Table of Contents:
What is Kaizen?
Kaizen is a tool of continuous improvement processes in management that focuses on small, positive changes that can lead to significant improvements. It’s typically based on cooperation, and commitment, and contrasts with top-down transformational approaches. Kaizen is the core of lean manufacturing and The Toyota Way. Kaizen process flow is whats created in the manufacturing industry to reduce defects, eliminate waste and increase productivity.
It’s a broad concept with many interpretations and has been used in many industries, including healthcare. It can be used in any industry and at any level. There are many tools and approaches to Kaizen. These include value stream mapping which documents, analyses and improves information flows or product production — and total quality management which enlists all workers to work towards improving quality. No matter what method you use, Kaizen is only successful in an organizational setting if there is support from all levels of the organization.
Kaizen in management is a combination of two Japanese words which translate to “good change” and “improvement”. Kaizen, however, has been interpreted as “continuous improvement” because of its association with lean principles and methodology.
Kaizen was born in post-World War II Japanese quality circles. These groups or circles of workers were focused on preventing Toyota defects. These circles were created partly as a response to American productivity consultants and management who visited Japan, particularly W. Edwards Deming who believed that quality control should be more directly in the hands of line workers. Masaaki Imai’s book Kaizen, The Key to Japan’s Competitive Successin 1986 brought Kaizen to the West.

Kaizen: 10 Principles
Kaizen in management is about fostering a culture of excellence in a company. These 10 principles are often referred to as the core of the philosophy. These are:
- Don’t hold on to your assumptions.
- Take the initiative to solve problems.
- Do not accept the status quo.
- Don’t be a perfectionist and adopt an attitude that is iterative and adaptive.
- As you make mistakes, look for solutions.
- Make sure everyone feels empowered to make a contribution.
- Do not accept the obvious problem; instead, ask five times “Why” to find the root cause.
- Collect information and opinions from many people.
- You can use your creativity to make small, low-cost improvements.
- Never stop learning.
How Kaizen works
Kaizen is based upon the belief that anything can be improved and nothing should remain the same. It is also based on the Respect for People principle. Kaizen is about identifying problems and opportunities, creating solutions, and rolling them out. Then, you cycle through the process for any issues or problems that have not been addressed. This cycle can be used to continuously improve and provide a method of executing the process. It consists of seven steps.
Continuous Improvement Through Kaizen Cycle
Kaizen process flow can be applied in seven steps to creating an environment that encourages continuous improvement. These steps are whats part of this systematic kaizen approach:
- Engage employees. Ask employees for their involvement, and ask them to help you identify problems. This will encourage employees to support change. This is often done by establishing specific groups of people who are responsible for gathering and relaying information from a larger group of employees.
- Collect feedback from employees to identify problems and possible solutions. If there are multiple issues, create a list.
- Find a solution. Inspire employees to come up with creative solutions. Choose one or more winning solutions from the suggestions.
- Use the winning solution to test it. Have everyone participate in the rollout. To test the solution, create pilot programs.
- Review the results. Make plans to monitor progress at various times. Develop specific plans that will identify who will be the point of contact and how to keep workers on the ground engaged. Find out how successful the change was.
- Positive results can be adopted throughout an organization.
- These seven steps need to be repeated regularly, with new solutions being tested as necessary or new problems being tackled.
Additional approaches to the Kaizen cycle exist, such as one that is condensed into four steps — plan, do, check, act, or PDCA. It is also known as the Shewhart cycle or Deming cycle.

Different Types of Kaizen Events
Kaizen’s process flow goal is to promote cultural change. However, Kaizen events can be used to kick-start these efforts or address a particular set of problems.
Kaizen is a concentrated effort to make short-term changes in order to reach a goal. Kaizen events are known by many names, such as the Kaizen blitz and Kaizen burst. These events can use a variety of tools or be focused on specific areas such as the 5S Framework, total productivity maintenance, and Value stream mapping.
Whats Kaizens’ main tools?
Different tools are used depending on the goals of the kaizen method. The 5S tool, for example, is used to lean manufacturing. It helps ensure safe, efficient, and productive workplaces. Inventory control is done using Kanban and JIT. The five whys (what when, where, and why) are a tool that can be used to identify the root cause of a problem. Value stream mapping can be used to find places where waste can be eliminated. To sustain improvements, follow-up events can be used.
Kaizen 5S framework
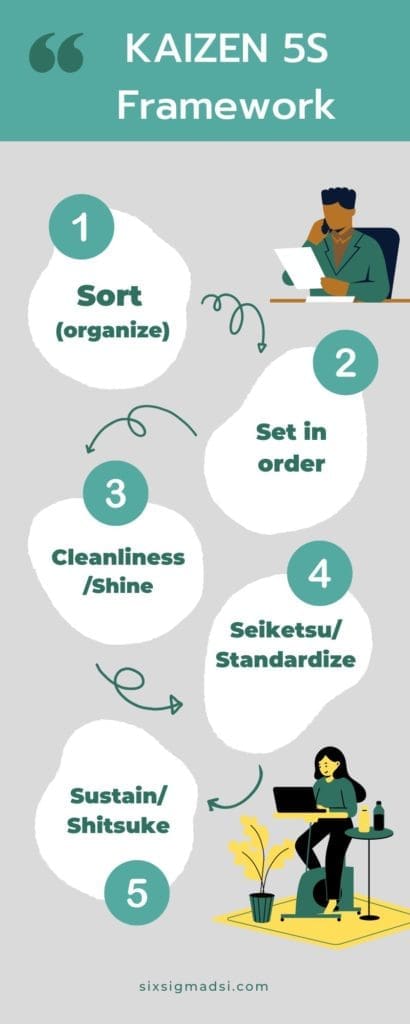
The Kaizen system is dependent on a 5S framework. It creates a perfect physical workplace. The 5Ses are focused on visual order, organization and cleanliness. This standardization will improve safety, profitability, efficiency, and service. Below is a list of the 5Ses in Japanese and their English translations.
- Sort (organize). Separate the essential workplace items from the unnecessary and get rid of them.
- Set in order/Create orderliness. Arrange items so that they are easy to find in a way that makes sense for your work.
- Cleanliness/Shine
- Seiketsu/Standardize (standardized cleaning). Systematize workplace cleanup best practices.
- Sustain/Shitsuke (discipline). Keep going.
Whats an Example of Kaizen?
Toyota is an example of a company that uses kaizen as a tool to maintain its success. Ford Motor Company is another well-known example of a kaizen at work. They adopted kaizen to reduce the time required to complete different manufacturing processes.
Kaizen’s Advantages and Disadvantages
Kaizen process flow can be a great tool for organizations for many reasons. However, it’s not always the best fit for every situation. These are some of Kaizen’s benefits and drawbacks:
Kaizen advantages
- Kaizen’s emphasis on gradual improvement can lead to a more gentle approach to change than big efforts that might be abandoned because of their tendency to cause resistance and pushback.
- Kaizen encourages the examination of processes to reduce waste and mistakes.
- There are fewer mistakes, which means that oversight and inspection requirements can be reduced.
- Kaizen promotes a sense of value and purpose, which improves employee morale.
- Employees think beyond their departments to increase teamwork.
- Employees become more attentive to customer needs, which increases client focus.
- To encourage improvements in both the short- and long-term, systems are in place.
Kaizen disadvantages
- Closed communication cultures and companies with a culture of territorialism may need to first focus on cultural changes in order to create an environment that is more open to new ideas.
- Kaizen events that are short-term may cause a temporary burst in excitement, but it is usually not sustainable.
Key Takeaways
- Kaizen, a Japanese business philosophy, focuses on improving productivity and making work environments more efficient.
- Kaizen encourages employees to make changes at any time.
- Kaizen is a Japanese word that means “change for the better” or continuous improvement.
- Kaizen can make small changes in quality control, just-in-time delivery, standard work, efficient equipment use, and elimination of waste.
- Kaizen emphasizes the importance of small changes that can make a big difference in the future.

About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.




















Your exploration of Kaizen management systems is both thorough and enlightening. Your article nicely highlights the continuous improvement aspect. I recently read an article on Benefits of Kaizen Management System Training delving into how Kaizen can enhance employee engagement and streamline workflows, leading to significant productivity gains. It’s fascinating how these small, incremental changes can continue to drive major business success.