A Risk Management Information System (RMIS) represents a sophisticated technology platform designed to streamline and centralize an organization’s entire risk management process. Furthermore, this comprehensive software solution enables businesses to identify, assess, monitor, and mitigate various risks across their operations while maintaining detailed documentation and reporting capabilities.
Modern RMIS platforms integrate multiple risk management functions into a single, unified system. Consequently, organizations can achieve better visibility into their risk landscape while improving decision-making processes. These systems typically encompass claims management, policy administration, loss prevention, regulatory compliance, and comprehensive analytics.
The evolution of risk management information systems has transformed how enterprises approach risk mitigation. Previously, organizations relied on disparate systems and manual processes to manage risks. However, today’s RMIS solutions provide automated workflows, real-time monitoring, and predictive analytics that significantly enhance risk management effectiveness.
Table of contents
What is a Risk Management Information System (RMIS)?
A Risk Management Information System (RMIS) is a software platform designed to collect, manage, analyze, and report all risk-related data within an organization31. RMIS systems centralize information from various sources, automate risk management processes, and provide actionable insights to help companies identify, assess, and mitigate risks effectively35.
RMIS meaning:
The acronym RMIS stands for “Risk Management Information System.” It is sometimes referred to as a risk information management system or risk management system software.
Public, Onsite, Virtual, and Online Six Sigma Certification Training!
- We are accredited by the IASSC.
- Live Public Training at 52 Sites.
- Live Virtual Training.
- Onsite Training (at your organization).
- Interactive Online (self-paced) training,
Why Do Organizations Need an RMIS?
Traditional risk management methods—like spreadsheets and manual tracking—are time-consuming, error-prone, and often lead to fragmented risk information. An RMIS consolidates all risk data into one place, streamlining workflows and improving decision-making. With a robust RMIS, risk teams can:
- Automate data collection and reporting
- Gain a holistic view of risk exposure
- Track and manage claims, incidents, and compliance
- Enhance collaboration across departments
- Reduce costs and improve accuracy
Did you know?
Over 78% of organizations use an RMIS to manage risk, reflecting its growing importance in today’s business landscape.
RMIS vs. Traditional Risk Management Systems
| Feature | Traditional Systems (Spreadsheets) | RMIS Software |
| Data Centralization | Fragmented | Unified |
| Automation | Manual | Automated |
| Reporting | Time-consuming | Real-time, customizable |
| Collaboration | Limited | Cross-functional |
| Compliance Tracking | Challenging | Built-in, automated |
| Scalability | Difficult | Easily scalable |
Core Components and Features of RMIS Systems
Centralized Risk Management Database
The foundation of any effective RMIS lies in its centralized risk management database. This comprehensive repository stores all risk-related information, including incident reports, claims data, policy details, and compliance records. Moreover, the database architecture ensures data integrity while providing authorized users with instant access to critical information.
Claims Management and Processing
Claims management represents a crucial component of risk management systems software. This module automates the entire claims lifecycle, from initial reporting through final settlement. Furthermore, integrated workflows ensure consistent processing while reducing administrative overhead and improving accuracy.
Policy Administration and Tracking
RMIS software provides comprehensive policy administration capabilities that streamline insurance management processes. These features enable organizations to track policy terms, monitor renewal dates, and manage coverage limits across multiple insurance programs. Additionally, automated alerts ensure timely policy renewals and prevent coverage gaps.
Analytics and Reporting Capabilities
Modern RMIS systems incorporate advanced analytics engines that transform raw data into actionable insights. These analytical tools enable organizations to identify trends, predict potential risks, and optimize their risk management strategies. Moreover, customizable dashboards provide real-time visibility into key risk metrics and performance indicators.
Also Read: Master Project Risk Management: The Step-by-Step Process
Benefits of Implementing RMIS Solutions
Enhanced Risk Visibility and Control
RMIS implementation significantly improves risk visibility across the organization. By centralizing risk data and processes, these systems eliminate information silos that previously hindered effective risk management. Furthermore, real-time monitoring capabilities enable proactive risk identification and mitigation.
Improved Operational Efficiency
Risk management information systems dramatically improve operational efficiency by automating manual processes and reducing administrative burden. Automated workflows streamline routine tasks such as incident reporting, claims processing, and compliance monitoring. Consequently, risk management teams can focus on strategic initiatives rather than administrative activities.
The efficiency gains from RMIS implementation often result in significant cost savings.
Better Compliance Management
RMIS compliance features help organizations navigate complex regulatory requirements across multiple jurisdictions. These systems maintain comprehensive audit trails and generate compliance reports that demonstrate adherence to applicable regulations. Furthermore, automated compliance monitoring alerts organizations to potential violations before they become serious issues.
The compliance management capabilities of modern RMIS platforms extend beyond basic regulatory requirements.
Cost Reduction and ROI Optimization
Effective RMIS implementation delivers substantial cost reductions through improved claims management, better insurance negotiations, and enhanced loss prevention. By providing detailed claims analytics, these systems help organizations identify cost drivers and implement targeted cost reduction strategies. Additionally, comprehensive policy management enables better insurance program optimization.
The return on investment from RMIS implementation typically becomes apparent within the first year of deployment.
Popular Uses for RMIS
Organizations use RMIS systems for a variety of risk management tasks, such as:
| RMIS Function | What It Does | Why It Matters |
| Certificate Management | Tracks certificates of insurance for compliance | Reduces exposure from partners and vendors |
| Claims Administration | Manages claims from reporting to resolution | Speeds up claims handling and reduces costs |
| Regulatory Compliance | Monitors regulations and automates compliance tasks | Avoids penalties and ensures legal compliance |
| Cost Allocations | Allocates insurance premiums and fees accurately | Improves accountability and budgeting |
| Exposure Management | Tracks and updates loss exposures in real time | Prevents gaps in coverage and ensures accurate renewal |
| Incident Management | Captures and investigates safety incidents | Protects reputation and prevents future incidents |
| Insurance Management | Manages policies, premiums, and coverage details | Simplifies insurance administration |
| Reporting & Analytics | Delivers real-time insights and visualizations | Drives better risk decisions |
How Does an RMIS Work?
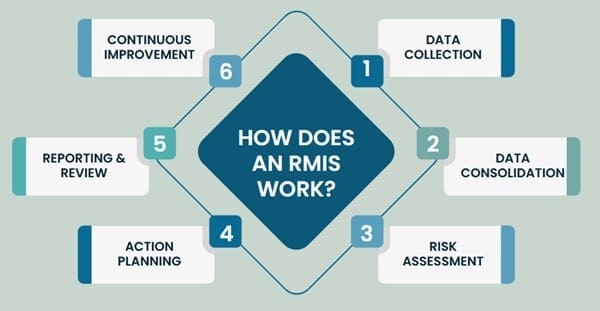
An RMIS acts as the central nervous system of your risk management strategy. Here’s a simplified workflow:
- Data Collection:
Risk data is gathered from internal systems (HR, finance, operations) and external sources (insurers, vendors). - Data Consolidation:
The RMIS centralizes all information, eliminating silos and providing a unified view. - Risk Assessment:
Built-in tools help identify, measure, and prioritize risks based on likelihood and impact. - Action Planning:
The system suggests or tracks mitigation strategies, assigns tasks, and monitors progress. - Reporting & Review:
Dashboards and reports provide real-time insights for leadership and stakeholders. - Continuous Improvement:
Ongoing monitoring allows for adjustments, ensuring risk management remains agile and effective.
Types of Risk Management Systems
Enterprise Risk Management Platforms
Enterprise-level RMIS platforms provide comprehensive risk management capabilities for large organizations with complex risk profiles. These systems integrate multiple risk management disciplines, including operational risk, financial risk, strategic risk, and compliance risk. Furthermore, they offer advanced analytics and reporting capabilities that support enterprise-wide risk governance.
Enterprise RMIS solutions typically feature sophisticated workflow engines, extensive customization options, and robust integration capabilities. Consequently, these platforms can adapt to unique organizational requirements while maintaining scalability for future growth.
Specialized Industry Solutions
Many RMIS vendors offer specialized solutions tailored to specific industry requirements. For example, healthcare organizations require systems that address medical malpractice risks, patient safety concerns, and HIPAA compliance. Similarly, manufacturing companies need systems that focus on workplace safety, product liability, and environmental risks.
These specialized RMIS platforms incorporate industry-specific features, templates, and compliance frameworks. Therefore, organizations can implement solutions that address their unique risk challenges while leveraging best practices from their industry.
Small Business Risk Management Tools
Smaller organizations often require simplified RMIS solutions that provide essential risk management capabilities without the complexity of enterprise platforms. These systems typically focus on core functions such as incident tracking, basic claims management, and compliance monitoring. Moreover, they offer cost-effective deployment options that make risk management technology accessible to smaller businesses.
Small business RMIS tools often feature user-friendly interfaces and simplified workflows that require minimal training. Additionally, cloud-based deployment models reduce infrastructure requirements and ongoing maintenance costs.
Also Read: The Best Risk Management Tools
Key Features to Look for in RMIS Software
Integration Capabilities
Modern RMIS software must integrate seamlessly with existing business systems, including ERP platforms, financial systems, and human resources databases. These integrations eliminate data silos and ensure consistent information across the organization. Furthermore, API-based integration capabilities enable custom connections with specialized business applications.
The integration capabilities of RMIS platforms extend to external systems such as insurance carrier portals, regulatory databases, and third-party risk assessment tools. Consequently, organizations can create comprehensive risk management ecosystems that leverage multiple data sources and services.
Mobile Accessibility
Mobile accessibility has become essential for modern RMIS platforms as organizations embrace remote work and field-based operations. These applications enable users to report incidents, access risk information, and perform routine tasks from any location. Additionally, offline capabilities ensure continued functionality even in areas with limited connectivity.
Mobile RMIS applications typically feature intuitive interfaces optimized for smartphone and tablet use. These applications often include photo capture capabilities, GPS location services, and push notifications that enhance user productivity and engagement.
Scalability and Performance
Effective RMIS platforms must scale efficiently to accommodate organizational growth and changing requirements. Cloud-based architectures provide the flexibility needed to handle increasing data volumes and user loads without performance degradation. Moreover, modern systems utilize distributed computing technologies that ensure consistent performance across global deployments.
Scalability considerations extend beyond technical capacity to include functional flexibility. Organizations need RMIS platforms that can adapt to new risk types, regulatory requirements, and business processes without requiring extensive customization or redevelopment.
Security and Data Protection
Security represents a critical consideration for RMIS selection and implementation. These systems handle sensitive information including claims data, financial records, and personally identifiable information. Therefore, robust security measures including encryption, access controls, and audit logging are essential requirements.
Modern RMIS platforms implement multi-layered security architectures that protect data both in transit and at rest. Additionally, these systems incorporate advanced threat detection capabilities and compliance frameworks that address evolving cybersecurity risks.
Implementation Best Practices
Strategic Planning and Requirements Analysis
Successful RMIS implementation begins with comprehensive strategic planning and requirements analysis. Organizations must clearly define their risk management objectives, identify specific functional requirements, and establish success metrics. Furthermore, stakeholder engagement throughout the planning process ensures broad organizational support for the implementation.
The requirements analysis phase should address both current needs and future growth projections. Organizations must consider factors such as user volume, data requirements, integration needs, and regulatory compliance obligations when defining system specifications.
Vendor Selection and Evaluation
RMIS vendor selection requires careful evaluation of multiple factors including functionality, scalability, support quality, and total cost of ownership. Organizations should develop comprehensive evaluation criteria that reflect their specific requirements and business priorities. Moreover, reference checks and pilot implementations can provide valuable insights into vendor capabilities and system performance.
The vendor evaluation process should include technical assessments, financial analysis, and cultural fit considerations. Organizations must ensure that selected vendors can provide ongoing support and development resources to maintain long-term system effectiveness.
Change Management and User Adoption
Effective change management strategies are crucial for successful RMIS implementation. Organizations must address user concerns, provide comprehensive training, and establish clear communication channels throughout the implementation process. Additionally, change champions within different departments can help drive user adoption and system utilization.
User training programs should address both technical system usage and risk management best practices. Ongoing training and support ensure continued user engagement and system optimization over time.
Leading RMIS Vendors and Solutions
Enterprise RMIS Providers
Several established vendors dominate the enterprise RMIS market, offering comprehensive platforms with extensive functionality and proven track records. These vendors typically provide industry-specific solutions, extensive customization capabilities, and global support networks. Furthermore, they invest heavily in research and development to maintain competitive advantages and address emerging risk management needs.
Major enterprise RMIS vendors often offer cloud-based deployment options alongside traditional on-premises installations. This flexibility allows organizations to choose deployment models that align with their technical infrastructure and security requirements.
Emerging Technology Providers
The RMIS market continues to evolve with new vendors introducing innovative technologies and approaches. These emerging providers often focus on specific market segments or leverage advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain to differentiate their offerings. Additionally, they may offer more flexible pricing models and faster implementation timelines.
Emerging RMIS vendors typically emphasize user experience, modern interface design, and simplified workflows. These characteristics make their solutions particularly attractive to organizations seeking to modernize their risk management processes.
Specialized Niche Solutions
Numerous specialized vendors provide RMIS solutions tailored to specific industries or risk management disciplines. These vendors offer deep expertise in particular areas such as environmental risk, cyber risk, or regulatory compliance. Moreover, their specialized focus often results in more sophisticated functionality within their areas of expertise.
Niche RMIS providers may offer better value propositions for organizations with specific requirements that are not well-addressed by general-purpose platforms. However, organizations must carefully evaluate integration capabilities and long-term viability when considering specialized solutions.
Cost Considerations and ROI Analysis
Total Cost of Ownership Factors
RMIS total cost of ownership includes multiple components beyond initial software licensing fees. Organizations must consider implementation costs, training expenses, ongoing maintenance fees, and potential customization requirements. Additionally, infrastructure costs for on-premises deployments or cloud service fees for hosted solutions represent significant ongoing expenses.
Hidden costs often emerge during RMIS implementation, including data migration expenses, integration development, and extended training requirements. Therefore, comprehensive cost analysis should include contingency budgets to address unforeseen expenses.
ROI Measurement and Metrics
RMIS return on investment measurement requires careful tracking of both cost savings and efficiency improvements. Common ROI metrics include reduced claims processing costs, improved loss ratios, decreased regulatory penalties, and enhanced operational efficiency. Furthermore, intangible benefits such as improved risk visibility and better decision-making contribute to overall system value.
Organizations should establish baseline metrics before RMIS implementation to enable accurate ROI measurement. Regular performance reviews and system optimization efforts help maximize return on investment over time.
Future Trends in Risk Management Information Systems
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are increasingly integrated into RMIS platforms to enhance predictive capabilities and automate complex decision-making processes. These technologies enable systems to identify patterns in historical data, predict future risks, and recommend optimal mitigation strategies. Consequently, organizations can transition from reactive to proactive risk management approaches.
AI-powered RMIS platforms can automate routine tasks such as claims triage, fraud detection, and regulatory compliance monitoring. Additionally, natural language processing capabilities enable systems to analyze unstructured data sources and extract relevant risk information.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
IoT sensors and devices are creating new opportunities for real-time risk monitoring and prevention. RMIS platforms increasingly integrate with IoT networks to collect continuous data about operational conditions, equipment performance, and environmental factors. Furthermore, this integration enables predictive maintenance programs and proactive risk mitigation strategies.
IoT-enabled RMIS solutions can monitor everything from building security systems to industrial equipment performance. The resulting data streams provide unprecedented visibility into risk factors and enable automated responses to potential threats.
Regulatory Technology (RegTech) Advances
Regulatory technology solutions are becoming integral components of modern RMIS platforms. These technologies automate compliance monitoring, regulatory reporting, and policy management across multiple jurisdictions. Moreover, they help organizations stay current with changing regulations and reduce compliance-related risks.
RegTech integration enables RMIS platforms to automatically update compliance requirements, generate regulatory reports, and alert organizations to potential violations. This automation reduces manual compliance efforts while improving accuracy and consistency.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does RMIS stand for in risk management?
RMIS stands for Risk Management Information System, which is a comprehensive software platform designed to centralize and streamline an organization’s risk management processes, including claims management, policy administration, compliance monitoring, and risk analytics.
How do risk management information systems improve business operations?
RMIS platforms improve business operations by automating manual processes, centralizing risk data, providing real-time visibility into risk exposures, enabling better decision-making through analytics, and ensuring consistent compliance with regulatory requirements across the organization.
What are the key features to look for when selecting RMIS software?
Essential RMIS features include centralized data management, claims processing automation, policy administration capabilities, comprehensive reporting and analytics, integration capabilities with existing systems, mobile accessibility, robust security measures, and scalability to accommodate organizational growth.
How much does RMIS implementation typically cost?
RMIS implementation costs vary significantly based on organization size, system complexity, and vendor selection. Costs typically range from tens of thousands of dollars for small business solutions to millions of dollars for enterprise-wide implementations, including software licensing, implementation services, training, and ongoing maintenance.
What industries benefit most from RMIS solutions?
While RMIS solutions benefit organizations across all industries, they are particularly valuable for industries with high risk exposures such as healthcare, manufacturing, construction, transportation, financial services, and government entities that face complex regulatory requirements and significant liability exposures.

About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.




















