The problem statement highlights the issue you are addressing and provides context for why it is important to explore this matter. In academic and professional research, the problem statement is a guiding force that influences the research questions, methodology, and analysis.
Table of contents
What is a Problem Statement?
A problem statement is a formal description of an issue or concern that requires resolution through research or investigation. It serves as the foundation of any research study, helping to define the scope and direction of the study.
In essence, a well-crafted problem statement allows researchers to clearly communicate the issue at hand, explain the need for the research, and establish its relevance to a specific field of study. It is a concise yet informative paragraph (or sometimes a single sentence) that sets the stage for the entire research process.
Components
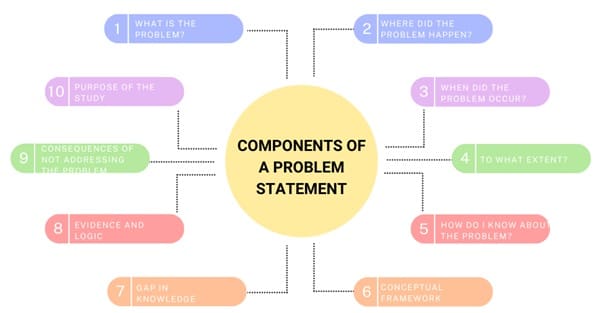
A well-organized problem statement includes several key components that outline the problem, its context, and its importance. Here are the essential elements:
- What is the Problem? The first step in writing a problem statement is to clearly define it. This involves articulating the issue that the research aims to address. You should state the problem concisely, focusing on its core aspects. By defining the problem clearly, you set the direction for the entire study, ensuring that the research questions and methodology align directly with the issue at hand.
- Where Did the Problem Happen? Identifying the location or setting of the problem helps provide the context for the research. This could be a specific geographical area, a particular industry, a community, or any other relevant setting. Describing where the problem has occurred helps the reader understand the scope of the issue and the factors contributing to it.
- When Did the Problem Occur? The timing of the problem is another critical factor to mention in the problem statement. This includes the temporal aspect of the problem—when it started, whether it’s a current issue, or if it has been an ongoing concern. The timing of the problem might also include the circumstances or environment that contributed to the problem’s emergence.
- To What Extent? To emphasize the significance of the problem, it is essential to explain the extent or magnitude of the issue. This could include data or qualitative descriptions that reveal the seriousness and widespread nature of the problem. By providing this information, the researcher can highlight why the issue requires immediate attention.
- How Do I Know About the Problem? It’s important to explain how the researcher has come to know about the problem. This could be through personal experience, observations, or data. Citing sources or prior studies that document the existence or relevance of the problem adds credibility to the statement and demonstrates that the researcher has a firm understanding of the issue.
- Conceptual Framework The problem statement often includes an outline of the conceptual framework that will guide the research. This framework defines the key constructs, variables, and their relationships that the researcher assumes based on the problem being studied. The framework helps provide a theoretical foundation for the study.
- Gap in Knowledge One of the most critical aspects of the problem statement is identifying the gap in existing knowledge. This gap is the specific area where further research is needed. By identifying the gap, the researcher demonstrates the importance and uniqueness of their study. It also justifies why the research is relevant and necessary.
- Evidence and Logic To establish the need for the research, the researcher must provide logical reasoning and evidence from existing literature or personal experience that highlights the significance of the problem. This could involve presenting facts, statistics, or expert opinions that underscore the importance of addressing the issue.
- Consequences of Not Addressing the Problem The problem statement should also address the potential consequences of failing to conduct the research. This could include negative impacts on society, business, or any relevant field. By highlighting these consequences, the researcher can emphasize the urgency of resolving the problem.
- Purpose of the Study The problem statement should conclude with a clear articulation of the study’s purpose. This involves defining the objectives of the research, what the study aims to achieve, and how it will contribute to resolving the problem. The researcher should also provide a brief overview of the methodology they plan to use in their study.
Three Key Elements of Research Problem Statement
A typical research problem statement often has three primary elements:
- The Problem Itself: This is the central issue that requires investigation. It should be clearly stated with enough contextual detail to demonstrate why it’s important. For example, a problem statement could address issues like declining sales, lack of innovation, employee dissatisfaction, or the impact of certain policies.
- The Method of Solving the Problem: This element outlines how the researcher plans to approach solving the problem. This might include research questions, hypotheses, or a theoretical framework for understanding the problem. It also often includes a claim or working thesis that presents a potential solution or approach.
- The Purpose and Scope: The problem statement should also clarify the purpose of the research and the scope of the study. This outlines what the study will focus on and what it seeks to achieve. The scope should be well-defined to avoid ambiguity.
Criteria for Writing a Problem Statement
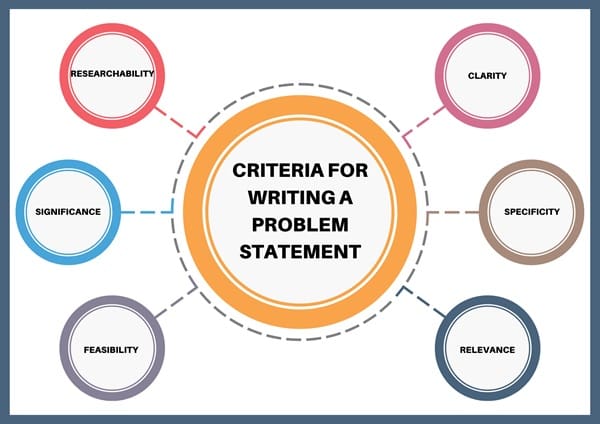
An effective problem statement should meet certain criteria to ensure it serves its purpose. These criteria include:
- Clarity: The problem statement should be clear and free from ambiguity. The issue should be defined in simple, straightforward terms.
- Specificity: A problem statement should avoid being too vague or broad. It must be specific enough to guide the research, but not so narrow that it overlooks the wider context.
- Relevance: The problem should be of current relevance. The statement should answer why the research is important at this moment in time and how it will contribute to solving or understanding the issue.
- Feasibility: The problem statement should focus on a problem that is manageable and within the scope of the researcher’s abilities and resources. It should be realistic in terms of time, data availability, and methodology.
- Significance: The problem should have enough significance to justify the research. It should impact a sizable population, industry, or field of study.
- Researchability: A good problem statement must define a problem that researchers can investigate. Furthermore, it should be suitable for exploration using available research methods and tools.
Sources
A problem statement may arise from various sources, including:
- Personal Experience: Researchers may identify problems based on their professional or personal experiences in the field of study.
- Theoretical Frameworks: A gap in theory or unexplained phenomena within a particular discipline can provide a basis for developing a problem statement.
- Previous Literature: Reviewing existing research can help identify unresolved issues or areas requiring further investigation.
- Practical Issues: Real-world problems, whether related to business, technology, healthcare, or social issues, can also lead to the development of a problem statement.
Writing a Problem Statement
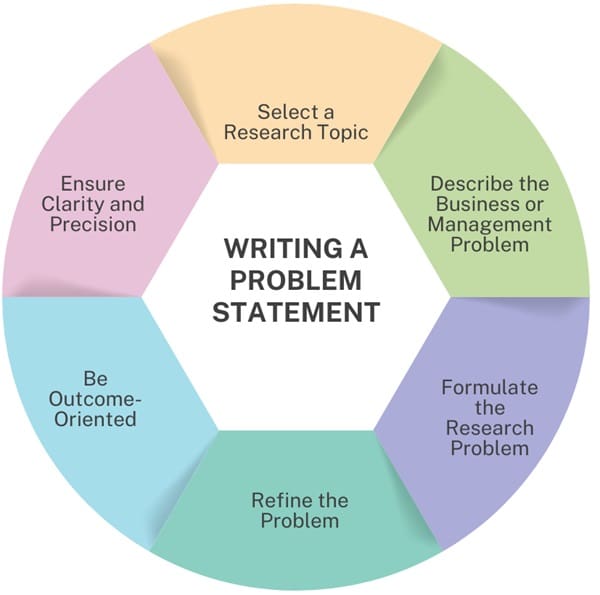
To write an effective problem statement, follow these steps:
- Select a Research Topic: Identify the issue or subject you plan to investigate. This step will set the direction for your research and help define your problem statement.
- Describe the Business or Management Problem: If your research pertains to a business issue, clearly define it and include relevant data, statistics, or industry reports to support your claims.
- Formulate the Research Problem: Distinguish the research problem from the business problem. Specifically, a research problem addresses the unknown aspects of a business issue and should be framed as a research question.
- Refine the Problem: If the problem involves multiple aspects or sub-issues, break them down into manageable sub-problems. Address each sub-problem individually in your research.
- Be Outcome-Oriented: Use outcome-based verbs like “evaluate,” “analyze,” or “investigate” instead of process-based verbs like “discuss” or “explore” to emphasize your research goals.
- Ensure Clarity and Precision: Avoid vagueness by making sure your problem statement is direct and to the point, enhancing understanding and focus.
Importance of a Well-Defined Problem Statement
The importance of a problem statement in research cannot be overstated. A clear and well-articulated problem statement is essential for several reasons:
- Guides the Research: The problem statement sets the direction for the entire research process. By defining the problem early on, researchers ensure that their study remains focused and that they address the core issue effectively.
- Establishes Relevance: A well-crafted problem statement demonstrates why the research is important. It justifies the need for the study and shows how it will contribute to existing knowledge or address an existing gap.
- Defines Objectives:The problem statement helps researchers define the research objectives. It ensures that the research questions directly relate to the problem being addressed. Additionally, this alignment enhances the overall focus of the study.
- Facilitates Decision Making: A clear problem statement helps researchers identify the appropriate methodology, data sources, and analysis techniques to tackle the problem.
How to Write a Problem Statement?

Writing a problem statement requires careful consideration and a structured approach. Below are the steps to follow:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a research topic that addresses a specific issue. The topic should be something that has relevance in your field of study and interests you.
- Describe the Problem: After selecting the topic, the next step is to describe the problem in detail. This involves clearly defining the issue, its context, and its significance.
- State the Research Problem: The research problem is the unknown or unresolved aspect of the issue. It should be formulated as a question or a clear statement that highlights the gap in knowledge.
- Provide Evidence: Support your problem statement with evidence from existing research, case studies, or personal experience. This helps to establish the credibility of the problem and justifies the need for research.
- Identify the Purpose: Conclude the problem statement by outlining the purpose of the research and the objectives you hope to achieve. This includes explaining how you plan to address the problem and what you aim to contribute to the field.
- Keep It Concise: A problem statement should typically be one page long. It should be clear and focused, providing only the essential information needed to understand the issue.
Final Words
A problem statement is a crucial component of any research study. It serves as the foundation for the research process, outlining the issue being addressed and providing a roadmap for the investigation.
A well-written problem statement not only guides the researcher but also establishes the relevance and importance of the study, ensuring that the research will contribute meaningfully to the field. By following a structured approach and clearly defining the problem, researchers can ensure that their study remains focused and impactful, leading to valuable insights and solutions.


















