Total Productive Maintenance has become a powerful tool to increase equipment efficiency and minimize downtime. This comprehensive guide will explore the meaning, benefits and application of TPM, as well as its pillars.
Table of contents
What is Total Productive Maintenance?
Total Productive Maintenance is an approach to maintenance. It aims to involve all levels within an organization to maximize the effectiveness of production equipment.
TPM is a proactive maintenance strategy that emphasizes preventive maintenance, unlike traditional maintenance strategies which focus on reactive repairs. TPM’s goal is to achieve “perfect manufacturing” – a state in which breakdowns, accidents, and defects are eliminated.
Public, Onsite, Virtual, and Online Six Sigma Certification Training!
- We are accredited by the IASSC.
- Live Public Training at 52 Sites.
- Live Virtual Training.
- Onsite Training (at your organization).
- Interactive Online (self-paced) training,
Benefits of Total Productive Maintenance
Implementing TPM has many benefits both direct and indirect. These are:
- Reduced unplanned downtime: By switching from reactive to proactive equipment maintenance, TPM can reduce unplanned equipment failures, and the associated downtime. This leads to an increase in Overall Equipment Effectiveness.
- Improved product quality: TPM improves product quality by identifying and eliminating defects. This results in better-quality products with fewer complaints from customers.
- Reduced manufacturing costs: TPM reduces manufacturing costs by maximizing equipment reliability and efficiency. This increases profitability and minimizes expenditures on equipment repair and replacement.
- Enhanced workplace safety: TPM promotes workplace safety by fostering a culture that encourages preventive maintenance, as well as identifying hazards. This reduces the risk of accidents and even injuries.
Also Read: Maintenance Planning: Optimize Asset Uptime & Efficiency
How Total Productive Maintenance Works?
TPM is based on the principle that employees of all levels should be involved in equipment maintenance and operations. It involves:

- Autonomous Maintenance: Allowing operators to perform routine maintenance tasks such as cleaning, inspecting, lubricating and repairing equipment.
- Planned Maintenance: Schedule maintenance based on historical data and predictive analytics to optimize resource usage and minimize downtime.
- Quality management: Integrated defect prevention measures in production processes for consistent product quality.
- Early equipment management: Design and install equipment with reliability and maintainability in mind to reduce future maintenance requirements.
- Safety, Health, and Environment: Ensure that environmental sustainability and safety are considered throughout the entire maintenance process to create a safe and hazard free workplace.
- TPM in administration: Streamlining administrative functions such as order processing, procurement and other areas to maximize production efficiency and minimize delay.
Implementing Total Productive Maintenance: Step-by-Step Guide
There are several steps to implementing TPM:
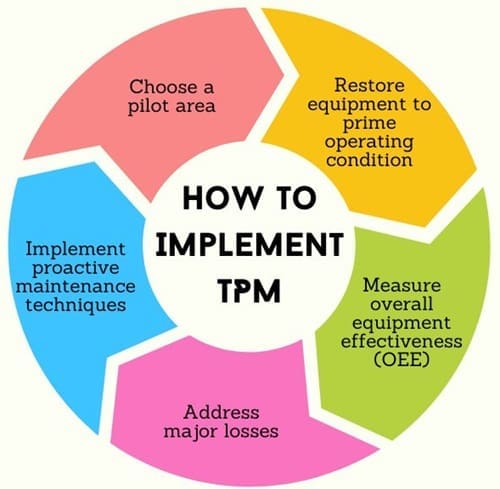
- Choose a pilot area: Select an area or piece equipment that will serve as a test bed for the implementation of TPM principles.
- Restore equipment to prime operating condition: Use the 5S method to organize your workspace and teach operators how to perform autonomous maintenance.
- Measure overall equipment effectiveness (OEE): It is to identify areas of improvement and assess equipment performance.
- Address major losses: Create cross-functional teams that will address the root causes of downtime, and find effective solutions.
- Implement proactive maintenance techniques: Integrate proactive maintenance techniques that are based on wear analyses and failure predictions.
Also Read: What is Total Quality Management (TQM)?
The Eight Pillars of Total Productive Maintenance
TPM is supported on eight pillars. Each pillar represents a fundamental element of the maintenance process.
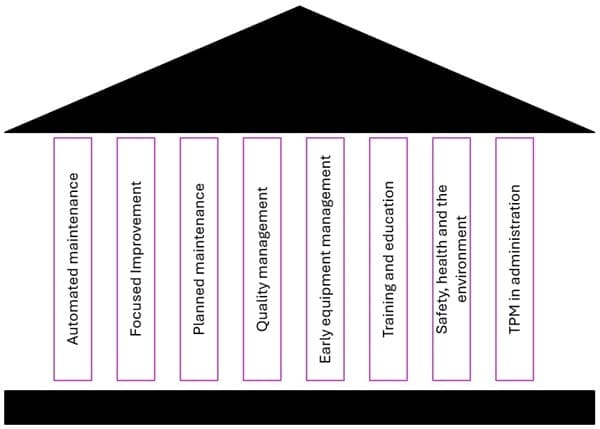
- Automated maintenance: Give operators the autonomy to perform routine maintenance and take responsibility for equipment care.
- Focused Improvement: Encourage continuous improvements through small, incremental modifications to processes and procedures.
- Planned maintenance: Schedule maintenance activities using predictive analytics to optimize resource usage and minimize downtime.
- Quality management: Incorporate defect prevention measures in production processes to ensure consistent quality.
- Early equipment management: Design equipment to be reliable and maintainable, and install it early. This will reduce future maintenance costs.
- Training and education: Train operators, managers and maintenance personnel in TPM.
- Safety, health and the environment: Make sure to prioritize safety and environmental sustainability in all maintenance processes.
- TPM in administration: Streamline administrative tasks to maximize production efficiency and minimize delay.
Evolution of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
Total Productive Maintenance has evolved since its conception. It is no longer a maintenance-centric philosophy, but a holistic approach that encompasses all aspects of manufacturing. Traditional TPM focuses on equipment reliability and maintenance, while advanced TPM includes a wider range of initiatives.
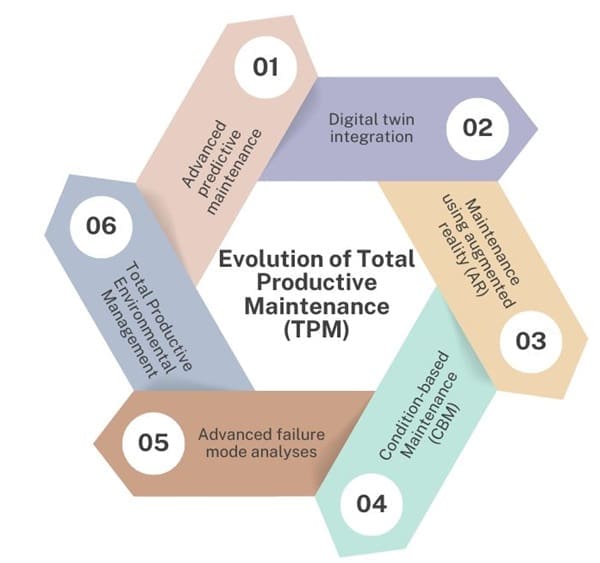
Advanced predictive maintenance
Using cutting-edge technology such as machine learning, predictive analytics and IoT sensors to predict equipment failures and maximize asset utilization.
Digital twin integration
Integration of digital twin technology in TPM practices allows for the creation of virtual replicas of assets. This allows real-time monitoring and simulation of equipment performance, and optimization of maintenance strategies.
Maintenance using Augmented Reality (AR)
AR is used to give maintenance personnel intuitive, hands-free instructions and guidance during equipment inspections and repairs. This increases efficiency and accuracy.
Condition-based Maintenance (CBM)
A transition from time-based schedules to condition-based strategies where maintenance activities can be triggered by real-time data or asset health indicators. This results in optimal maintenance intervals and lower operational costs.
Advanced failure mode analyses
Using sophisticated failure mode techniques such as fault tree (FTA) analysis and failure mode effect analysis (FMEA), identify, prioritize and mitigate potential failures and their associated risks. This will enhance equipment reliability and safety.
Total Productive Environmental Management
Extending the scope of TPM, to include environmental sustainability efforts such as energy efficiency improvement, waste reduction strategies and carbon footprint minimization, while aligning maintenance practices with corporate sustainability goals.
Applications of Advanced TPM
Advanced TPM is used in a wide range of industries, from pharmaceuticals to consumer electronics. Among the notable applications are:
- Smart factories: In an era of Industry 4.0 and advanced TPM, smart factories use data-driven, interconnected manufacturing ecosystems, where equipment, processes and personnel work together seamlessly to maximize production efficiency, flexibility and quality.
- High-tech manufacturing: In high-tech manufacturing industries like semiconductor fabrication and electronic assembly, advanced TPM methods play a crucial role in ensuring reliability and performance of precision-engineered, complex equipment and processes.
- Pharmaceutical production: Advanced TPM practices in pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities are crucial for maintaining compliance with strict regulatory requirements, while maximising equipment uptime, quality of product, and operational efficiency.
- Automotive production: Advanced TPM techniques in automotive assembly plants enable Just-in-Time (JIT), lean production and continuous improvement initiatives. This drives cost reduction, quality improvement, and competitive edge.
Also See: Kaizen in Management
Final Words
TPM is more than just a strategy for maintaining equipment. It’s an integrated approach that maximizes efficiency, reduces downtime and fosters a culture of continual improvement. Through the use of proactive maintenance and engaging employees on all levels, companies can achieve “perfect productivity” and reap many benefits from TPM.

About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.





















Helpful to learn about Lean and Lean Six Sigma. How to learn about Lean Construction Techniques ? How can we know some successful case studies of applying Lean Six Sigma?
Syed, read: https://www.boomandbucket.com/blog/lean-six-sigma-in-construction-process-improvement.