Effective Supplier Quality Management is a collaborative and proactive process that integrates closely with a company’s overall supply chain strategy. It starts early in the supplier selection phase and continues through the entire product life cycle. The goal of SQM is to ensure that suppliers provide consistent, high-quality products and services that align with a company’s specifications and customer needs, ultimately contributing to business success.
Table of contents
What is Supplier Quality Management?
Supplier Quality Management (SQM) refers to the process of overseeing and controlling the quality of materials, products, or services provided by suppliers. It involves systematically evaluating supplier performance, ensuring that suppliers meet specific quality standards, and proactively managing the relationship between the buyer and supplier to optimize quality, minimize risks, and reduce costs.
SQM is essential for organizations that rely on external suppliers to deliver raw materials or services, as any failure in supplier quality can have significant consequences for the company, including product defects, customer dissatisfaction, and regulatory compliance issues.
Key Components of Supplier Quality Management
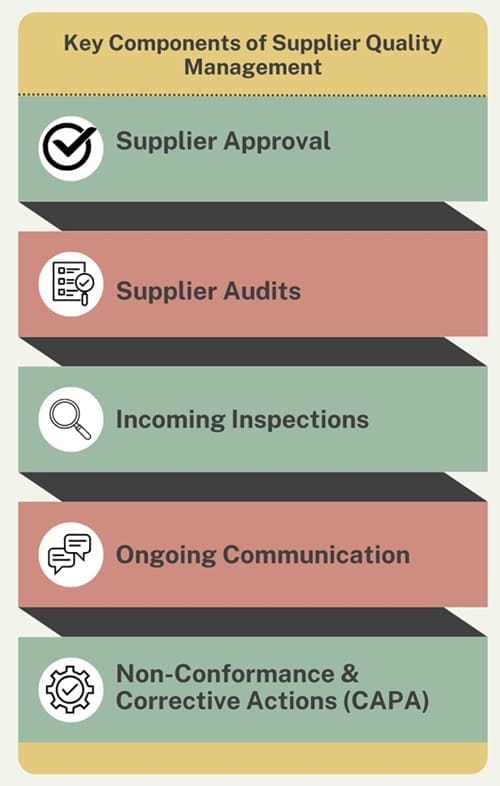
To effectively manage supplier quality, businesses need to focus on several core components:
- Supplier Approval
Before a company can work with a supplier, it must assess their capabilities to meet quality standards. This process often involves evaluating the supplier’s quality management system (QMS), reviewing their past performance, and ensuring that they meet the company’s requirements for product quality, delivery timelines, and regulatory compliance. - Supplier Audits
Regular audits help assess whether suppliers maintain the required quality standards. These audits can be internal or conducted by third-party organizations and should include detailed checks on quality control processes, production practices, and compliance with relevant standards. - Incoming Inspections
Businesses should perform thorough inspections on materials or products received from suppliers. These inspections ensure that the incoming goods meet predefined quality specifications before they enter the production line. - Ongoing Communication
Continuous communication with suppliers is essential for maintaining quality. This includes sharing expectations, addressing issues as they arise, and ensuring that suppliers are aware of any changes in requirements. Open communication helps prevent misunderstandings and fosters stronger, long-term relationships. - Non-Conformance & Corrective Actions (CAPA)
If a supplier provides defective products or materials, the company needs to have a system for reporting and addressing non-conformances. Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA) are used to determine the root cause of quality issues and implement measures to prevent them from occurring in the future.
How is Supplier Quality Management Measured?

Measuring supplier quality is an essential aspect of SQM. Businesses use a set of predefined metrics and performance indicators to evaluate suppliers and track improvements over time. These performance metrics often include:
- Quality Metrics
This includes the rate of defects per unit, the number of returns or complaints from customers, and adherence to quality standards. - On-Time Delivery
Suppliers must meet agreed delivery schedules. Delays can disrupt the production process and impact customer satisfaction. On-time delivery rates are a key performance indicator. - Responsiveness and Communication
A supplier’s responsiveness to inquiries, issue resolution, and willingness to collaborate is an important metric. Effective communication helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures that quality issues are resolved quickly. - Cost Efficiency
Companies often measure the total cost of working with a supplier, including product costs, transportation, handling fees, and potential penalties for late deliveries or quality failures. Supplier performance is often linked to overall cost reduction. - Compliance with Standards
Suppliers need to meet both internal quality standards and external industry regulations. This may include certifications such as ISO 9001, environmental certifications, or safety standards.
How to Choose the Right Suppliers?

Choosing the right suppliers is crucial for effective supplier quality management. The selection process typically involves evaluating the following factors:
- Cost of Quality
This refers to the total cost of producing a quality product, including both the cost of good quality (preventive actions) and the cost of poor quality (defects, rework, and waste). A supplier with a low cost of quality is more likely to provide consistent and reliable products. - On-Time Delivery
Reliable suppliers who consistently meet delivery deadlines are essential for maintaining production schedules and customer satisfaction. - Compliance
The supplier’s ability to comply with relevant laws, standards, and certifications is crucial for reducing regulatory risks. - Technology and Equipment
The supplier’s capabilities, such as their manufacturing technology and equipment effectiveness, should align with your business’s needs. Suppliers with advanced capabilities can offer higher-quality products and better efficiency. - Reputation and Track Record
A supplier’s reputation within the industry is an indicator of their reliability and commitment to quality. Checking references and reviewing case studies can provide insight into their past performance. - Capacity for Innovation
Suppliers who can adapt to changing product requirements and innovate in response to market demands can be valuable long-term partners.
Best Practices for Supplier Quality Management

To ensure effective SQM, companies should implement the following best practices:
- Establish Clear Quality Requirements
Clearly define the quality standards that suppliers must meet. This includes specifications, regulatory requirements, and performance expectations. - Regular Supplier Audits and Evaluations
Conduct regular audits and evaluations to ensure that suppliers are meeting their obligations. This can include both scheduled audits and random checks to assess compliance. - Implement Corrective and Preventive Actions
When quality issues arise, implement corrective actions to address the immediate problem and preventive actions to stop it from reoccurring. - Use Data and Metrics
Track supplier performance using key performance indicators (KPIs). This data helps identify areas of improvement, as well as the most reliable suppliers to work with. - Collaboration and Communication
Maintain open lines of communication with suppliers. Work together to solve problems, improve processes, and share best practices. - Supplier Development
Work with suppliers to improve their processes, quality systems, and capabilities. Supplier development initiatives can help strengthen relationships and ensure that suppliers meet evolving business needs.
Importance of Supplier Quality Management
In today’s competitive global market, businesses are increasingly reliant on external suppliers for raw materials, components, and services. As a result, supplier performance directly impacts a company’s ability to deliver high-quality products to customers. Supplier Quality Management plays a crucial role in maintaining product quality, minimizing risks, and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
The importance of Supplier Quality Management lies in its ability to reduce operational risks, such as product recalls, compliance violations, and reputational damage. Poor supplier performance can lead to defects, delays, and even legal issues, all of which can significantly affect the company’s bottom line. Therefore, effective SQM helps ensure that suppliers meet quality standards, reduce the likelihood of defects, and increase overall supply chain efficiency.
Additionally, an effective SQM strategy can help businesses strengthen relationships with their suppliers, encourage innovation, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. By working closely with suppliers, organizations can achieve better product quality, lower costs, and ultimately provide superior value to customers.
Benefits of Supplier Quality Management
Implementing a strong Supplier Quality Management system offers a wide range of benefits for businesses. Some of the key advantages include:
- Improved Product Quality: Regular monitoring and evaluation of supplier performance help ensure that the materials and components provided meet predefined quality standards, leading to consistent product quality.
- Reduced Risk: By proactively managing supplier relationships, companies can identify potential issues early on, reducing the risk of product defects, recalls, or safety concerns.
- Cost Savings: Supplier Quality Management helps identify inefficiencies in the supply chain, leading to cost reductions in production, materials, and logistics. In the long term, managing supplier quality helps prevent costly mistakes that can affect profitability.
- Enhanced Supplier Relationships: SQM fosters collaboration and trust between suppliers and buyers. A strong partnership with suppliers can lead to better communication, quicker problem resolution, and improved innovation.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Many industries require strict adherence to regulatory standards (e.g., ISO 9001, FDA compliance). A robust SQM system ensures that suppliers meet these requirements, helping businesses maintain regulatory compliance and avoid penalties.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: By ensuring high-quality materials and timely deliveries, SQM directly impacts the quality of the end product, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Supplier Selection Criteria and Strategies
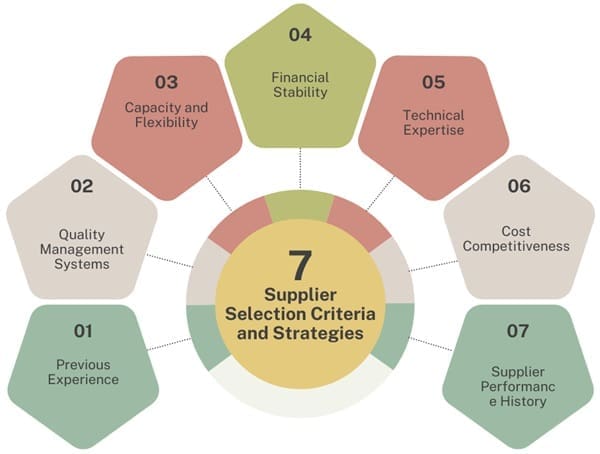
The process of selecting the right suppliers is a critical aspect of Supplier Quality Management. The supplier selection process should be thorough and involve a cross-functional team from departments such as purchasing, quality control, engineering, and production. The criteria for selecting suppliers should be aligned with the company’s business goals and quality standards.
Common supplier selection criteria include:
- Previous Experience: The supplier’s track record with similar products or services is crucial for evaluating their reliability and quality.
- Quality Management Systems: A supplier’s quality management system, including certifications like ISO 9001, is an important indicator of their ability to meet quality standards.
- Capacity and Flexibility: The supplier should have the capacity to meet current and future demands. Flexibility is important in case of fluctuations in demand or changes in production schedules.
- Financial Stability: A financially stable supplier is less likely to encounter disruptions that could impact their ability to deliver products on time.
- Technical Expertise: The supplier should possess the necessary technical capabilities to meet specific product or service requirements, including the ability to collaborate on product development and process optimization.
- Cost Competitiveness: While price is important, it should not be the sole determining factor. The total cost of dealing with the supplier—including transportation, inventory management, and verification of materials—should be considered.
- Supplier Performance History: Past performance, including on-time delivery, defect rates, and customer satisfaction, should be reviewed when selecting a supplier.
Supplier Quality Certifications
Supplier certifications are a crucial component of SQM, as they serve as proof that a supplier follows specific quality standards and regulatory requirements. Certifications such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management System), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management System), and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) provide assurance that a supplier is committed to quality and continuous improvement.
In some industries, such as automotive or aerospace, specific certifications may be required to ensure compliance with industry standards. For example, the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) provide certification programs to ensure suppliers meet the rigorous standards of the automotive industry.
Having certified suppliers can reduce the need for frequent inspections, audits, and corrective actions, streamlining the supply chain and improving efficiency.
Managing Supplier-Buyer Relationships
A successful Supplier Quality Management system goes beyond simply monitoring supplier performance. It also involves building strong, collaborative relationships with suppliers. These relationships are essential for ensuring consistent product quality, resolving issues quickly, and fostering innovation.
Key elements of managing supplier-buyer relationships include:
- Clear Communication: Open lines of communication are crucial for understanding supplier capabilities, addressing issues, and aligning on quality expectations.
- Regular Performance Reviews: Supplier performance should be regularly reviewed using key performance indicators (KPIs) such as delivery performance, defect rates, and cost management.
- Problem-Solving: Establishing a process for quickly identifying and resolving quality issues is vital for maintaining a positive supplier relationship. Both parties should work together to implement corrective actions and prevent recurrence.
- Collaboration on Improvement: Suppliers should be viewed as partners in the process of continuous improvement. Joint efforts to optimize quality, reduce costs, and streamline operations can benefit both parties in the long run.
“Cost Out” vs. “Price Down” Strategies
When working with suppliers, businesses often face the dilemma of reducing costs. This can be approached in two ways: “cost out” and “price down” strategies.
- Price Down: This strategy focuses on negotiating lower prices from suppliers. While this may reduce immediate costs, it can sometimes lead to compromises in quality, which could ultimately result in higher costs due to defects, rework, or customer dissatisfaction.
- Cost Out: This approach focuses on reducing the total cost of goods or services by improving processes, increasing efficiency, or finding ways to reduce waste in the supply chain. “Cost out” strategies aim to improve both quality and efficiency without necessarily lowering prices, resulting in long-term cost savings.
A balanced approach to cost reduction, which combines both price negotiation and process optimization, is often the most effective strategy for managing supplier relationships and ensuring consistent product quality.
Supplier Quality Resources
To effectively manage supplier quality, businesses need access to various tools, resources, and systems. These may include:
- Supplier Audits: Regular audits and inspections of supplier facilities can help identify potential risks and ensure that suppliers meet quality standards.
- Quality Management Software (QMS): Software systems such as Supplier Quality Management (SQM) tools enable companies to monitor supplier performance, track quality metrics, and manage supplier documentation and certifications.
- Training and Development: Ongoing training for both internal teams and suppliers is essential for ensuring that quality standards are consistently met.
- Supplier Scorecards: These tools track supplier performance across various metrics, including quality, delivery, cost, and service. Supplier scorecards provide valuable data to support decision-making and improve supplier relationships.
Final Words
Supplier Quality Management is a vital aspect of any business that depends on suppliers to provide raw materials, components, or services. Effective SQM ensures that suppliers consistently meet quality standards, which ultimately impacts product quality, customer satisfaction, and brand reputation. By selecting the right suppliers, fostering strong relationships, and continuously monitoring performance, businesses can reduce risks, improve quality, and optimize supply chain efficiency.
With the right Supplier Quality Management system in place, businesses can make data-driven decisions, minimize compliance risks, and work collaboratively with suppliers to drive continuous improvement. As competition increases and customer expectations rise, ensuring supplier quality is more important than ever for businesses striving to deliver high-quality products and services consistently.


















