Six Sigma is a method that helps businesses improve their processes by reducing mistakes and increasing quality. It uses a belt system to categorize the level of knowledge and expertise individuals have in Six Sigma practices. Each belt represents a different level of understanding and responsibility in projects to improve processes.
In this guide, we will explore the different Six Sigma belt levels in detail, what they mean, and how they can benefit your career.
Table of contents
What is Six Sigma?
Before diving into the belt levels, let’s briefly discuss Six Sigma. Six Sigma is a data-driven approach that focuses on improving the quality of a process by identifying and removing the causes of defects and minimizing variability. The goal is to reach a level of quality where there are no more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities, which is considered “Six Sigma quality.”
Six Sigma uses various tools and techniques to analyze processes and identify areas for improvement. By employing statistical methods, businesses can make informed decisions that lead to better outcomes. This method is applicable in many industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and service sectors.
Six Sigma Certification Levels
The Six Sigma belt system categorizes individuals based on their knowledge and skills in the methodology. The belts range from White to Master Black, each representing a higher level of expertise and responsibility. Here’s a closer look at each belt level.
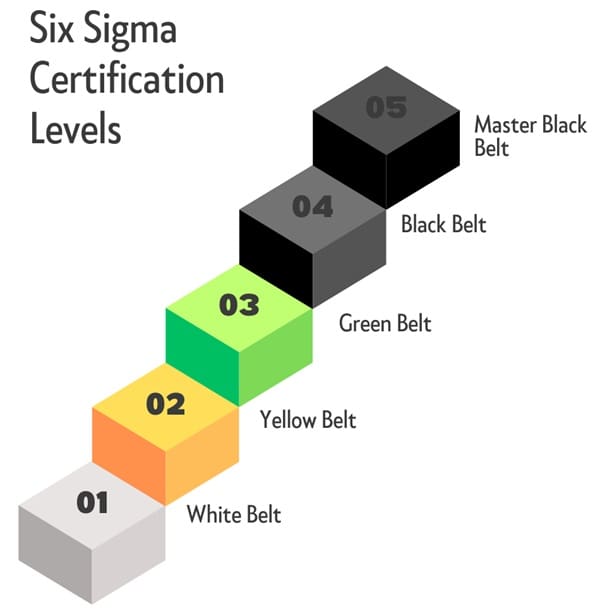
1. Six Sigma White Belt Certification
The White Belt is the entry-level certification in Six Sigma. It provides a basic understanding of Six Sigma principles and concepts.
Role and Responsibilities:
- White Belts participate in local problem-solving teams.
- They learn the basic terminology and concepts of Six Sigma, allowing them to support more experienced team members.
- While they may not lead projects, their role is essential in contributing to quality improvement efforts.
Typical Job Titles: Some job titles that may require a White Belt include:
- Transition Project Managers
- Change Management Specialists
- Integration Project Managers
Skills Learned:
- Understanding basic Six Sigma terminology
- Participating in team discussions
- Supporting project teams
2. Six Sigma Yellow Belt Certification
Overview: The Yellow Belt represents a step up from the White Belt. It indicates that the individual has a deeper understanding of Six Sigma concepts and how they apply to the workplace.
Role and Responsibilities:
- Yellow Belts work as part of project teams and can take on more responsibilities than White Belts.
- They may lead small-scale projects or assist in larger ones by gathering data and conducting analyses.
- Yellow Belts are trained in the DMAIC process (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) and can apply these steps to improve processes.
Typical Job Titles: Common job titles for Yellow Belts include:
- Data Governance Analysts
- Commissioning Engineers
- Laboratory Operations Managers
Skills Learned:
- Applying basic Six Sigma tools
- Leading small projects
- Collaborating with team members on process improvements
Average Salary: The average salary for a Yellow Belt is approximately $85,200.
3. Six Sigma Green Belt Certification
The Green Belt is a significant step up in the Six Sigma hierarchy. Green Belts have a solid understanding of Six Sigma principles and tools, allowing them to lead and manage projects effectively.
Role and Responsibilities:
- Green Belts lead quality improvement projects and work closely with Black Belts.
- They are responsible for analyzing data, identifying problems, and implementing solutions using the DMAIC process.
- Green Belts may also mentor Yellow Belts and contribute to team efforts.
Typical Job Titles: Roles that often require a Green Belt certification include:
- Quality Engineers
- Continuous Improvement Managers
- Business Process Analysts
Skills Learned:
- Advanced data analysis techniques
- Leading teams and projects
- Using Six Sigma tools like control charts and process mapping
Average Salary: The average salary for a Green Belt is around $95,600.
4. Six Sigma Black Belt Certification
Overview: The Black Belt is an advanced level of Six Sigma certification. Black Belts have a deep understanding of Six Sigma methodologies and lead complex projects that require significant expertise.
Role and Responsibilities:
- Black Belts lead and manage large projects, often overseeing a team of Green and Yellow Belts.
- They conduct advanced statistical analyses and are responsible for driving significant process improvements.
- Black Belts serve as mentors to lower-level belts, sharing knowledge and guiding teams through Six Sigma projects.
Typical Job Titles: Common job titles for Black Belts include:
- Project Managers
- Operations Managers
- Management Analysts
Skills Learned:
- Expert-level problem-solving and analysis
- Leadership and team management
- Advanced statistical methods and tools
Average Salary: The average salary for a Black Belt is approximately $120,200.
5. Six Sigma Master Black Belt Certification
Overview: The Master Black Belt is the highest level of Six Sigma certification. This designation indicates a high level of expertise and leadership within the Six Sigma framework.
Role and Responsibilities:
- Master Black Belts oversee multiple projects and provide strategic direction for Six Sigma initiatives across the organization.
- They mentor Black and Green Belts and often act as internal consultants for Six Sigma projects.
- Master Black Belts are responsible for developing training programs and ensuring that Six Sigma practices align with organizational goals.
Typical Job Titles: Positions that may require a Master Black Belt certification include:
- Senior Project Managers
- Lean Transformation Experts
- Senior Process Engineers
Skills Learned:
- Strategic planning and direction
- Coaching and mentoring
- Advanced project management and leadership
Average Salary: The starting salary for a Master Black Belt is around $132,000 and can exceed $200,000.
6. Six Sigma Champion
Overview: While not a formal belt level, the Champion plays a critical role in Six Sigma initiatives within an organization. Champions are typically upper-level managers who drive Six Sigma projects forward.
Role and Responsibilities:
- Champions ensure that Six Sigma projects align with business objectives and support strategic initiatives.
- They provide resources, remove obstacles, and mentor project teams.
- Champions track the progress of Six Sigma initiatives and help maintain organizational commitment to process improvement.
Skills Learned:
- Strategic alignment of projects
- Resource allocation and management
- Leadership and mentoring
How Six Sigma Certification Can Advance Your Career?
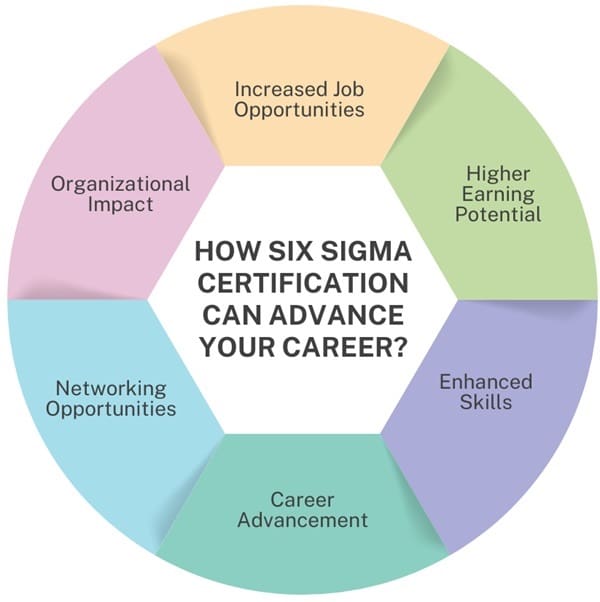
Earning Six Sigma certification can significantly boost your career prospects and enhance your professional skills. Here are some key benefits of obtaining Six Sigma certification:
- Increased Job Opportunities: Many companies actively seek Six Sigma-certified professionals to lead their process improvement initiatives. Having a Six Sigma certification can set you apart from other candidates in the job market.
- Higher Earning Potential: Certified professionals often earn higher salaries compared to their non-certified peers. Each belt level typically correlates with increased pay, reflecting the greater responsibilities and expertise required.
- Enhanced Skills: Six Sigma training equips you with valuable problem-solving, data analysis, and project management skills. These skills are applicable across various industries, making you a versatile candidate.
- Career Advancement: Many organizations offer opportunities for advancement to employees who pursue Six Sigma certifications. Your dedication to professional development can lead to promotions and leadership roles.
- Networking Opportunities: Becoming certified can connect you with a network of professionals who share similar interests in process improvement. This network can provide support, mentorship, and job leads.
- Organizational Impact: As a Six Sigma-certified professional, you can make a significant impact on your organization by improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing customer satisfaction. This not only benefits the company but also showcases your value as an employee.’
Comparison of Six Sigma Certification Levels
| Belt Level | Overview | Role and Responsibilities | Skills Learned | Typical Job Titles |
| White Belt | Entry-level certification with basic understanding. | Participates in local problem-solving teams; supports higher-tier individuals. | Basic Six Sigma terminology; team participation. | Transition Project Managers, Change Management Specialists. |
| Yellow Belt | Intermediate level with more in-depth knowledge. | Works on project teams; can lead small projects; assists managers; applies DMAIC. | Basic tools application; leading small projects. | Data Governance Analysts, Commissioning Engineers. |
| Green Belt | Solid understanding and ability to lead projects. | Leads quality improvement projects; analyzes data; assists Black Belts. | Advanced data analysis; project management. | Quality Engineers, Continuous Improvement Managers. |
| Black Belt | Advanced certification with deep expertise. | Leads large projects; conducts advanced statistical analyses; mentors lower belts. | Expert problem-solving; leadership and team management. | Project Managers, Operations Managers. |
| Master Black Belt | Highest certification level with extensive experience. | Oversees multiple projects; provides strategic direction; mentors Black and Green Belts. | Strategic planning; coaching and mentoring. | Senior Project Managers, Lean Transformation Experts. |
Final Words
Understanding the Six Sigma belt levels is essential for anyone looking to advance their career in process improvement and quality management. Each belt signifies a different level of expertise and offers unique opportunities for growth and development.
By pursuing Six Sigma certifications, you equip yourself with the skills and knowledge necessary to drive meaningful change within your organization.
Whether you are starting your career with a White Belt or aiming for the prestigious Master Black Belt, Six Sigma provides a structured pathway for professional development. As businesses continue to prioritize efficiency and quality, the demand for
Six Sigma-certified professionals will only increase, making this certification a valuable asset in today’s competitive job market. Embrace the journey of Six Sigma, and unlock the potential for both personal and professional growth.

About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.



















