A Pugh Matrix, also known as a decision matrix or Pugh chart, represents a systematic decision-making tool that helps teams evaluate multiple alternatives against predefined criteria. This powerful decision making matrix provides a structured approach for comparing different concepts, solutions, or options in engineering design, product development, and business decision-making processes.
The Pugh matrix methodology was developed by Stuart Pugh, a British design engineer, who recognized the need for a systematic approach to concept selection. This decision matrix tool eliminates subjective bias and emotional decision-making by providing an objective framework that considers multiple evaluation criteria simultaneously.
Table of contents
What is a Pugh Matrix?
A Pugh Matrix is a decision-making tool used to evaluate and compare multiple options against a set of criteria. It helps teams or individuals make informed choices by systematically scoring and ranking alternatives based on how well they meet specific requirements.
The process involves listing options (like design concepts or solutions) and criteria (like cost, feasibility, or performance), assigning weights to the criteria based on their importance, and then scoring each option against each criterion.
The scores are multiplied by the weights and summed to give a total score for each option, making it easier to identify the best choice. It’s particularly useful in engineering, product development, or any situation where you need to balance trade-offs and make objective decisions.
Public, Onsite, Virtual, and Online Six Sigma Certification Training!
- We are accredited by the IASSC.
- Live Public Training at 52 Sites.
- Live Virtual Training.
- Onsite Training (at your organization).
- Interactive Online (self-paced) training,
What is a Decision Matrix in practical terms?
It serves as a visual representation that organizes decision criteria along one axis and potential solutions along another, creating a grid where each intersection represents an evaluation score. This decision making grid enables teams to make informed choices based on comprehensive analysis rather than intuition alone.
Key Concepts and Definitions
| Term | Meaning |
| Pugh Matrix | A decision-making matrix for comparing alternatives against criteria and a baseline. |
| Decision Matrix | Generic term for tools like the Pugh Matrix. |
| Weighted Decision Matrix | A matrix where criteria are assigned weights to reflect their importance. |
| Pugh Chart | Another name for the Pugh Matrix. |
| Decision Criteria | The factors or requirements used to evaluate each option |
| Baseline/Reference | The current solution or a standard used for comparison |
Core Components of Decision Matrices
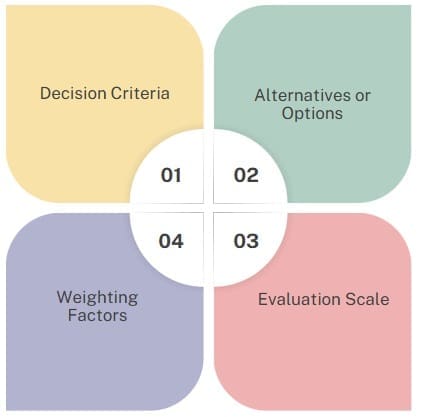
Decision matrices consist of several essential elements that work together to facilitate systematic evaluation. Understanding these components ensures effective implementation of the Pugh decision matrix methodology.
Decision Criteria: These represent the factors that matter most for your specific decision. Decision criteria should be measurable, relevant, and aligned with project objectives or organizational goals.
Alternatives or Options: The options matrix includes all potential solutions, concepts, or choices being evaluated. Each alternative represents a viable path forward that requires systematic assessment.
Evaluation Scale: Most decision matrix examples use numerical scales (such as 1-5 or 1-10) or qualitative ratings (poor, good, excellent) to score how well each alternative meets specific criteria.
Weighting Factors: Weighted decision matrix approaches assign different importance levels to various criteria, recognizing that some factors carry more significance than others.
Also Read: What is Stakeholder Analysis Matrix?
How Does the Pugh Matrix Work?
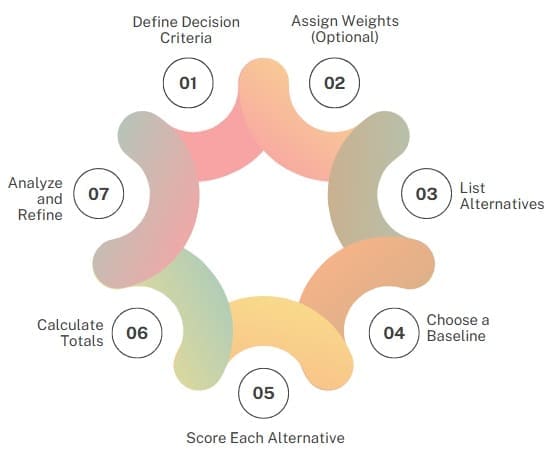
The Pugh Matrix follows a systematic process:
1. Define Decision Criteria
List the attributes or requirements that matter most for your decision. For example, cost, reliability, user experience, and scalability.
2. Assign Weights (Optional)
If some criteria are more important than others, assign weights to reflect their relative significance. This creates a weighted decision matrix.
3. List Alternatives
Identify all the options or solutions you want to compare. These could be design concepts, suppliers, locations, or project strategies.
4. Choose a Baseline
Select a reference point—often the current solution or a standard approach. Each alternative will be compared to this baseline.
5. Score Each Alternative
For each criterion, rate how each alternative compares to the baseline:
- +1 (better than baseline)
- 0 (same as baseline)
- -1 (worse than baseline)
If using weights, multiply each score by the criterion’s weight.
6. Calculate Totals
Add up the scores (or weighted scores) for each alternative. The option with the highest total is typically the best choice.
7. Analyze and Refine
Review the results. Sometimes, combining features from top alternatives leads to a hybrid solution that’s even better.
Pugh Matrix Example
Suppose a team must select a new project management tool. Their criteria are cost, ease of use, and integration. The current tool is the baseline.
| Criteria | Weight | Tool A | Tool B | Tool C |
| Cost | 3 | +1 | 0 | -1 |
| Ease of Use | 2 | 0 | +1 | -1 |
| Integration | 1 | +1 | -1 | 0 |
Weighted Scores:
- Tool A: (3×+1) + (2×0) + (1×+1) = 3 + 0 + 1 = 4
- Tool B: (3×0) + (2×+1) + (1×-1) = 0 + 2 – 1 = 1
- Tool C: (3×-1) + (2×-1) + (1×0) = -3 – 2 + 0 = -5
Conclusion: Tool A is the best choice.
Decision Matrix Definition and Purpose
The decision matrix definition encompasses both the tool itself and its underlying philosophy of structured decision-making. What can we use the decision making matrix for? Applications span numerous domains including engineering design, business strategy, project management, and personal decision-making scenarios.
Decision matrix meaning extends beyond simple comparison tools. These matrices provide a framework for transparent, defendable decisions that stakeholders can understand and support. The systematic approach helps teams avoid common decision-making pitfalls like analysis paralysis, confirmation bias, and group-think.
Types of Decision Matrices
Standard Pugh Matrix Approach
The traditional Pugh matrix uses a baseline concept for comparison, typically rating alternatives as better (+), worse (-), or equivalent (S) to the reference solution. This approach provides quick visual feedback about relative performance across different criteria.
Pugh analysis benefits include:
- Simple implementation and understanding
- Quick identification of promising concepts
- Clear visualization of trade-offs
- Effective team communication tool
Weighted Decision Matrix Implementation
These methodologies assign numerical importance factors to different criteria, allowing for more nuanced evaluation. Weighted matrix calculations multiply criterion scores by weighting factors to generate composite scores for each alternative.
Weighted decision matrix example scenarios include:
- Product feature prioritization
- Vendor selection processes
- Technology platform decisions
- Investment opportunity evaluation
Engineering Decision Matrix Applications
Engineering decision matrix tools address specific technical challenges in design and development processes. Design matrix engineering applications include material selection, manufacturing process optimization, and system architecture decisions.
Decision matrix engineering benefits encompass:
- Objective technical comparisons
- Documentation of design rationale
- Risk assessment integration
- Stakeholder alignment facilitation
How to Create an Effective Decision Matrix?
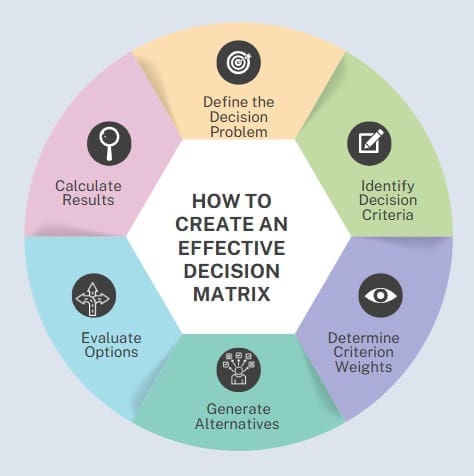
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
How to make a decision matrix requires systematic planning and execution. Following a structured approach ensures comprehensive evaluation and reliable results.
Step 1: Define the Decision Problem Clearly articulate what decision needs to be made and establish the scope of evaluation. This foundation guides all subsequent matrix development activities.
Step 2: Identify Decision Criteria Develop comprehensive criteria that capture all important factors affecting the decision. Decision criteria should be specific, measurable, and relevant to desired outcomes.
Step 3: Determine Criterion Weights For weighted decision matrix approaches, assign importance ratings to each criterion based on stakeholder priorities and project objectives.
Step 4: Generate Alternatives Brainstorm and document all viable options or solutions that address the decision problem. Ensure alternatives represent genuinely different approaches.
Step 5: Evaluate Options Score each alternative against every criterion using consistent evaluation methods and scales.
Step 6: Calculate Results Compute total scores for each alternative, applying appropriate weighting factors where applicable.
Also Read: What is the Eisenhower Matrix?
Pugh Matrix Template Development
Creating a Pugh matrix template streamlines future decision-making processes and ensures consistency across different projects. Effective templates include:
- Standardized evaluation scales
- Common criterion categories
- Calculation formulas
- Documentation sections
Decision matrix tool templates should be customizable to accommodate different decision types while maintaining structural consistency.
Practical Applications and Examples
Business Decision Making
Project decision matrix applications help organizations evaluate competing initiatives, allocate resources effectively, and prioritize strategic investments. Solution selection matrix methodologies guide teams through complex business challenges systematically.
How is using a decision matrix helpful when researching financial accounts or products? The structured approach enables objective comparison of features, costs, risks, and benefits across multiple options, reducing the likelihood of overlooking important factors.
Design Process Integration
Why is a decision matrix an important tool to use in the design process? Design decisions often involve multiple competing objectives, technical constraints, and stakeholder requirements. Design decision matrix tools help engineers balance these factors systematically.
Applications of Design matrix engineering include:
- Concept selection phases
- Material and component choices
- Manufacturing process decisions
- System configuration options
Risk Assessment Applications
List two ways the decision-making matrix is used to consider risk:
- Risk Criterion Integration: Including risk factors as evaluation criteria enables systematic risk assessment across all alternatives
- Scenario Analysis: Creating multiple matrices for different risk scenarios helps understand decision robustness under various conditions
Advanced Decision Matrix Techniques
Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis
Advanced decision analysis matrix approaches incorporate sophisticated mathematical techniques for complex decisions. These methods extend basic matrix concepts through:
- Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP)
- TOPSIS (Technique for Order Preference by Similarity)
- ELECTRE (Elimination and Choice Translating Reality)
Decision Support Systems
Modern decision support matrix tools integrate with software platforms that automate calculations, generate visualizations, and facilitate collaborative decision-making. Decision matrix maker tools enable teams to work together effectively regardless of geographic location.
Understanding how changes in criteria weights or scores affect final rankings helps validate decision robustness. Sensitivity analysis identifies critical factors that most significantly influence outcomes.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Implementation Pitfalls
Decision making grids can produce misleading results when poorly implemented. Common issues include:
- Unclear or overlapping criteria
- Inconsistent evaluation scales
- Inadequate alternative generation
- Biased scoring processes
Quality Assurance Strategies
Ensuring decision matrix analysis reliability requires:
- Multiple evaluator perspectives
- Clear scoring guidelines
- Regular calibration sessions
- Documentation of assumptions
Stakeholder Engagement
Successful decision-making matrix implementation requires active stakeholder participation throughout the process. Engagement strategies include:
- Collaborative criterion development
- Transparent evaluation sessions
- Regular communication updates
- Decision rationale documentation
Also Read: What is Impact-Effort Matrix?
Technology Integration and Tools
Software Solutions
Modern decision matrix tool platforms provide enhanced functionality including:
- Automated calculations and rankings
- Sensitivity analysis capabilities
- Collaborative evaluation features
- Report generation tools
Template Customization
Pugh matrix template adaptation enables organizations to standardize their decision-making processes while maintaining flexibility for specific applications.
Integration with Other Methods
Criteria matrix tools work effectively alongside other decision-making methodologies including:
- SWOT analysis
- Cost-benefit analysis
- Risk assessment frameworks
- Strategic planning processes
Best Practices and Recommendations
Methodology Guidelines
Effective Pugh matrix implementation follows proven best practices:
- Start with clear problem definition
- Involve relevant stakeholders throughout
- Use consistent evaluation approaches
- Document all assumptions and rationale
- Validate results through sensitivity analysis
Team Facilitation
Decision making matrix sessions benefit from skilled facilitation that ensures:
- Equal participation opportunities
- Objective evaluation processes
- Constructive discussion management
- Consensus building activities
Organizations should regularly review and refine their decision matrix processes based on:
- Outcome effectiveness assessments
- Stakeholder feedback collection
- Process efficiency evaluations
- Best practice benchmarking
Also See: Best Lean Six Sigma Training in Toronto
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between a standard Pugh Matrix and a weighted decision matrix?
A standard Pugh Matrix compares alternatives against a baseline using simple +/0/- ratings, while a weighted decision matrix assigns numerical importance factors to criteria and uses numerical scoring scales for more precise evaluation.
How many criteria should be included in a decision matrix?
Typically 5-15 criteria work best for most applications. Too few criteria may miss important factors, while too many can create analysis paralysis and reduce evaluation quality.
Can decision matrices be used for personal decisions?
Absolutely! Decision matrices work effectively for personal choices like career decisions, home purchases, investment options, or any situation requiring systematic evaluation of multiple factors.
How do you handle situations where criteria conflict with each other?
Conflicting criteria are common and highlight the trade-offs inherent in most decisions. The matrix helps quantify these trade-offs and enables informed choices based on relative importance weights.
What should you do if two alternatives have very similar scores?
Similar scores suggest the alternatives are roughly equivalent. Consider conducting sensitivity analysis, gathering additional information, or evaluating secondary factors not included in the original matrix.
How often should decision matrix criteria and weights be updated?
Criteria and weights should be reviewed whenever project objectives change, new stakeholder requirements emerge, or external conditions significantly shift that affect decision priorities.

About Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc.
Six Sigma Development Solutions, Inc. offers onsite, public, and virtual Lean Six Sigma certification training. We are an Accredited Training Organization by the IASSC (International Association of Six Sigma Certification). We offer Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Black Belt, and Yellow Belt, as well as LEAN certifications.
Book a Call and Let us know how we can help meet your training needs.




















