Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become indispensable tools for modern businesses aiming to integrate and streamline their various functions and processes into a unified system. This comprehensive software solution not only enhances operational efficiency but also provides real-time insights and facilitates decision-making across all levels of the organization.
Table of contents
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a centralized software system that integrates essential business processes such as finance, HR, supply chain, manufacturing, and CRM into a unified platform. It enables organizations to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enhance decision-making by providing real-time insights and standardized processes across departments.
ERP systems facilitate data accuracy, collaboration, and strategic planning, helping businesses optimize resources, reduce costs, and respond agilely to market dynamics.
Core Functions of ERP
ERP systems are software solutions designed to manage and integrate core business processes such as finance, human resources, supply chain, manufacturing, procurement, sales, and customer relationship management (CRM). These systems operate on a centralized database, allowing different departments to access and share information seamlessly. The primary functions of ERP include:
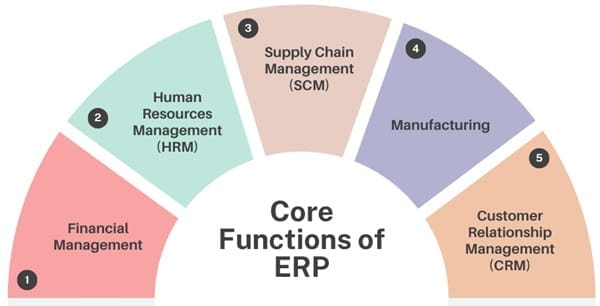
- Financial Management: Handling financial transactions, general ledger, accounts payable/receivable, budgeting, and financial reporting.
- Human Resources Management (HRM): Managing employee data, payroll, benefits administration, training, and recruitment.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): Monitoring inventory levels, supplier relationships, procurement processes, and logistics.
- Manufacturing: Planning production schedules, managing workflows, and optimizing manufacturing processes.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Managing customer interactions, sales pipeline, marketing campaigns, and customer service.
Benefits of Implementing ERP Systems
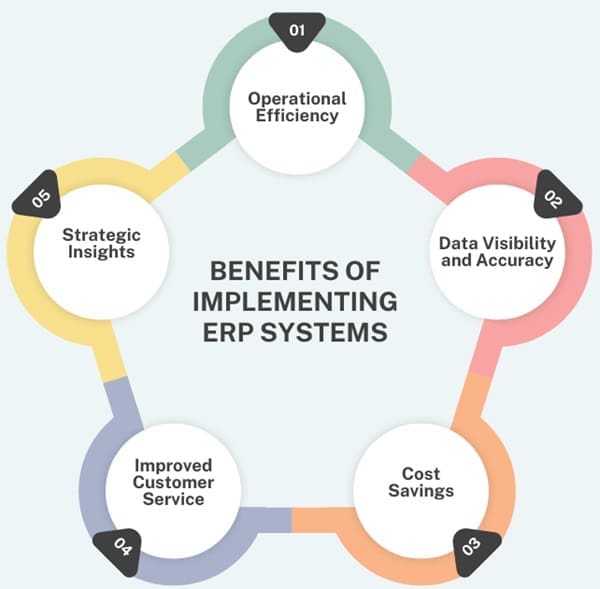
Implementing an ERP system offers numerous benefits that contribute to the overall efficiency and profitability of an organization:
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlines business processes, reduces manual tasks, and eliminates redundant data entry.
- Data Visibility and Accuracy: Provides real-time data access across departments, ensuring consistent and accurate information for decision-making.
- Cost Savings: Reduces operational costs by improving resource allocation, inventory management, and procurement processes.
- Improved Customer Service: Enhances customer satisfaction through better order tracking, faster issue resolution, and personalized service.
- Strategic Insights: Enables data-driven decision-making with comprehensive analytics and reporting capabilities.
Challenges in ERP Implementation
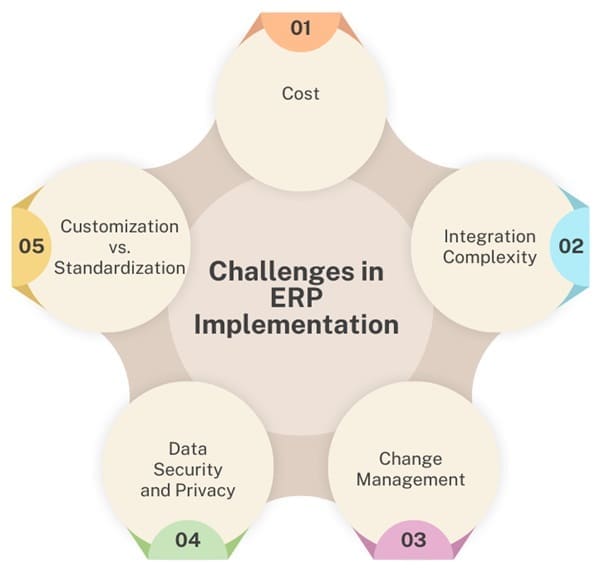
While the benefits are compelling, ERP implementation can be complex and challenging, requiring careful planning and execution:
- Cost: Initial investment in ERP software, customization, training, and ongoing maintenance can be substantial.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating ERP with existing systems and legacy software can be challenging, requiring extensive customization and data migration.
- Change Management: Resistance to change among employees and stakeholders can hinder adoption and efficiency gains.
- Data Security and Privacy: Centralized data storage increases security risks, requiring robust security measures and compliance with data protection regulations.
- Customization vs. Standardization: Balancing the need for customized ERP solutions with the benefits of standardized processes can be a dilemma for organizations.
ERP Implementation Process
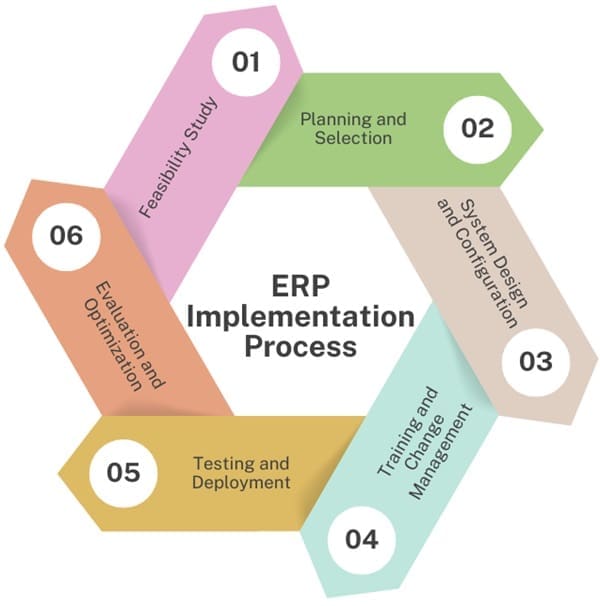
Successful ERP implementation follows a structured process to ensure alignment with organizational goals and minimal disruption to operations:
- Feasibility Study: Assessing organizational readiness, identifying requirements, and evaluating ERP vendors.
- Planning and Selection: Formulating an implementation strategy, selecting suitable ERP modules, and establishing project goals and timelines.
- System Design and Configuration: Customizing ERP modules to align with business processes, configuring workflows, and defining user roles and permissions.
- Training and Change Management: Training employees on new processes and software usage, managing resistance to change, and fostering organizational buy-in.
- Testing and Deployment: Conducting comprehensive testing to ensure system functionality, data integrity, and user acceptance before full deployment.
- Evaluation and Optimization: Monitoring ERP performance, gathering user feedback, and continuously optimizing processes to maximize ROI.
Issues in ERP Implementation
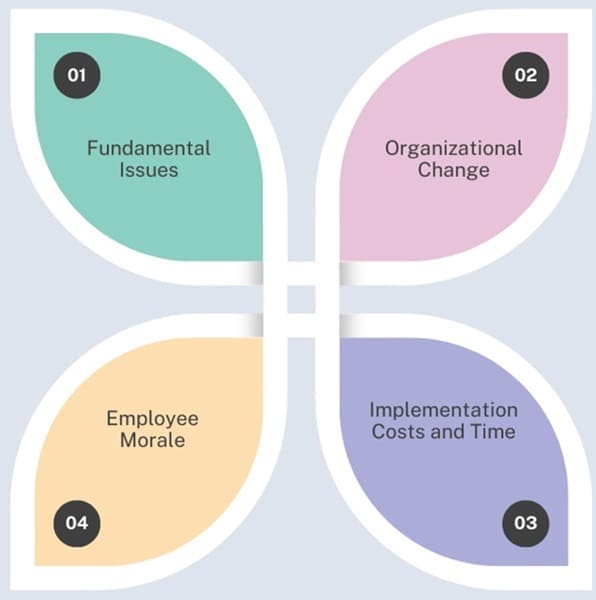
- Fundamental Issues: Costly and time-consuming.
- Organizational Change: Requires business process reengineering.
- Implementation Costs and Time: Can exceed initial estimates.
- Employee Morale: Long hours and stress can affect morale.
Also See: Lean Six Sigma Certification Programs, Greensboro, North Carolina
Traps in ERP Implementation
- Change Management: Resistance to new processes.
- Business Process Reengineering: Balancing system vs. process changes.
- Poor Planning: Inadequate preparation for complexities.
- Underestimating IT Skills: Skills required for new technology.
- Technology Trials: Unexpected challenges in customization.
- Executive Buy-in: Senior management support is crucial.
- Resource Allocation: Budgets often underestimate needs.
Difference Between ERP and CRM
| Feature | ERP | CRM |
| Focus | Internal operations and resources management | Customer-facing interactions and relationships |
| Scope | Integrates across the entire organization | Specific to sales, marketing, and customer service |
| Primary Function | Streamline business processes and workflows | Manage customer interactions and relationships |
| Modules | Finance, HR, manufacturing, supply chain, etc. | Sales force automation, marketing automation, customer service |
| Data Management | Centralizes data for operational efficiency | Centralizes customer data for relationship management |
| Integration | Integrates across entire organization | Integrates with ERP, marketing, and other systems |
| Users | Used by employees across various departments | Used primarily by sales, marketing, and service teams |
| Goal | Improve internal efficiency and productivity | Enhance customer satisfaction and retention |
| Examples | SAP, Oracle ERP, Microsoft Dynamics | Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM |
Open Source ERP Solutions
Open-source ERP solutions have gained popularity for their affordability, flexibility, and community-driven support:
- Cost Savings: Eliminates licensing fees associated with proprietary ERP software, reducing initial investment and ongoing expenses.
- Customization: Offers greater flexibility for customization and integration with other software systems based on open-source code availability.
- Community Support: Access to a community of developers and users for troubleshooting, updates, and enhancements.
- Popular Open Source ERP Solutions:
- Openbravo: Web-based ERP for SMEs with finance, supply chain, and manufacturing functionalities.
- PostBooks: Accounting and CRM package for small to mid-sized businesses, built on PostgreSQL database.
- OpenERP (Odoo): Modular ERP system for various business functions like accounting, CRM, HR, and inventory management.
- ERP5: Python-based ERP suitable for multinational organizations, focusing on finance and logistics.
- Limitations: Potential challenges include increased complexity in implementation, limited vendor support, and compatibility issues with proprietary software.
- Selected Open Source ERP Software
| Title | Functionalities | Technical / Platform | Website |
| Openbravo | Finance, supply chain, manufacturing | Java, JavaScript, SQL, PL/SQL, XML | Openbravo |
| SQL-Ledger | Accounting, ERP system | Platform independent | SQL-Ledger |
| PostBooks | Accounting, CRM | Linux, Mac, Windows | PostBooks |
| OpenERP | Modular ERP system | Windows, Mac, Linux, FreeBSD, OpenSolaris | OpenERP |
| FireERP | ERP, CRM, eBusiness, SCM/SRM | J2EE, JDO, Eclipse RCP | FireERP |
| ERP5 | Finance, accounting | Python | ERP5 |
| Project-open | CRM, project planning, collaboration | Web-based | Project-open |
ERP Security Considerations
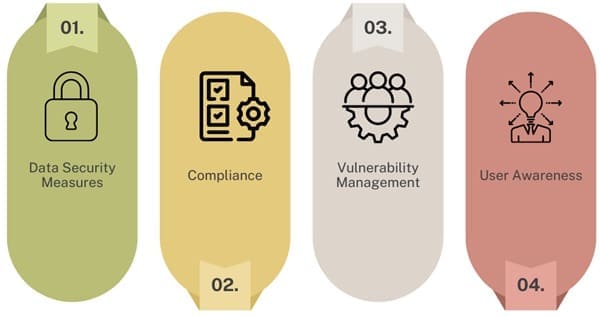
Security is a critical aspect of ERP systems, given their role in managing sensitive business data and processes:
- Data Security Measures: Implementing role-based access controls (RBAC), encryption, and secure authentication mechanisms to protect data integrity and confidentiality.
- Compliance: Ensuring ERP systems comply with industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS to avoid legal and financial repercussions.
- Vulnerability Management: Regularly updating ERP software, conducting vulnerability assessments, and patching security flaws to mitigate risks.
- User Awareness: Educate employees about security best practices, phishing attacks, and social engineering tactics to prevent unauthorized access.
Popular ERP Systems
1. SAP ERP
- Features: Comprehensive functionality, scalability, and integration capabilities.
- Target Market: Large enterprises across various industries.
2. Oracle ERP
- Features: Strong finance and accounting capabilities, and robust cloud-based solutions.
- Target Market: Medium to large enterprises, particularly those needing strong financial management.
3. Microsoft Dynamics
- Features: User-friendly interface, seamless integration with other Microsoft products.
- Target Market: Small to medium-sized businesses.
4. Infor ERP
- Features: Industry-specific solutions, user-friendly interface, flexible deployment options.
- Target Market: Medium to large enterprises, particularly in manufacturing, healthcare, and distribution.
5. NetSuite ERP
- Features: Cloud-based, scalable, and easy to deploy.
- Target Market: Small and growing businesses, and startups.
Final Words
ERP systems play a pivotal role in transforming organizational processes, enhancing efficiency, and enabling data-driven decision-making.
Despite the challenges associated with implementation and maintenance, the benefits of ERP systems outweigh the risks, making them indispensable tools for modern enterprises. Whether opting for proprietary solutions or exploring open-source alternatives, organizations must carefully evaluate their requirements, consider implementation best practices, and prioritize security to maximize the ROI of their ERP investments.
By embracing ERP systems, businesses can streamline operations, optimize resource allocation, and achieve sustainable growth in today’s competitive landscape.

About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.