Business Process Management (BPM) refers to the systematic approach to improving an organization’s workflows and operational processes. It aims to make these processes more efficient, effective, and adaptable, so that they consistently produce desired outcomes.
BPM is all about managing and optimizing these chains of activities to enhance overall business performance, focusing on complete processes rather than isolated tasks.
Table of contents
- Understanding Business Processes
- What is Business Process Management?
- Related Disciplines
- Modern BPM Tools and Suites
- BPM and Process Improvement Phases
- Foundations of BPM
- Benefits of BPM
- BPM Lifecycle
- Principles of Business Process Management
- Final Words
- About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
- Related Articles
Understanding Business Processes
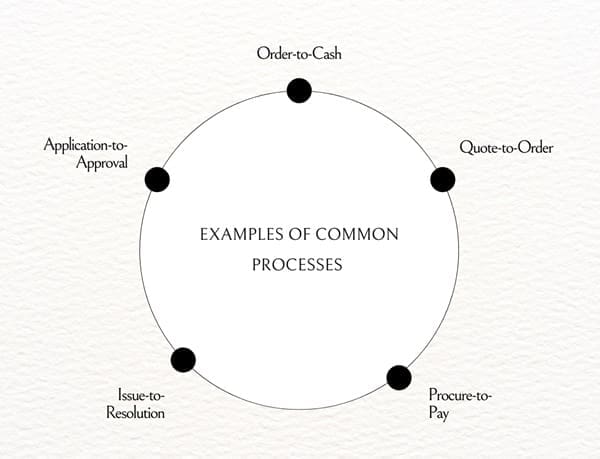
A business process is a sequence of interconnected activities and decisions that work together to achieve a specific goal. Examples of common processes include:
- Order-to-Cash: This process starts with a customer order and ends with payment. It covers steps like order verification, shipment, invoicing, and payment collection.
- Quote-to-Order: Starting from when a customer requests a quote, it concludes when the customer places an order.
- Procure-to-Pay: This process is about managing purchases, from identifying the need for goods or services to payment after delivery.
- Issue-to-Resolution: This handles customer complaints or issues, from reporting a problem to reaching an agreed resolution.
- Application-to-Approval: Typically found in administrative and regulatory contexts, this process involves evaluating applications for permits, approvals, or similar requests.
What is Business Process Management?
Business Process Management (BPM) refers to a set of techniques, structured methods, and tools aimed at improving the efficiency and effectiveness of an organization’s operations. Essentially, BPM helps businesses streamline their workflows by identifying and refining existing processes to better align with desired goals. While BPM involves various methodologies and tools, its primary focus is on enhancing business processes rather than merely implementing technology or automation.
BPM involves a holistic view of processes, examining them from the customer’s perspective to optimize outcomes. It’s essential to understand that BPM is distinct from change management, Six Sigma, or technology implementation; rather, it encompasses these elements to create an overall approach to process management.
History of Business Process Management
The roots of BPM can be traced back to early 20th-century industrial engineering practices.
Frederick Taylor, an early proponent of process improvement, focused on standardizing industrial processes to enhance efficiency. His work paved the way for later methodologies, such as Six Sigma, which emerged in the 1980s. Six Sigma emphasizes process improvement by reducing errors and variability, aiming to enhance output quality.
The Lean methodology, derived from Toyota’s production system in the 1990s, introduced the concept of eliminating waste from processes. While Six Sigma focuses on reducing errors, Lean emphasizes eliminating non-value-adding steps, thus improving efficiency.
Today, BPM integrates elements from both Lean and Six Sigma, among other approaches, to provide a comprehensive framework for process improvement. By combining these methodologies, BPM enables organizations to address a broad spectrum of operational challenges.
Core Principles of BPM
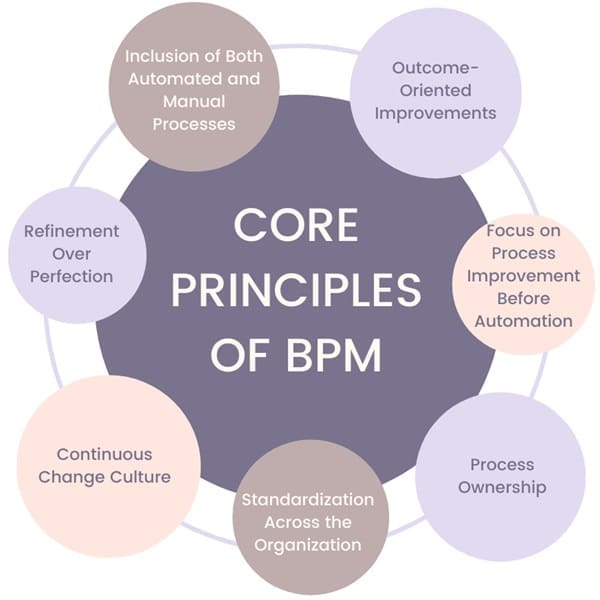
To implement BPM successfully, organizations should focus on several key principles:
- Outcome-Oriented Improvements: BPM emphasizes organizing process improvements around specific outcomes rather than individual tasks. This approach helps ensure that each change has a clear purpose and measurable impact.
- Focus on Process Improvement Before Automation: It’s vital to identify and correct process inefficiencies before automating them. Automation without proper analysis can lead to amplified inefficiencies.
- Process Ownership: Every process should have a designated owner responsible for overseeing and improving it. This creates accountability and ensures consistent oversight.
- Standardization Across the Organization: BPM works best when processes are standardized throughout the enterprise. Consistent processes simplify management and provide a foundation for continuous improvement.
- Continuous Change Culture: Establishing a culture that embraces continuous change is essential for BPM success. Incremental improvements over time yield more sustainable results than pursuing drastic transformations.
- Refinement Over Perfection: BPM emphasizes improving existing processes rather than building perfect or entirely new processes. It’s about optimizing what’s already in place to better meet business objectives.
- Inclusion of Both Automated and Manual Processes: Effective BPM encompasses both automated and manual processes. By applying BPM principles to all types of processes, businesses can achieve a comprehensive and balanced approach to improvement.
Why Implement BPM?
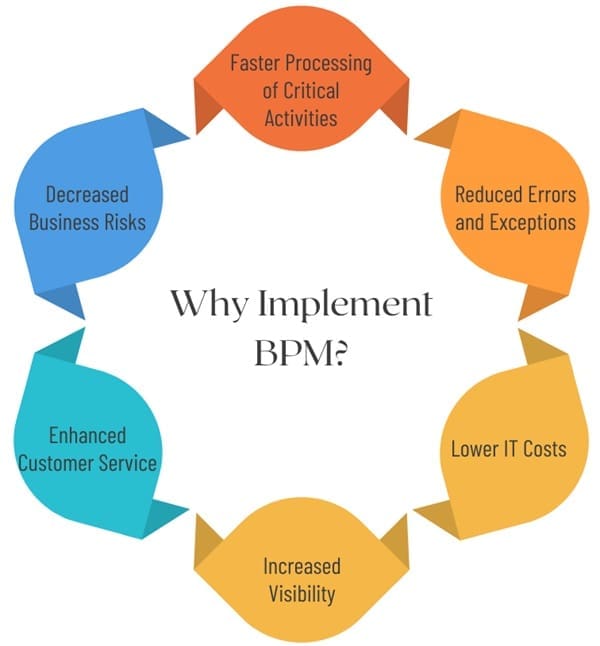
Organizations adopt BPM to enhance their operational performance in various ways, including:
- Faster Processing of Critical Activities: BPM helps reduce the time required to execute essential tasks by eliminating unnecessary steps and streamlining workflows.
- Reduced Errors and Exceptions: By standardizing processes, BPM minimizes the potential for errors and reduces the occurrence of exceptions that can disrupt operations.
- Lower IT Costs: Implementing BPM often leads to more efficient IT resource allocation, resulting in lower operational costs over time.
- Increased Visibility: BPM provides insight into operational bottlenecks and inefficiencies, enabling organizations to address issues proactively.
- Enhanced Customer Service: By improving processes, organizations can provide faster and more reliable services, leading to higher customer satisfaction and retention.
- Decreased Business Risks: BPM helps identify and mitigate risks associated with inefficient or outdated processes, improving overall business stability.
Key Elements of BPM
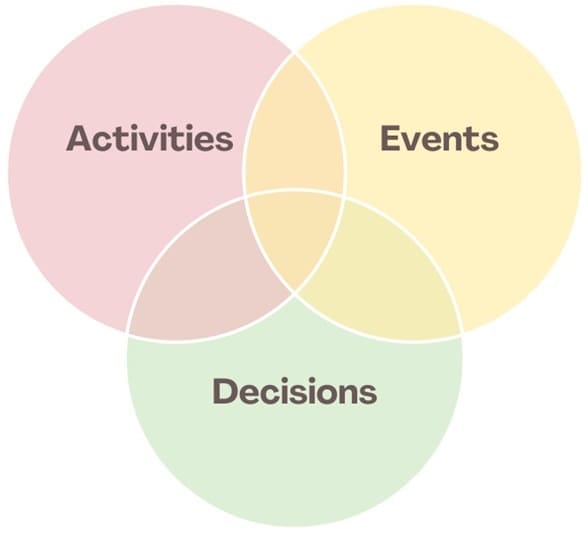
At the core of BPM are the elements that make up a business process, such as:
- Activities: These are the specific tasks that need to be completed within the process.
- Events: Events mark the start, end, or transition between activities.
- Decisions: These determine the pathway of a process based on conditions or choices.
By focusing on these elements, BPM helps organizations gain a comprehensive view of their processes, allowing them to identify inefficiencies and improvement opportunities.
Related Disciplines
BPM often intersects with other management approaches like:
- Total Quality Management (TQM): While TQM focuses on continuous quality improvement in products and services, BPM seeks to enhance the processes that lead to these outcomes.
- Operations Management: This field deals with optimizing production processes. While it often maintains existing processes, BPM aims to continuously adapt and improve processes.
- Lean: Originating from manufacturing, Lean management focuses on eliminating waste and enhancing customer value. BPM takes on Lean principles, especially in reducing non-value-adding activities.
- Six Sigma: Concentrating on reducing defects, Six Sigma uses data-driven methods to improve process quality. BPM adopts Six Sigma techniques to fine-tune processes for better accuracy and reliability.
Modern BPM Tools and Suites
Modern BPM software has significantly evolved from its beginnings in the 1990s. Originally, BPM tools were limited to basic modeling and workflow management. However, today’s BPM suites offer an extensive range of features, including workflow automation, user interface design, reporting, data modelling, and system integration.
A contemporary BPM suite supports the full lifecycle of process management, including:
- Process Discovery: Engaging stakeholders in documenting and understanding the current state of processes to identify areas for improvement.
- Modeling: Creating visual representations of processes to facilitate understanding, testing, and refinement. This often involves modelling user interfaces, data flows, and decision points within the process.
- Execution: Running the process in a real-world setting to validate its effectiveness. Modern BPM suites allow seamless transitions from modelling to execution, enabling rapid iterations and adjustments.
- Process Improvement: Using data gathered during execution to identify areas for enhancement. Continuous improvement is integral to BPM, as it enables organizations to adapt to changing conditions and optimize their operations over time.
BPM and Process Improvement Phases
BPM projects generally follow a structured series of phases:
- Discovery: Documenting the current state of processes to identify inefficiencies. This phase often involves gathering insights from stakeholders and mapping out workflows.
- Modeling: Building a visual model of the process that includes all relevant steps, decision points, and interactions. Modern BPM tools enable collaborative modeling, allowing multiple stakeholders to contribute to the process design.
- Execution: Implementing the process in a live environment. At this stage, the process is tested under real-world conditions, allowing for further refinement.
- Improvement: Based on performance data, processes are continually analyzed and adjusted. Improvements might include removing bottlenecks, automating manual steps, or refining workflows for greater efficiency.
Foundations of BPM
BPM has its roots in two main areas: statistical process control and business process reengineering.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC) and Quality Movement:
- Origins: SPC emerged from the work of Walter Shewhart and W. Edwards Deming, who emphasized reducing process variability through careful measurement and statistical techniques. This approach laid the groundwork for the quality movement and Six Sigma methodologies.
- Principles: The main principles of SPC focus on measuring outcomes, using data to pinpoint the root causes of issues, and striving for continuous improvement. The emphasis is on using performance metrics to monitor processes and make improvements based on hard data rather than assumptions.
- Limitations: While SPC emphasizes consistency, consistent performance does not always mean excellent performance. An organization could achieve consistent results that still fall short of customer expectations.
- Business Process Reengineering (BPR):
- Concept: Developed by Michael Hammer, BPR sought to revolutionize business processes by redesigning them entirely. Instead of minor improvements, BPR aimed at fundamental rethinking of how processes operate.
- Focus: BPR introduced the concept of end-to-end processes that create customer value, such as order fulfillment or procurement, rather than focusing on isolated tasks.
- Impact: BPR aimed to eliminate inefficiencies caused by fragmentation across departments, which often led to delays, errors, and increased complexity.
- Challenges: BPR was seen as a one-time effort rather than a continuous process, making it difficult to adapt to ongoing changes.
Benefits of BPM
Implementing BPM provides a range of operational and strategic advantages:
- Operational Efficiency: BPM helps reduce costs, enhance speed, improve accuracy, and reduce redundancy across processes.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: By focusing on processes that directly impact customers, BPM enhances service quality and response times.
- Flexibility and Agility: BPM enables organizations to adapt quickly to market changes by making it easier to monitor and adjust processes in response to shifts in performance metrics.
- Strategic Alignment: BPM provides a framework that can integrate various improvement initiatives, ensuring they all work towards a common goal.
BPM Lifecycle
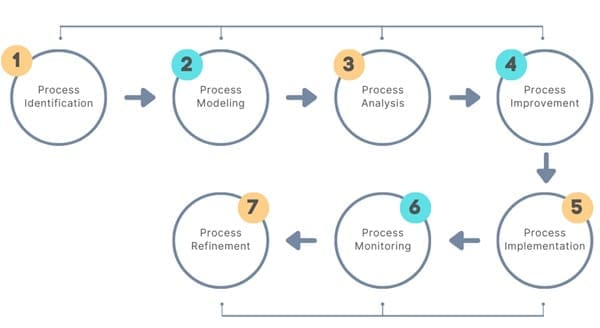
A BPM initiative typically follows a lifecycle, which includes the following stages:
- Process Identification: The team determines which processes need improvement. They identify existing problems, set objectives, and map out relevant processes.
- Process Modeling: Here, the team visually maps out the process steps and workflows. This helps identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and opportunities for improvement.
- Process Analysis: The team assesses the current process performance using metrics like cost, time, and error rates.
- Process Improvement: The team then identifies potential solutions and makes adjustments to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve quality.
- Process Implementation: Changes are put into action, which may involve updating technology, training employees, and redesigning workflows.
- Process Monitoring: The improved process is monitored to ensure it meets the desired performance metrics.
- Process Refinement: Based on monitoring data, further tweaks and refinements may be necessary to optimize performance continuously.
BPM Cycle in Action
The BPM cycle involves a series of steps, from defining processes to implementing improvements and measuring results:
- Design and Document Processes: The cycle begins by defining and documenting processes, ensuring they are well-structured and align with organizational objectives.
- Set Performance Targets: Once the process is defined, performance metrics are established based on customer needs, competitor benchmarks, and company goals.
- Measure and Analyze Performance: Performance is then measured and compared against targets to identify any gaps or shortcomings. This helps to determine if the issue is with the process design or execution.
- Identify and Address Root Causes: If performance falls short, the underlying causes are identified and addressed. Execution issues often relate to training or resource allocation, while design flaws may require a more substantial overhaul.
- Continuous Improvement: BPM is not a one-time event; it involves ongoing monitoring, analysis, and adjustments to ensure processes continue to meet evolving customer needs and business goals.
Principles of Business Process Management
- All Work is Process Work Every task in an organization, whether routine or creative, follows a process. Processes are not limited to structured activities like customer service or order fulfillment but also apply to creative work like product development. Processes ensure that each activity, routine or innovative, aligns with other activities to achieve the organization’s goals. Broadly, there are three types of processes:
- Core Processes: These directly create value for customers, such as sales or product delivery.
- Enabling Processes: These support core processes and cater to internal stakeholders, like HR or IT services.
- Governing Processes: These are management-related, like strategic planning or performance management.
- Any Process is Better than No Process Without a defined process, work can become chaotic, relying on improvisation. A defined process provides a framework that ensures repeatable and predictable results, reducing reliance on individual heroics.
- A Good Process is Better than a Bad Process While having a process is essential, the design of that process is crucial. A well-designed process aligns with organizational goals and is efficient. If a process is not yielding desired results, it needs redesigning.
- Standardization of Processes Standardizing processes across an organization promotes uniformity, reducing complexity and costs in areas like training and IT. However, it’s essential to balance standardization with the unique needs of different departments or regions.
- Effective Execution is Key A well-designed process needs to be executed effectively to realize its potential. This involves training, oversight, and consistent application to ensure the process works as intended.
- Continuous Improvement Even a good process can be improved. Regular evaluation and minor adjustments can enhance process efficiency and effectiveness over time, responding to feedback and changing needs.
- Processes Need Updating No process remains effective forever. As external factors like technology and customer preferences change, processes must be revisited and adapted. A process that was once optimal might become outdated and require a complete overhaul.
Final Words
In essence, BPM is a holistic approach that emphasizes the ongoing management of business processes to enhance organizational performance and meet customer expectations. By continuously monitoring and refining processes, BPM enables organizations to remain competitive and responsive in a rapidly changing business environment.

About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.



















