Mind mapping is a powerful visual tool. It helps you organize information, generate ideas, and streamline your thought process. Whether you’re a student, professional, or creative thinker, mind mapping offers a dynamic way to enhance learning, improve memory, and solve complex problems.
In this guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of mind mapping. We’ll also cover its history, applications, and how to use it effectively to boost productivity and creativity in various aspects of life.
Table of contents
What is Mind Mapping?
At its essence, a mind map is a diagram that visually represents concepts, ideas, or tasks linked around a central theme or keyword. This central idea serves as the focal point from which all related ideas branch out, much like the branches of a tree radiating from its trunk.
The structure is radial, meaning it spreads outwards from the centre, making it a non-linear approach to capturing and organizing thoughts.
Mind maps are more than just diagrams; they are a cognitive tool that mirrors the way our brain naturally processes information.
By using a combination of keywords, images, colours, and symbols, mind maps allow us to visually map out our thoughts in a way that makes connections more apparent and ideas more accessible. This visual format not only aids in understanding but also enhances memory retention and recall.
Origin
Mind mapping, as we know it today, was popularized by Tony Buzan. He is a British author and educational consultant, in the 1970s. Buzan was inspired by the brain’s natural way of processing and storing information in a non-linear, associative manner. He developed mind mapping as a way to harness this cognitive process, making it easier to capture, organize, and retrieve information.
Buzan’s work has since gained worldwide recognition, and it has become a popular tool in education, business, and personal development. It’s now used by millions of people around the globe to enhance their learning and thinking processes.
Key Characteristics of a Mind Map
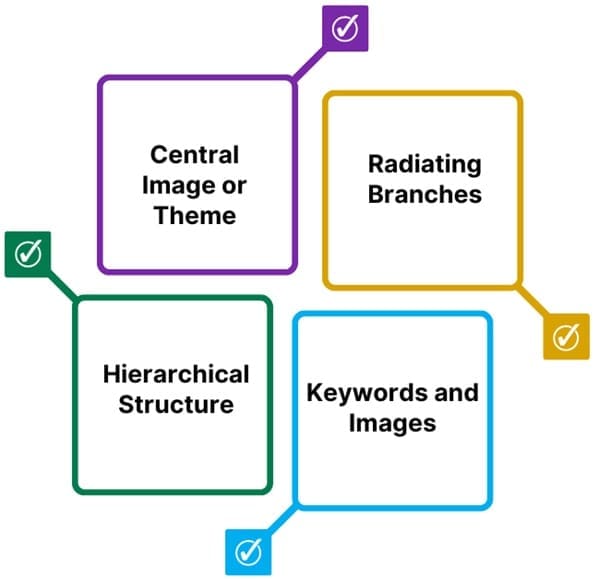
It has four essential characteristics:
- Central Image or Theme: The core idea or topic is crystallized in a central image or keyword. This serves as the starting point for the mind map.
- Radiating Branches: The main themes or ideas related to the central topic radiate outwards as branches. Each branch represents a different aspect or sub-topic of the central theme.
- Keywords and Images: Each branch contains a keyword or image that represents the core idea of that branch. These keywords or images are often placed on lines that connect them to the central theme.
- Hierarchical Structure: Lesser important ideas or sub-topics are represented as smaller branches attached to the main branches, creating a connected, hierarchical structure.
Benefits
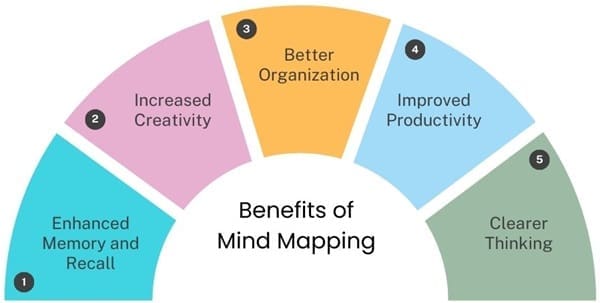
It offers numerous benefits, making it an invaluable tool for anyone looking to improve their cognitive abilities:
- Enhanced Memory and Recall: The visual and associative nature of mind maps makes it easier to remember and recall information. By engaging both the left and right hemispheres of the brain, mind maps help solidify information in your memory.
- Increased Creativity: It encourages free-form thinking and the exploration of ideas without the constraints of linear note-taking. This allows for more creative and innovative solutions to problems.
- Better Organization: It helps you organize your thoughts and ideas in a way that’s easy to follow and understand. By visually mapping out information, you can see the relationships between different ideas and how they fit together.
- Improved Productivity: By providing a clear and organized visual representation of your thoughts, mind maps can help you save time and increase efficiency. When you plan a project or brainstorm ideas, mind maps simplify getting started. They also help you stay focused.
- Clearer Thinking: The process of creating a mind map forces you to clarify your thoughts and break down complex ideas into more manageable parts. This leads to clearer, more structured thinking.
How to Create a Mind Map?
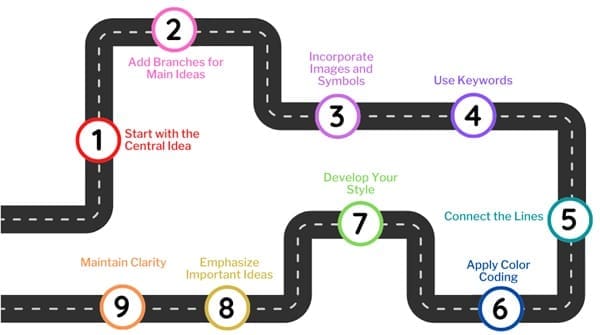
Here are the steps for creating a mind map:
- Start with the Central Idea: Begin by placing the central idea or theme in the middle of the page. This could be a keyword, phrase, or image that represents the topic you’re focusing on. Use at least three different colours to make it stand out and capture your attention.
- Add Branches for Main Ideas: From the central idea, draw branches outward to represent the main ideas or sub-topics related to the central theme. Each branch should be labelled with a keyword or phrase that summarizes the main idea.
- Incorporate Images and Symbols: Where possible, use images, symbols, and icons to represent ideas. Visual elements can make the mind map more engaging and memorable.
- Use Keywords: Choose keywords that capture the essence of each idea. These should be concise and easy to understand. Print them in either upper or lower case letters based on your preference.
- Connect the Lines: Ensure that all lines are connected, starting from the central idea and radiating outward. The central lines should be thicker and more organic, becoming thinner as they move away from the centre.
- Apply Color Coding: Use different colours to differentiate between branches and ideas. This can help you quickly identify different sections of the mind map.
- Develop Your Style: As you become more comfortable with mind mapping, develop your personal style. This could include specific symbols, line styles, or ways of organizing information that works best for you.
- Emphasize Important Ideas: Use bold text, larger images, or thicker lines to emphasize the most important ideas in your mind map.
- Maintain Clarity: Keep your mind map clear and easy to follow. Use radial hierarchy, numerical order, or outlines to keep the structure organized and avoid clutter.
Applications of Mind Mapping
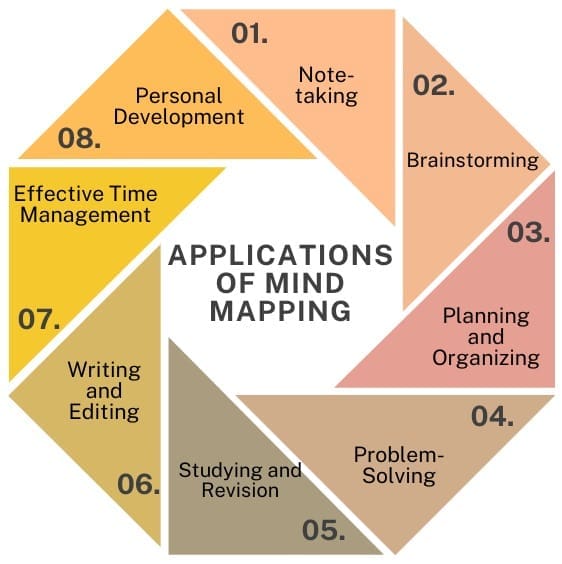
It is a versatile tool that can be applied in various contexts. Here are some of the most common uses:
- Note-taking: It is a great alternative to traditional note-taking. Instead of writing down information linearly, you can capture the most important points in a visual format that’s easier to review and understand later.
- Brainstorming: When you’re generating ideas, mind maps can help you quickly capture and organize your thoughts. The non-linear format encourages creativity and makes it easier to see connections between different ideas.
- Planning and Organizing: It helps you structure your ideas and ensure that nothing is overlooked. They are useful whether you’re planning a project, writing an essay, or organizing your thoughts on a complex topic.
- Problem-Solving: It can help you break down complex problems into more manageable parts. By visually mapping out the different aspects of a problem, you can identify potential solutions and weigh the pros and cons of each option.
- Studying and Revision: Students can use mind maps to summarize and visualize information, making it easier to remember and review material before exams.
- Writing and Editing: Writers can use mind maps to outline their work, develop characters, or organize research material. Editors can use mind maps to review and refine content, ensuring that all elements of a piece are cohesive and well-structured.
- Effective Time Management: Use mind maps to plan your day, week, or month. You can prioritize tasks, set goals, and track your progress, all in one visual format.
- Personal Development: Mind maps can help you clarify your goals, identify areas for improvement, and develop strategies for achieving your objectives.
Real-Life Examples of Mind Mapping
You can use mind maps to explore a wide range of topics. Here are a few examples of how you might use mind maps in different contexts:
The Greenhouse Effect
You could use a mind map to explore the causes, effects, and potential solutions to the greenhouse effect. Branches could include topics like “carbon emissions,” “global warming,” “renewable energy,” and “policy changes.”
Social Software
You could use a mind map to organize information about different types of social software, their uses, and their impact on society. Branches might include “social networks,” “communication tools,” “collaboration platforms,” and “privacy concerns.”
Computer Science
Students studying computer science could use a mind map to outline key concepts, from “algorithms” to “data structures.” Each branch could represent a different area of study, with sub-branches for specific topics or concepts.
Laws of Motion
A physics student could create a it to summarize the laws of motion. Branches could include “Newton’s First Law,” “Newton’s Second Law,” “Newton’s Third Law,” and “applications in real life.”
Lecture Notes
Instead of taking linear notes during a lecture, a student could use it to capture the most important points. The central theme could be the lecture topic, with branches for each main idea covered in the lecture.
Reading Strategies
You could use a mind map to summarize different reading strategies, such as “skimming,” “scanning,” “detailed reading,” and the “SQ3R method.” Each branch could include tips and techniques for using each strategy effectively.
Final Words
Mind mapping is not just a technique; it’s a transformative way of thinking that can revolutionize the way you learn, create, and solve problems. By harnessing the power of visual thinking and leveraging the brain’s natural associative processes, it allows you to tap into your full cognitive potential.
Whether you’re a student looking to improve your study habits, or a professional seeking to enhance.

About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.



















