Organizations use Project Portfolio Management (PPM) as a structured approach to manage a collection of projects and programs. PPM ensures that the organization’s projects align with its strategic objectives and that resources are used effectively to maximize value.
By managing a portfolio of projects, businesses aim to achieve long-term success, maximize returns, and make well-informed decisions that support overall strategy.
Many think their projects are unique and don’t need to follow a structured process. However, the challenge remains: businesses face limited resources, numerous project ideas, and constantly changing conditions.
This is where PPM comes in, helping businesses prioritize, allocate resources, and assess risks. It helps leaders make tough decisions on which projects to invest in, and how to handle changes as they arise.
In this article, we’ll explore the definition, benefits, processes, and challenges of Project Portfolio Management.
Table of contents
- What Is Project Portfolio Management?
- Key Processes of Project Portfolio Management
- How Project Portfolio Management Works?
- Benefits of Project Portfolio Management
- Challenges in Project Portfolio Management
- Governance in Project Portfolio Management
- Project Portfolio Management Tools and Techniques
- Final Words
- Related Articles
What Is Project Portfolio Management?
PPM manages a group of projects to ensure the company invests its resources in the most valuable and strategic initiatives.
According to the Project Management Institute (PMI), PPM involves managing the selection, prioritization, and execution of projects to achieve organizational goals and maximize value.
Cooper et al. (1997) define it as a dynamic process where businesses constantly review and update their active projects. The team evaluates and selects new projects, while it may accelerate, de-prioritize, or cancel existing projects. The team continually reallocates resources to ensure that the most strategic projects receive the necessary attention.
The primary objective of PPM is to maximize the value of the portfolio by choosing the right mix of projects. Additionally, PPM ensures the projects align with organizational goals, creating a strategic balance. It’s also essential for managing risks and ensuring that the right resources are allocated effectively.
Evolution of Project Portfolios
Just like organizations, project portfolios evolve over time. As projects progress and the organization’s strategy shifts, the portfolio’s structure and priorities will change. Project portfolios are dynamic entities that need constant attention to ensure they align with the evolving needs of the business.
Managing the evolution of a project portfolio involves regularly reviewing and adjusting the portfolio’s composition, resource allocation, and strategic alignment. This process ensures that the portfolio continues to add value to the organization and supports its long-term goals.
Components of Project Portfolio Management
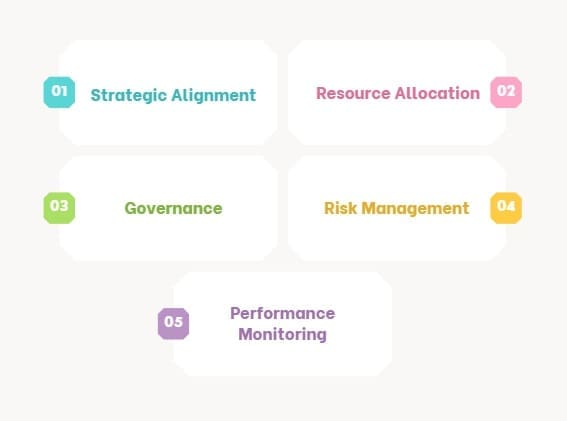
PPM involves several critical components:
- Strategic Alignment: Projects must support the organization’s overall strategy to ensure that every project contributes to the broader goals.
- Resource Allocation: The organization must allocate resources, including time, money, and human capital, efficiently across all projects.
- Governance: The organization must establish clear decision-making processes to evaluate and prioritize projects.
- Risk Management: The team must identify and manage risks at the portfolio level to ensure that potential problems are addressed before they affect the business.
- Performance Monitoring: The team must track projects continuously to measure progress and make adjustments as necessary.
Importance of Strategy in Project Portfolio Management
Strategic alignment is one of the most crucial aspects of PPM. Without a clear strategy, projects may not contribute effectively to organizational goals. A business strategy defines where the company wants to go and how it plans to get there. PPM ensures that the selected projects are aligned with this strategy.
According to Sun Tzu, “Strategy without tactics is the slowest route to victory. Tactics without strategy is the noise before defeat.” This highlights the importance of aligning projects with broader organizational goals. PPM helps businesses translate their strategy into specific projects, ensuring that each project contributes to the overall mission.
Effective Project Portfolio Management is crucial for any organization because it helps make decisions about which projects to pursue, how to prioritize them, and where to allocate resources.
This process plays a vital role in today’s fast-paced business environment, where organizations often face limited resources and numerous projects compete for attention. PPM helps prevent chaos by providing a structured approach to managing multiple projects simultaneously.
Key Processes of Project Portfolio Management
PPM divides into two main process groups: Aligning and Monitoring & Controlling. Each of these process groups contains several steps to ensure that the team manages the projects within the portfolio effectively and aligns them with the organization’s strategy.
Aligning Process Group
The aligning group focuses on categorizing, evaluating, selecting, and including projects in the portfolio. This process is most active when the organization refreshes its strategic goals and defines new short-term budgets and plans.
Identification
The first step in this process is identifying new and ongoing projects. This list should contain enough information to make decisions about whether projects should be included in the portfolio.
Categorization
Next, the identified projects are grouped into relevant business categories. This categorization helps to apply decision-making filters and criteria for evaluating, selecting, and prioritizing the projects.
Evaluation
Once projects are categorized, they are evaluated based on predefined criteria. This step involves gathering relevant data and using models to score and assess each project’s potential value to the organization.
Selection
After evaluating the projects, they are selected for inclusion in the portfolio. This step produces a shortlist of projects that meet the organization’s strategic goals.
Prioritization
The selected projects are then ranked based on their importance. Prioritization helps to decide which projects should take precedence, considering factors like risk, return on investment, and strategic alignment.
Portfolio Balancing
This step involves balancing the portfolio by adding new projects that have been prioritized. It also includes identifying and eliminating projects that no longer align with strategic objectives or are underperforming.
Authorization
Finally, the organization allocates the necessary resources and budget to the selected projects. This step formally authorizes the projects to move forward.
Monitoring & Controlling Process Group
The monitoring and controlling group ensures that the portfolio is regularly assessed to confirm that it continues to meet organizational goals and perform as expected.
Portfolio Reporting and Review
Regular reports and reviews help the organization track progress and performance. These reviews ensure that the portfolio remains aligned with strategic objectives.
Strategic Change
As business conditions evolve, the portfolio must adapt. This process allows the portfolio to respond to strategic changes and ensure that it continues to support the organization’s goals.
How Project Portfolio Management Works?
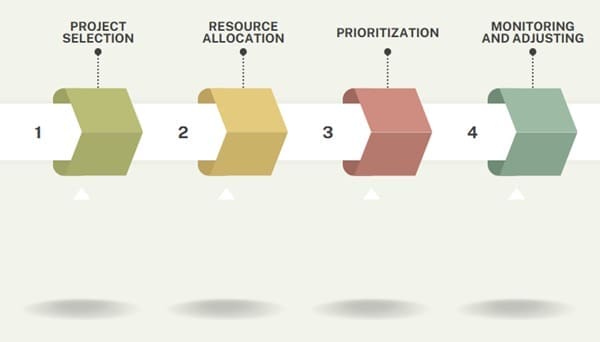
PPM requires the careful selection and evaluation of projects based on strategic objectives, available resources, and expected outcomes. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
- Project Selection: The team evaluates each project against a set of criteria that aligns with the company’s strategic goals. They rank projects based on their expected value and impact on the business.
- Resource Allocation: The team assigns resources such as time, budget, and personnel to projects. They balance the available resources with the needs of each project.
- Prioritization: After selecting projects, the team prioritizes them. PPM helps determine which projects to execute first based on factors like urgency, importance, and return on investment.
- Monitoring and Adjusting: The team continuously monitors the portfolio throughout the project lifecycle. If a project fails to deliver as expected, they may reallocate resources or cancel or postpone the project.
Benefits of Project Portfolio Management
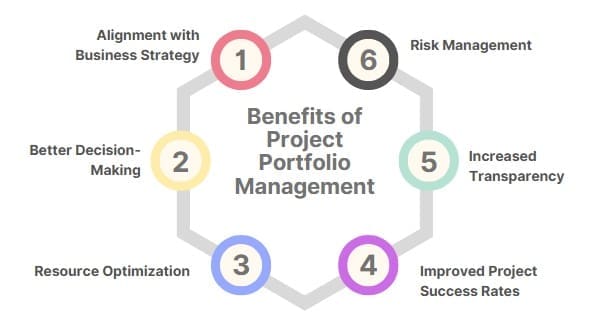
PPM provides several benefits to organizations, making it an essential part of strategic planning and execution.
- Alignment with Business Strategy
PPM ensures that projects align with the organization’s overall strategy, helping the business achieve its goals. It ensures that resources are allocated to projects that have the greatest impact on strategic objectives. - Better Decision-Making
PPM enables decision-makers to make informed choices by providing relevant data and analysis. By evaluating and prioritizing projects systematically, organizations can avoid the pitfalls of subjective decision-making. - Resource Optimization
PPM helps organizations allocate resources efficiently, ensuring that limited resources are used for the most valuable projects. This reduces waste and improves project success rates. - Improved Project Success Rates
By selecting and prioritizing projects that align with strategic objectives, PPM increases the likelihood of project success. Projects are more likely to be completed on time, within budget, and with the desired results. - Increased Transparency
PPM provides transparency into the portfolio, helping stakeholders understand the status of projects and how they contribute to organizational goals. This fosters accountability and better communication within the organization. - Risk Management
PPM helps identify and mitigate risks by continuously monitoring the portfolio’s performance. It ensures that risks are assessed and managed at both the project and portfolio levels.
Add link here: Lean Six Sigma Certification Programs, Santa Clarita, California
Challenges in Project Portfolio Management
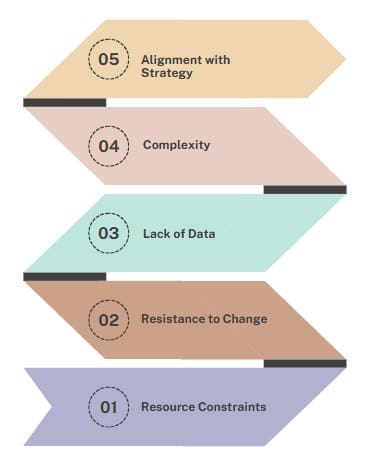
While PPM offers numerous benefits, organizations may face challenges in its implementation. Some of these challenges include:
Resource Constraints
Organizations often face limited resources, making it difficult to manage multiple projects effectively. PPM helps prioritize projects, but resource allocation can still be a challenge.
Resistance to Change
Implementing PPM may require changes to existing processes, and some employees may resist these changes. Overcoming this resistance and gaining buy-in from stakeholders is essential for successful implementation.
Lack of Data
Inadequate or poor-quality data can hinder the decision-making process in PPM. Organizations must ensure that they have accurate, up-to-date data to make informed decisions.
Complexity
Managing a large number of projects can be complex, especially in organizations with multiple departments and stakeholders. Streamlining communication and coordination is crucial to managing the portfolio effectively.
Alignment with Strategy
Ensuring that every project aligns with the organization’s strategy can be difficult, especially when the strategy itself is not clear or evolves over time. Regular reviews and updates to the strategy are necessary for maintaining alignment.
Governance in Project Portfolio Management
Project Portfolio Management is closely linked with organizational governance. Governance refers to the rules, processes, and practices that help manage projects and ensure they meet strategic objectives.
PPM governance helps establish clear decision-making frameworks, ensuring that projects are selected and executed in a transparent manner. It also ensures accountability at every level of the organization, from project managers to senior leaders.
Role of Organizational Governance
Governance in PPM involves defining roles and responsibilities, ensuring transparency, and aligning projects with organizational goals. It also involves monitoring the performance of the portfolio and ensuring that the projects meet expected outcomes.
Organizational governance helps to establish clear lines of authority, enabling the business to make timely decisions about which projects to continue, which to halt, and which to prioritize. Effective governance helps avoid project failure, resource mismanagement, and missed opportunities.
Project Portfolio Management Tools and Techniques
To effectively manage a project portfolio, organizations rely on various tools and techniques. Some common tools include:
Scoring Models
The team uses a scoring model as a quantitative tool to evaluate and prioritize projects. They rate each project based on predefined criteria such as ROI, strategic fit, and risk. These scores help decision-makers rank projects according to their relative importance.
Portfolio Balancing Techniques
The team uses balancing techniques to ensure that the portfolio is diverse and aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives. They balance high-risk, high-reward projects with low-risk, steady-return projects to create a portfolio that meets both short-term and long-term goals.
Performance Metrics
The team uses performance metrics to measure the progress and success of projects within the portfolio. Common metrics include ROI, Net Present Value (NPV), and alignment with strategic goals. These metrics help decision-makers monitor the portfolio’s health and make adjustments as needed.
Final Words
Organizations use Project Portfolio Management as a critical process to ensure that their projects align with strategic goals and that they use resources efficiently. By evaluating, prioritizing, and managing projects at the portfolio level, businesses can make informed decisions that drive long-term success.
While implementing PPM can be challenging, especially with resource constraints and organizational resistance, the benefits are significant. Organizations that successfully adopt PPM can optimize their resources, reduce risks, and achieve their strategic objectives more effectively.
By fostering a culture of strategic alignment, transparency, and continuous monitoring, businesses can unlock the full potential of their project portfolio and move toward sustained success.

About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.



















