Lean Project Management (LPM) is an approach that focuses on delivering value to customers. It aims to minimize waste in the project management process.
The principles of Lean were originally developed in manufacturing. Toyota pioneered these concepts in the mid-20th century. Over time, Lean principles have been adapted to various industries, including project management.
At its core, Lean seeks to streamline processes and reduce inefficiencies. It also emphasizes continuous improvement in the quality of deliverables to meet or exceed customer expectations.
Table of contents
What is Lean Project Management?
Lean Project Management is an approach to managing projects. It focuses on improving efficiency by reducing waste and enhancing value. It also aims to create a smooth, continuous flow of work.
Originally derived from Lean Manufacturing, Toyota pioneered this approach in the 1940s. Since then, many sectors, including software development, healthcare, and project management, have applied Lean principles.
The central tenet of Lean Project Management is to maximize customer value. At the same time, it minimizes waste. Lean achieves this by eliminating anything that doesn’t add value, streamlining processes, and ensuring efficient resource use.
In Lean Project Management, the goal is not to do more with less. Instead, it aims to do more with better. This involves optimizing work processes so that projects are completed efficiently and on time. By adopting Lean principles, project managers can increase success rates, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
History and Evolution of Lean Management
The concept of Lean began in the early 20th century. It emerged alongside the rise of mass production techniques, particularly in the automobile industry.
Henry Ford’s assembly line was one of the first attempts to streamline production. However, it was Toyota’s approach in the 1940s that laid the foundation for Lean Manufacturing. The Toyota Production System (TPS) introduced key concepts such as continuous improvement (Kaizen) and Just-In-Time production. It also emphasized respect for people, which became core principles of Lean.
As the years progressed, Lean methodology evolved beyond manufacturing. In the 1990s, Lean thinking was applied to software development through the Lean Startup movement. This approach shared the same core principles but focused on reducing waste in developing new products or services. Today, Lean principles are widely used across various industries and have been adapted for project management.
Core Principles of Lean Project Management
Lean Project Management applies the core principles of Lean thinking to managing projects. These principles help project managers create value, reduce waste, and improve workflows to meet customer needs.
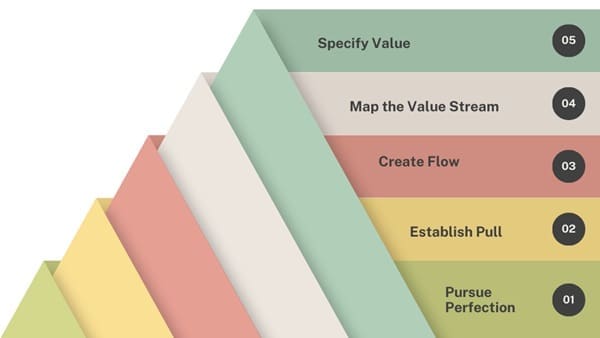
The five core principles of Lean Project Management, outlined in the book Lean Thinking by Womack and Jones, are as follows:
- Specify Value: The first step in Lean Project Management is to identify what constitutes value in the eyes of the customer. Value is defined as the benefit that the customer receives from project deliverables, whether it’s a product, service, or outcome. Understanding value involves grasping the customer’s needs and ensuring that all project activities align with delivering that value.
- Map the Value Stream: Value stream mapping is a key technique in Lean Project Management. It involves mapping out all the steps in the project process, from initial concept to completion. This helps identify activities that contribute to value and those that constitute waste. The goal is to pinpoint areas where inefficiencies, delays, or bottlenecks occur.
- Create Flow: After identifying waste through value stream mapping, the next step is to create a smooth and continuous flow of work throughout the project. This means completing tasks with minimal interruptions and passing work seamlessly between different stages. The objective is to eliminate delays and ensure that work progresses without unnecessary stops.
- Establish Pull: In Lean, the concept of “pull” refers to producing work only when it is needed. This is important for projects involving complex tasks with multiple stakeholders. By establishing a “pull” system, project teams can complete work just in time. This approach reduces excess inventory, eliminates backlogs, and minimizes overproduction.
- Pursue Perfection: Continuous improvement is at the heart of Lean thinking. Lean Project Management is not a one-time fix but a journey toward ongoing process refinement. Teams regularly assess workflows, review performance data, and look for ways to eliminate waste and enhance value. The pursuit of perfection is a never-ending process.
Types of Waste in Lean Project Management
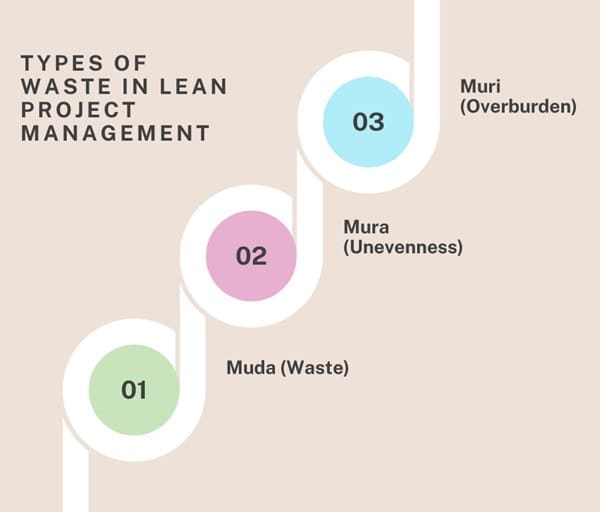
Lean Project Management seeks to identify and eliminate different types of waste that hinder project progress. In Lean thinking, waste is any activity that consumes resources but does not add value to the customer. There are three primary types of waste identified in Lean:
- Muda (Waste): This refers to activities that consume resources (time, materials, effort) but do not contribute to value. Examples include unnecessary meetings, excessive documentation, and redundant processes.
- Mura (Unevenness): This type of waste occurs when there is variability or inconsistency in the process, such as fluctuating workloads, resource shortages, or delays in project phases. Mura can lead to inefficiencies and reduced productivity.
- Muri (Overburden): This occurs when there is too much pressure placed on resources, whether it’s employees, equipment, or systems. Overburden can result in burnout, defects, or equipment breakdowns.
Reducing Muda, Mura, and Muri is critical to achieving Lean goals in project management.
Benefits of Lean Project Management
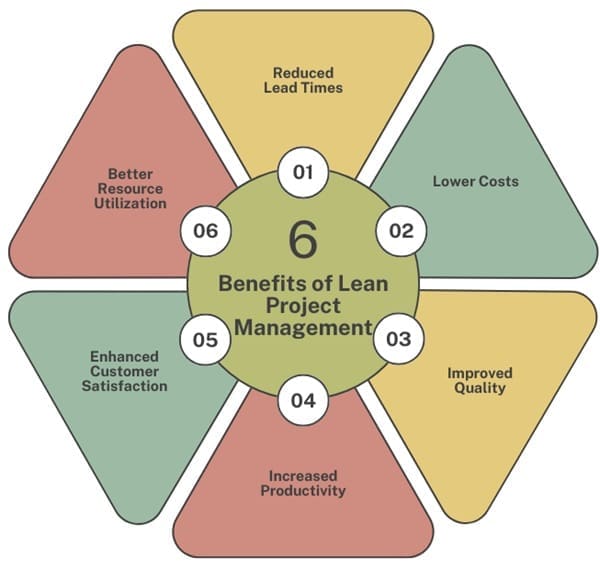
By implementing Lean principles in project management, organizations can expect several significant benefits, including:
- Reduced Lead Times: By eliminating delays and reducing inefficiencies, Lean helps speed up project completion, allowing teams to deliver results faster.
- Lower Costs: Lean reduces waste, such as unnecessary steps, excess materials, and inefficient resource use, which ultimately leads to cost savings.
- Improved Quality: Lean emphasizes continuous improvement and problem-solving, which helps ensure higher-quality deliverables that meet customer expectations.
- Increased Productivity: Lean processes encourage efficient work practices, eliminate bottlenecks, and ensure that teams focus on value-adding activities, leading to higher productivity.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Lean focuses on delivering exactly what the customer needs, when they need it, in the most efficient manner. This increases customer satisfaction by ensuring that the project delivers value and is completed on time.
- Better Resource Utilization: Lean projects make better use of human, financial, and material resources by eliminating wasteful practices and focusing on value creation.
Also See: Lean Six Sigma Certification Programs, Lexington, Kentucky
Lean vs. Traditional Project Management
In traditional project management, the focus is typically on meeting predefined project scope, timelines, and budgets. While this is important, the traditional approach can sometimes result in inefficiencies, overcomplicated processes, and a lack of focus on customer value.
In contrast, Lean Project Management prioritizes value delivery over strict adherence to fixed project schedules or budgets. By continuously identifying and eliminating waste, Lean encourages a more flexible, adaptive approach to project execution. Lean also places a greater emphasis on collaboration, transparency, and continuous feedback, which are often lacking in more traditional project management methods.
Lean Tools and Techniques
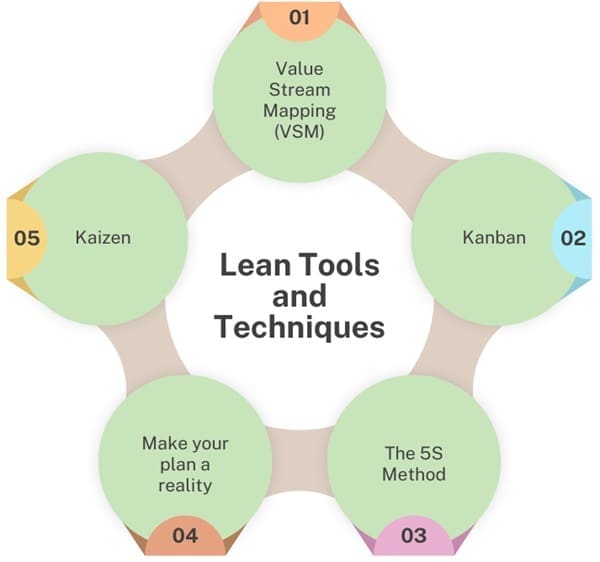
To implement Lean effectively, project managers use a variety of tools and techniques that support continuous improvement and waste reduction. Some common Lean tools include:
- Value Stream Mapping (VSM): A visual tool used to map out the steps in a project and identify areas of waste.
- Kanban: A system for managing work items and ensuring that work flows efficiently through each stage of the project. It uses visual boards to show the status of tasks and limit work in progress.
- The 5S Method: A system for organizing workspaces and processes to eliminate waste and improve efficiency. The five steps are Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain.
- Root Cause Analysis: A problem-solving technique used to identify the underlying causes of issues in the project process and address them to prevent recurrence.
- Kaizen: A philosophy of continuous improvement that encourages small, incremental changes to enhance processes.
Challenges of Implementing Lean Project Management
While Lean Project Management offers numerous benefits, it is not without its challenges. Some of the difficulties organizations may face when adopting Lean include:
- Cultural Resistance: Lean requires a shift in mindset from a traditional project management approach. Employees and managers may resist change, especially if they are accustomed to rigid processes or fixed schedules.
- Initial Setup Costs: Implementing Lean tools, such as value stream mapping or Kanban systems, can require an upfront investment in training and process redesign.
- Lack of Buy-In: For Lean to succeed, everyone involved in the project must be committed to the principles of waste reduction and continuous improvement. Lack of buy-in from key stakeholders can hinder the successful implementation of Lean.
Final Words
Lean Project Management is a powerful methodology that can help organizations deliver high-quality projects on time and within budget by focusing on value, minimizing waste, and continuously improving processes.
By applying Lean principles to project management, teams can enhance productivity, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. However, successful Lean implementation requires a cultural shift, commitment from all stakeholders, and a willingness to continuously refine and adapt processes to meet evolving customer needs.

About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.