Rectifying this fundamental issue led to a stable and reliable software system, showcasing the method’s impact on problem-solving.
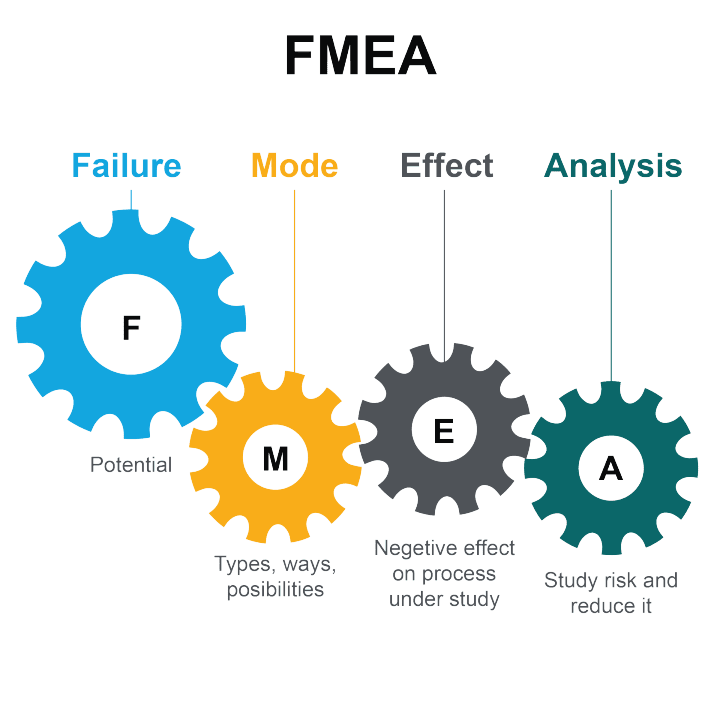
3. Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a proactive approach to root cause analysis, focusing on identifying and mitigating potential failures before they occur. This structured method involves evaluating and prioritizing potential failure modes in a system, ensuring organizations are well-prepared to address issues before they manifest.
Benefits and Purpose: FMEA encourages a proactive mindset, instilling a culture of continuous improvement and risk mitigation. By anticipating potential failures, organizations can implement preventive measures, saving both time and resources.
Real-World Impact: Imagine an aerospace company leveraging FMEA to assess potential failures in a critical aircraft component. This preemptive analysis allowed them to implement design changes, ensuring the safety and reliability of their aircraft in operation.
4. Statistical Process Control (SPC)
Statistical Process Control (SPC) empowers organizations to monitor and control processes in real-time by analyzing data. Establishing control limits and identifying variations allows teams to detect and address issues before they escalate, ensuring the stability and predictability of processes. Establish feedback from a list of root causes between SPC data and process improvement initiatives. Use the insights gained from SPC to make informed decisions about optimizing processes.
Benefits and Purpose: SPC provides a data-driven approach to maintaining process stability. By monitoring key variables, organizations can identify deviations early on, preventing potential quality issues and ensuring consistent production. SPC distinguishes between two types of process variations: common cause variation (inherent to the process) and special cause variation (resulting from specific, identifiable factors). Understanding these variations helps in determining whether adjustments to the process are needed.
Real-World Impact: A pharmaceutical company, for instance, utilized SPC to monitor the production of a critical medication. By closely monitoring key variables, they detected deviations early on, preventing potential quality issues and ensuring the consistent production of high-quality medicines.
5. Scatter Diagram
The Scatter Diagram is a graphical tool that unveils relationships between two variables, providing valuable insights into the complexity of systems. By visually representing data points, organizations can identify patterns, correlations, and potential outliers, facilitating effective decision-making. It consists of a series of data points plotted on a Cartesian plane, with one variable on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis.
Benefits and Purpose: The Scatter Diagram aids in understanding the intricate relationships within a system. By identifying correlations, organizations can make informed decisions and optimize processes for better outcomes. Scatter Diagrams help identify patterns or trends in the data. The visual representation allows analysts to quickly assess whether there is a relationship between the variables.
Real-World Impact: A retail chain, for example, used Scatter Diagrams to analyze the relationship between store layout and customer satisfaction. By identifying correlations, they optimized store layouts, leading to increased customer engagement and sales. In healthcare, Scatter Diagrams can be employed to examine the relationship between patient variables, such as age or lifestyle factors, and health outcomes.
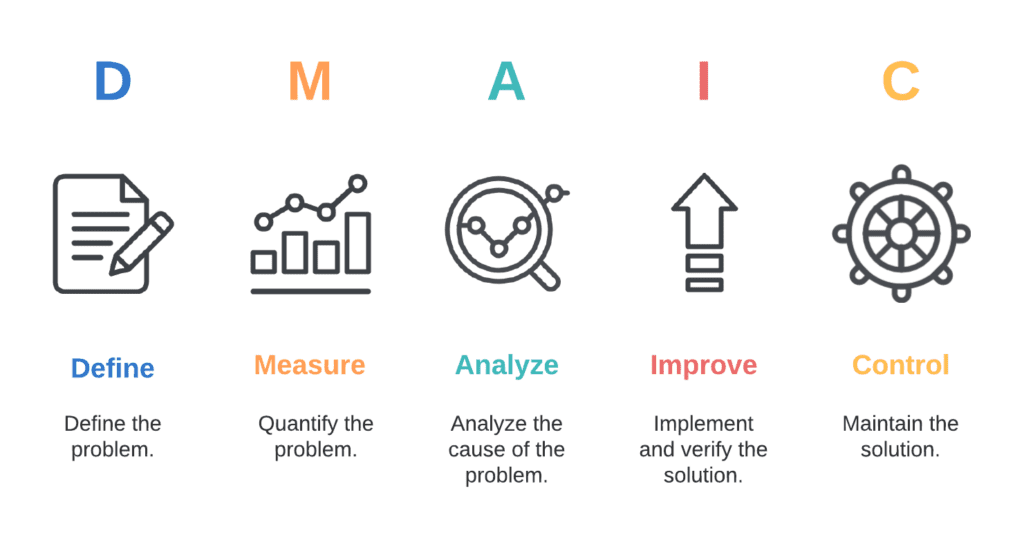
6. DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control)
The DMAIC Template, a cornerstone of the Lean Six Sigma methodology, provides a structured framework for problem-solving. DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control, offering a step-by-step approach to process improvement from a list of root causes. This template ensures a systematic and data-driven method, guiding teams through the complexity of problem-solving.
Benefits and Purpose: The DMAIC Template provides a structured and comprehensive approach to problem-solving. By defining, measuring, analyzing, improving, and controlling processes, organizations can achieve sustained excellence and continuous improvement.
Real-World Impact: A financial institution, for instance, employed the DMAIC Template to streamline its loan approval process. By systematically defining, measuring, analyzing, improving, and controlling the process, they reduced approval times, improving customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
The Bottom Line
In the ever-evolving landscape of business challenges, the use of the best root cause analysis tools becomes not just a choice but a strategic imperative. The journey into precision problem-solving requires a combination of these tools, each contributing a unique perspective to the overall understanding of issues. As a parting note, the adoption of the Lean Six Sigma methodology emerges as a beacon of excellence, encouraging organizations to navigate the complexities of problem-solving with finesse. In the world of Root Cause Analysis, these tools are not just instruments; they are the keys to unlocking the doors of sustainable growth and organizational resilience.

About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.



















