Table of contents
What is the Difference Between Lean and Six Sigma?
What is the Difference Between Lean and 6s Six Sigma (lean vs. six sigma)? Even the most successful business tools and methods must evolve over time to meet the changing market. The benefits of Six Sigma are no exception. It has many branches, disciplines, and schools of thought, which have evolved from its original concept over time to meet new needs.
Two different schools of thought were merged in one case to create a cohesive method that addresses multiple goals. Lean Six Sigma is a blend of management methods that use the principles and focus on efficiency. Both methods aim to achieve the same goal: more efficient processes that result in a higher bottom line. You can see the difference in how they approach this goal.
Henry Ford’s ideas and later the introduction of the Toyota production process led to Lean. Toyota developed a system that made it easier to set up and change over. Lean was popularized in the 1980s by many countries, including the United States.
Six Sigma was created at the same time that Toyota introduced Lean in the United States. Six Sigma was created by Bill Smith, Motorola to improve quality and measure defects. The manufacturing conglomerate GE further developed the original idea. Six Sigma was adopted by GE and others.
Lean vs. Six Sigma history is essential because it clearly demonstrates why and how these methodologies can be used in order to improve manufacturing efficiency. Today, Lean is used to ensure that manufacturing processes are efficient and waste-free. Six Sigma is named after a statistical bell curve. It examines the whole company, production, and non-production, in order to reduce waste.
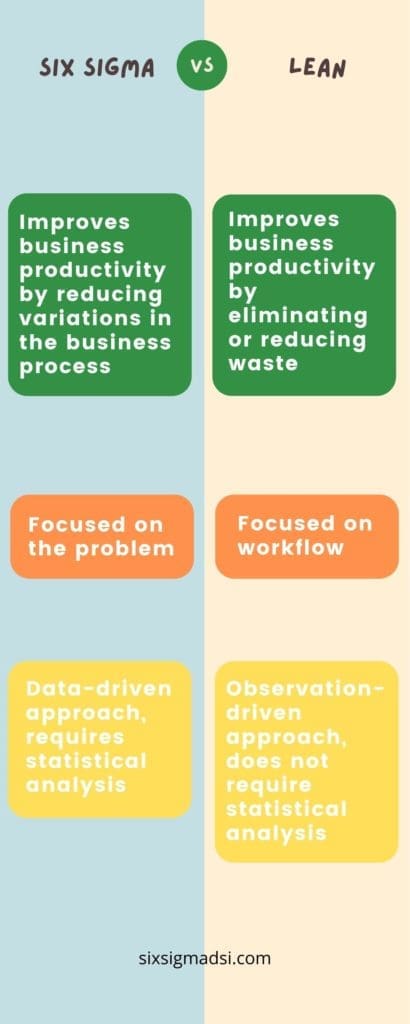
Six Sigma’s fundamental goal is to eliminate defects and reduce waste, while increasing quality and efficiency, improving business processes. This theory is applicable to all business areas of a company, from plant floors to accounting.
Lean can also be used to improve manufacturing processes. Lean is about removing unnecessary or inefficient steps from production and ensuring that only the essential steps are taken.

Six Sigma
Six Sigma was created with one goal in mind: To reduce variation and defects in production processes by statistical analysis. Six Sigma employs one of two five-step approaches to achieve this goal: either the DMAIC method or the DMADV .
Each method has its own uses. DMAIC stands to Define, Measure Analyze and Improve, and Control. The DMAIC process is about identifying the problem, taking stock of current processes, and then identifying and implementing a solution. This process is ideal for supply-chain performance issues, or where only minor adjustments are required and not a new function.
This is where DMADV (Define Measure, Analyze Design, Verify) comes into play. While the first phases are identical, the Design phase allows you to create a completely new tool to solve your problem. The Verify phase focuses on verifying that the solution continues to solve the problem.
Six Sigma is about identifying and fixing problems in the supply chain.
Lean Method
Lean, on the other hand, is all about eliminating waste and providing maximum value for customers with the lowest investment. Toyota’s Business System, which was a business philosophy that allowed the company to run efficiently, was the first to use Lean. It encompasses every level of an organization and helps to guide new processes as well as drive the allocation of resource. Six Sigma and Lean are different in that Six Sigma is more focused on manufacturing, while Lean often shapes all aspects of a company.
Lean Six Sigma blends these two approaches to create a powerful toolkit for reducing wasted materials. The DMAIC method is a great way for companies to identify and solve wasteful practices. The synergy of these methodologies is primarily designed to eliminate the 8 types of waste. This means that any material, time or effort taken out of a process, does not add value. These are the types of waste:
- Quality Standards Broken
- Overproduction: Exceeding demand, or producing more than what was ordered
- Waiting Process bottlenecks and downtime
- Unutilized Talent – Inefficiently using or misallocating human resource
- Transportation Inefficient shipping methods
- Inventory– Keeping on top of a surplus product or raw material
- Motion Unnecessary Moving of Product, Material, or People
- Additional Processing – More work than necessary
Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma: What’s the Difference?
Lean Six Sigma is an ideal fit for companies that want to improve their processes and offer the best value to customers. DMAIC’s phased thinking and clear path can be very useful when applied to any type of business case.
New methods and unique philosophies will emerge as the lines and benefits between Six Sigma and Lean continue to blur. These experts will be the next big innovation in Six Sigma thinking.
Six Sigma vs. Lean: Which is the better option for you?
If you are looking for a simple and continuous way to improve your company’s performance, Lean may be the right fit. Six Sigma might be better if your goal is to reduce unpredictability and increase efficiency in a more complex setting.
Combining the benefits of 6s Six Sigma and Lean can create a hybrid technique called Lean Six Sigma. This will allow you to combine the best of both methods. Lean Six Sigma can help organizations cut costs and reduce waste, while improving the quality and speed of operations and output.
Which do you prefer and why?
Let us know in the comments below.












