Kanban, a Japanese word meaning “visual card” or “signboard,” is a method used in lean production systems. It originated in the Toyota Production System (TPS) as a way to manage work and inventory efficiently, ensuring smooth production and minimizing waste.
This concept, first introduced by Taiichi Ohno, revolutionized manufacturing processes by introducing a visual workflow system to control inventory and production processes.
Table of contents
What is Kanban?
At its core, Kanban is a visual management tool designed to manage workflow and limit work in progress (WIP). By implementing Kanban, organizations visualize their workflow, identify bottlenecks, and limit how many tasks are in progress at a time. This approach improves efficiency and reduces waste. Additionally, it ensures that work processes align with real-time demand.
The main idea behind Kanban is to maintain just the right amount of WIP while moving tasks through the workflow. This prevents overproduction and reduces waste, making production more efficient and flexible to customer needs.
The system pulls tasks based on demand rather than pushing tasks regardless of immediate need. This makes it a pull-based scheduling system.
Origin of Kanban
Kanban originates from the lean manufacturing principles that Toyota developed in the 1940s and 1950s. Toyota industrial engineer Taiichi Ohno drew inspiration from supermarket stocking practices, where customers take only what they need and stores stock only what they expect to sell. This approach influenced the development of Kanban.
This observation led Ohno to create a system in which production would only occur in response to actual demand, minimizing excess inventory and optimizing resources.
At Toyota, Kanban cards were initially used to manage the flow of inventory and production on the factory floor. When a worker needed more materials, they would send a Kanban card to request additional stock. This ensured that production was based on real demand, rather than forecasts or predictions, and eliminated the problem of overproduction.
Over time, this system evolved to become an integral part of lean production methods, not only in manufacturing but also in various industries across the globe.
Key Principles of Kanban
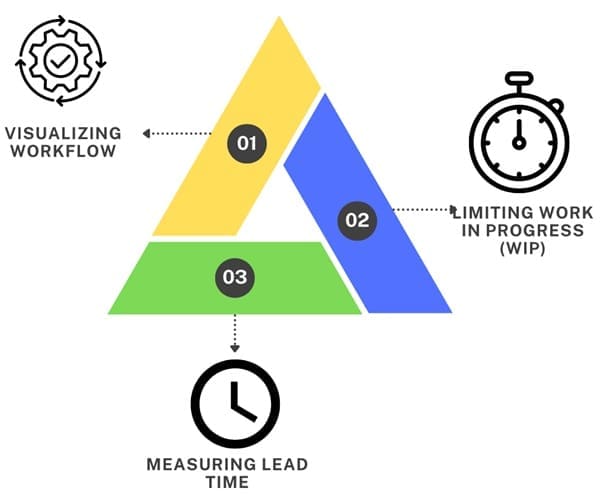
Kanban operates based on a few fundamental principles that drive its effectiveness:
- Visualizing Workflow: The first step in Kanban is visualizing the entire work process. One can usually accomplish this by splitting work into different stages, which you represent with columns on a board. Then, you write tasks on cards and place them in the appropriate columns according to their current stage in the workflow. This method allows teams to clearly see where each task is, track progress, and identify bottlenecks.
- Limiting Work in Progress (WIP): To avoid overloading the team and to prevent bottlenecks, each stage in the Kanban process has a limit on the number of tasks that can be in progress. Limiting WIP is crucial because it forces teams to complete current tasks before taking on new ones, ensuring continuous flow without overwhelming any part of the process.
- Measuring Lead Time: Lead time, or cycle time, represents the duration required to complete a task from start to finish. Teams measure lead time to monitor process efficiency and identify areas for improvement. By assessing lead time, they can make necessary adjustments. Consequently, these changes help ensure tasks are completed swiftly and predictably.
Benefits of Kanban
The Kanban system offers numerous advantages, particularly for industries or teams working in highly variable or uncertain environments. Some key benefits include:
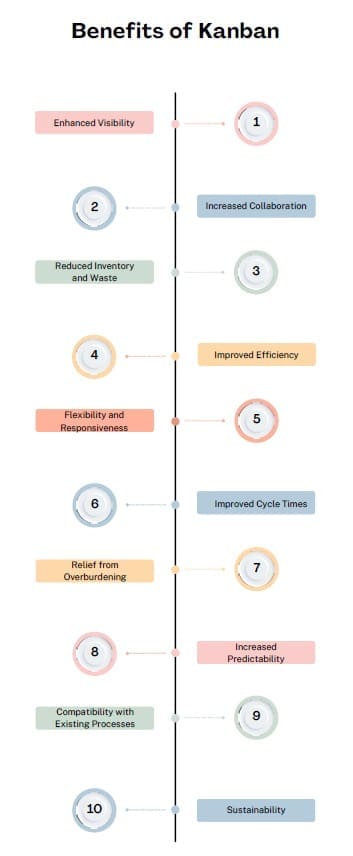
- Enhanced Visibility: Kanban’s visual representation of tasks and workflow stages makes it easy for team members to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement in real time.
- Increased Collaboration: Since the entire workflow is visible to everyone, team members tend to collaborate more effectively to resolve issues and ensure that tasks move smoothly through the process.
- Reduced Inventory and Waste: By using Kanban to manage WIP and limit overproduction, businesses can reduce inventory by 25-75%, saving costs and resources.
- Improved Efficiency: Kanban helps teams focus on completing tasks before starting new ones, which leads to higher efficiency, reduced wait times, and faster task completion.
- Flexibility and Responsiveness: Kanban systems enable teams to respond quickly to changing customer demands. Teams pull tasks based on current needs instead of pushing them forward based on predictions. Consequently, this approach helps them stay agile and efficient.
- Improved Cycle Times: Teams often experience significant improvements in how long it takes to complete tasks after adopting Kanban. This happens because bottlenecks and inefficiencies become more visible and easier to address.
- Relief from Overburdening: By limiting WIP, Kanban reduces the chances of teams becoming overwhelmed with too many tasks at once. This leads to a more manageable workload and a happier, more productive workforce.
- Increased Predictability: Kanban simplifies forecasting completion times for work. This clarity helps teams respond confidently to questions about delivery times and deadlines.
- Compatibility with Existing Processes: One of Kanban’s greatest strengths is its ability to integrate with almost any existing process. Moreover, this flexibility allows teams to implement Kanban alongside their current workflows with ease. This makes it highly versatile, whether a team is working in software development, manufacturing, or another industry.
- Sustainability: When applied strategically, Kanban can ensure that businesses operate sustainably by preventing burnout and fostering continuous improvement.
Kanban Practices

It relies on six core activities:
- Visualize the Workflow: The first step in Kanban is to create a clear, visual representation of the work process. You typically use a Kanban board to map out the stages of work. This allows team members to see the status of tasks at any given time. By visualizing tasks, potential bottlenecks or delays in the workflow become easier to identify.
- Limit Work in Progress (WIP): In Kanban, controlling how much work is in progress at any time is essential. By limiting WIP, teams avoid overloading themselves, which helps maintain focus and prevents inefficiencies that arise from multitasking. Work starts only when capacity is available. This approach ensures a steady flow of tasks through the system.
- Manage Flow: Kanban encourages teams to actively monitor and manage how work progresses through the system. The goal is to maintain a smooth, predictable flow that delivers value at a consistent rate. Teams focus on minimizing disruptions and resolving issues that could slow down progress.
- Make Policies Explicit: For Kanban to be effective, everyone involved must have a shared understanding of how tasks move through the workflow. This involves defining clear rules or policies for each stage of the process. These policies should be transparent to all team members to ensure consistency in decision-making.
- Implement Feedback Loops: Regular feedback is essential in Kanban to ensure continuous improvement. Teams use feedback loops to review their progress, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments. These can take the form of team meetings, retrospectives, or other forums for discussing workflow efficiency.
- Improve Collaboratively, Evolve Experimentally: Improvement in Kanban is achieved through collaboration and experimentation. Teams test small changes to the process and evaluate their impact before making broader adjustments.
Kanban vs. Scrum
Kanban and Scrum are both Agile frameworks that emphasize iterative work processes and continuous improvement. However, there are some key differences:
- Structure and Flexibility: Scrum operates within defined sprints (typically 1-4 weeks) where teams focus on delivering a shippable product. In contrast, Kanban has no fixed-length iterations. Teams continuously pull tasks from a prioritized backlog based on their capacity, which provides more flexibility.
- Releases: Scrum teams often release products at the end of each sprint. Kanban teams, on the other hand, release work continuously, as soon as it’s completed.
- Team Roles: Scrum has defined roles such as Product Owner and Scrum Master. Kanban, by contrast, doesn’t require changes to existing roles, allowing teams to work within their current structure.
- Work in Progress (WIP): Both methodologies limit WIP, but Kanban places a stronger emphasis on controlling the amount of ongoing work to maintain a steady flow.
Push vs. Pull Systems in Kanban
The Kanban system operates on a “pull” system rather than a “push” system, which is a significant departure from traditional production scheduling.
- Push System: In a push system, production is based on forecasts and schedules. Products are made in advance, regardless of when they are needed by the customer. This can lead to overproduction, excess inventory, and waste if demand doesn’t match the forecasts.
- Pull System: Kanban employs a pull system where actual customer demand drives production. Consequently, new tasks or products are initiated only when there is a request or need. This approach ensures that inventory levels stay low and production aligns with real-time demand. This minimizes waste and maximizes the efficient use of resources.
The Two-Bin and Three-Bin Systems
The organization can implement the Kanban system in various ways, depending on its needs. Two commonly used systems are the two-bin and three-bin systems, each of which provides a visual way to manage stock and production.
- Two-Bin System: This system involves using two bins to manage stock. When one bin empties, it signals that it needs a refill, while the second bin continues to supply the necessary materials. Initially, the UK used this system during World War II. Later, Toyota adopted it for managing inventory on the factory floor.
- Three-Bin System: This system expands on the two-bin system by introducing a third bin that connects different departments or even external suppliers. The process works as follows: the factory sends an empty bin to the store, the store refills the bin and sends an empty one to the supplier, and the supplier sends a full bin back to the store. This system ensures that materials are replenished based on real demand. Furthermore, it guarantees that nothing is moved without a specific request.
Role of Kanban Cards
Kanban cards are a critical part of the Kanban system.Kanban cards track the movement of materials, parts, or tasks through the workflow. When a task or material is consumed, the corresponding Kanban card signals that more needs to be produced or supplied.
The cards contain important information, such as the part description, quantity needed, lead time, and supplier details, ensuring that everyone involved in the process has the information they need to keep the workflow running smoothly.
These cards prevent overproduction by ensuring that tasks and materials only move forward when there is a demand signal. In this way, Kanban cards help create a demand-driven system that reduces waste, optimizes resource use, and enhances production efficiency.
Toyota’s Six Rules for Kanban
To ensure that the Kanban system runs smoothly, Toyota developed six key rules that guide its implementation:
- Each process must send requests for materials only after consuming what it has.
- Suppliers must produce and deliver only in response to those requests.
- No items are produced or delivered without a specific request.
- Kanban cards must be attached to the items they represent.
- Suppliers must maintain high-quality standards to ensure defect-free production.
- Limiting the number of requests reveals inefficiencies in the process, leading to continuous improvement.
These rules ensure that the Kanban system remains lean, responsive to demand, and focused on continuous improvement.
Final Words
Kanban is a powerful tool that helps organizations manage workflow, reduce waste, and improve efficiency. Its visual system allows you to easily track tasks and identify bottlenecks. Additionally, the pull-based approach ensures that production aligns with real demand. By implementing Kanban, organizations can optimize their processes, reduce costs, and respond quickly to changes in customer needs.
With its origins in Toyota’s lean manufacturing principles, Kanban has evolved to be applicable in various industries beyond manufacturing, including IT, healthcare, and service sectors. Its flexibility and focus on continuous improvement make it an indispensable tool for businesses looking to streamline their operations and increase productivity.

About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.



















